Method for extracting edible mushroom DNA
A technology for edible fungi and mycelium, applied in the field of edible fungi genetic engineering, can solve the problems of time-consuming and expensive, long extraction time, and high extraction cost, and achieve the effects of reducing test costs, good DNA integrity, and no environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1. Preparation of DNA from mushrooms, oyster mushrooms, enoki mushrooms, Agaricus bisporus, black fungus and Grifola frondosa.
[0026] 1. Materials
[0027] Lentinula edodes, Pleurotus ostreatus, Flammulina velutiper, Agaricus bisporus, Auricularia auricula-judae and Griflola frondosa varieties were all from Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences The culture preservation center of the Institute of Edible Mushrooms preserves the strains, and the preservation numbers are 4627, 0860, 0188, 0897, 0115 and 2611.
[0028] 2. Reagents
[0029] TE buffer: 10mmol / L Tris-HCl, 1mmol / L EDTA, pH8.0.
[0030] 3. DNA extraction
[0031] (1) Materials: Lentinus edodes, oyster mushroom, Flammulina velutipes, Agaricus bisporus, black fungus and Grifola frondosa mycelia were cultured and grown on PDA plates for 2 days, and the young aerial mycelia were scraped on the surface of the plate with a sterilized toothpick for 2~ 3 times until there is a small group of hyphae v...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment two, DNA content and purity detection
[0035] The DNA extracted in Example 1 was detected by a Thermo Company NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer for nucleic acid content and purity, and 0.1 g of mushroom hyphae DNA extracted by the CTAB method was used as a control. The test results show:
