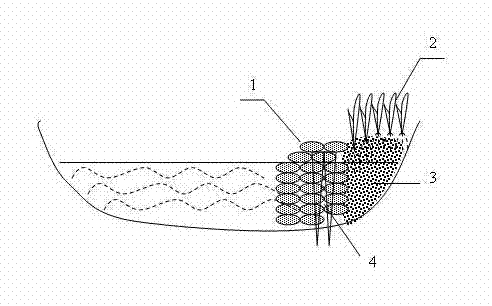
Method for disposing river or lake bottom mud on site
A technology of sediment and lakeshore, applied in biological sludge treatment, river remediation, climate change adaptation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] In an artificial lake with a water depth of 1m, take the mixed substrate of sediment and put it into an ecological bag, and pile up the ecological bag at a distance of 2 meters from the lake shore to form an ecological embankment. The embankment surface is 50cm above the water surface and anchored. The bottom mud mixed matrix is uniformly mixed with bottom mud, coarse material component slag, and fine material component vermiculite at a weight ratio of 40%: 40%: 20%, and then the bottom mud mixed matrix is filled in the original lakeshore and ecological embankment Between, and then plant 1 shrub willow and 5 carex per square meter.
Embodiment 2
[0029] On the river bank with a water body depth of 2 m, the bottom mud is uniformly mixed with the coarse material components slag and gravel, and the fine component perlite at a weight ratio of 40%:20%:40% to form a bottom mud mixed matrix, and the bottom mud is mixed The matrix is put into the ecological bag, and the ecological bag is piled up 1 meter away from the river bank to form an ecological embankment, which is anchored, and the embankment surface is 60cm above the water surface. Then fill the bottom mud mixed matrix between the original river bank and the ecological embankment, and then plant 1 shrub willow and 5 carex per square meter.
[0030]
Embodiment 3
[0032] On a river bank with a water depth of 3 m, the bottom mud was uniformly mixed with coarse material components steel slag and gravel, and fine material components perlite and volcanic ash at a weight ratio of 40%:30%:30% to form a bottom mud mixed matrix, which was taken as The bottom mud mixed matrix is put into an ecological bag, and the ecological bag is piled up 1.5 meters away from the river bank to form an ecological embankment, which is anchored, and the embankment surface is 70cm above the water surface. Then fill the bottom mud mixed matrix between the original river bank and the ecological embankment, and then plant 1 shrub willow and 5 carex per square meter.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com