[0036] (1) The nucleic acid concentrations of shiitake mushroom, oyster mushroom, Flammulina velutipes, Agaricus bisporus, black fungus, and Grifola frondosa were 65, 114, 140, 100, 53, and 27 ng / μL, respectively, with Grifola frondosa being the lowest and Flammulina velutipes the highest. The mushroom DNA extracted by the CTAB method is 730ng / μL, which needs to be diluted for conventional PCR reactions;
[0037] (2) The results of OD260 / 280 showed that the ratio of OD260 / 280 of shiitake and oyster mushrooms was between 2.0 and 2.2, which was comparable to that of the control, and that of the other four species were all between 1.6 and 2.0, indicating that there were protei...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment three, multiple PCR reaction verification
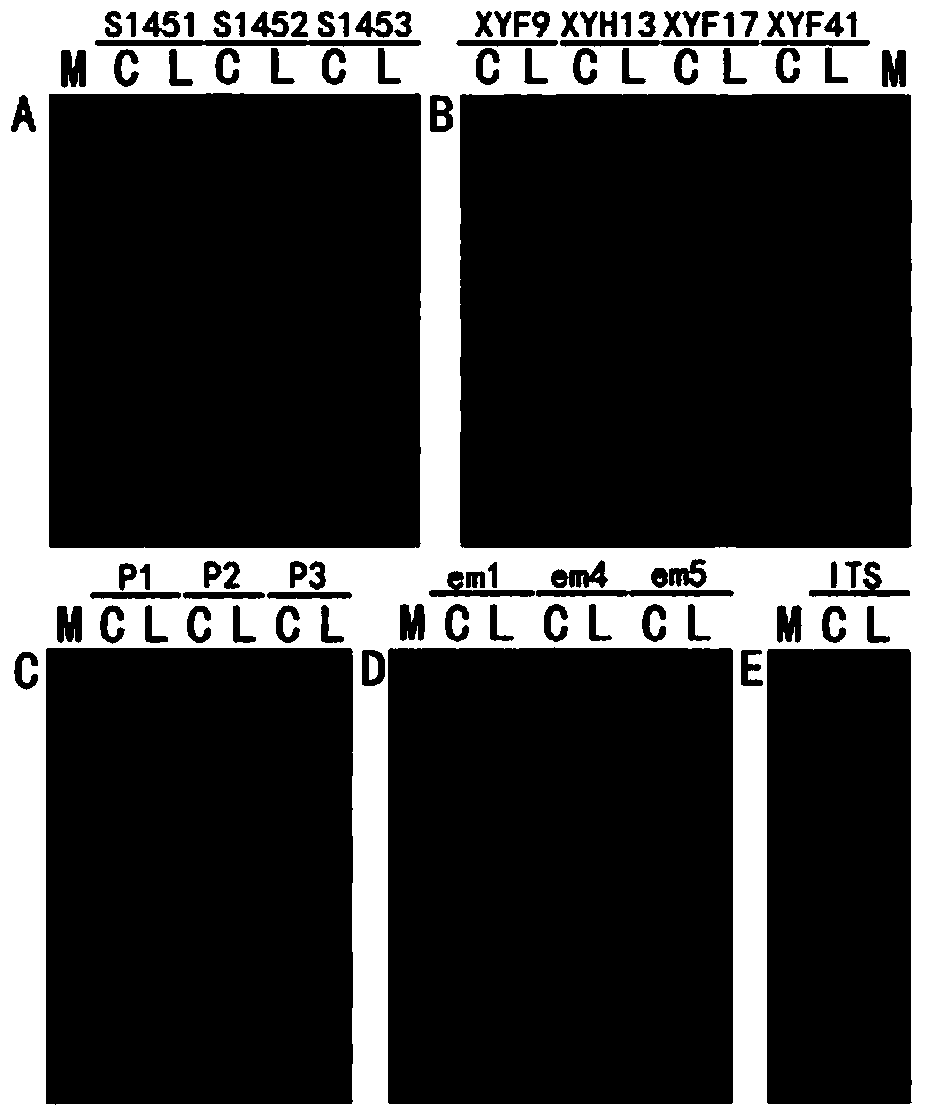
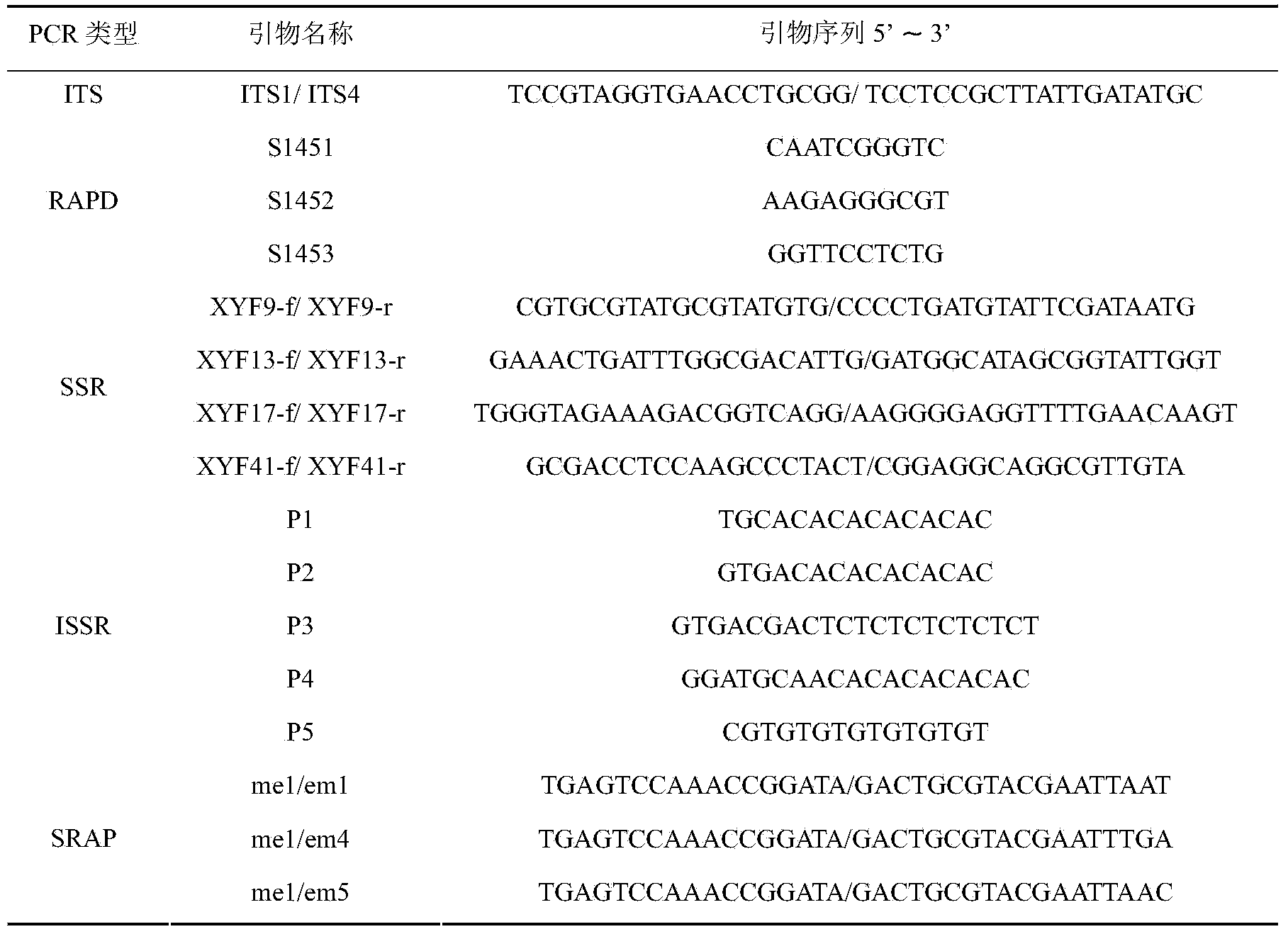
[0040] The mushroom DNA extracted in Example 1 was directly subjected to multiple PCR reactions without dilution to verify whether the content and purity of the DNA samples would meet the requirements of common PCR reactions. The DNA extracted by the CTAB method was diluted to a concentration of 50 ng / μL as a control, the ITS fragment was selected as a specific fragment amplification test, and RAPD, SSR, ISSR and SRAP were used for various molecular marker amplification tests. The primer sequences used are shown in Table 1. The PCR products were electrophoresed by PAGE and stained by silver staining. For the amplification effects of various PCR reactions, see figure 1 .
[0041] Table 1: ITS, RAPD, SSR, ISSR and SRAP primer sequences for PCR validation
[0042]
[0043] The PCR amplification effect shows that compared with the DNA extracted by the traditional CTAB method, the mushroom DNA extracted in Example 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com