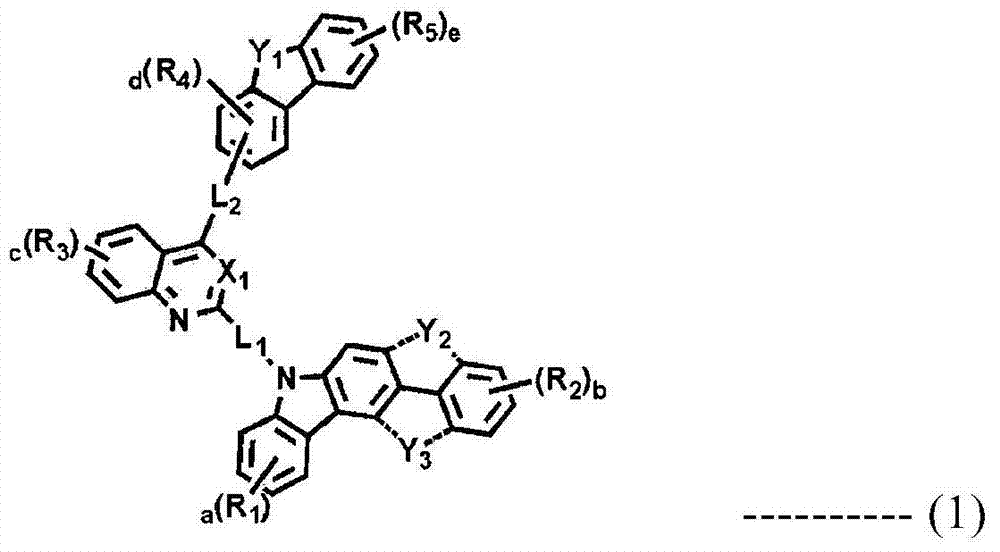
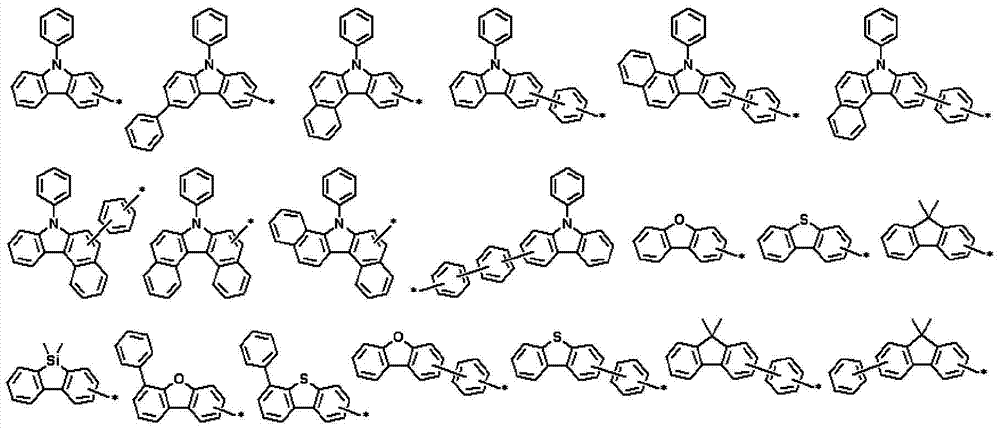
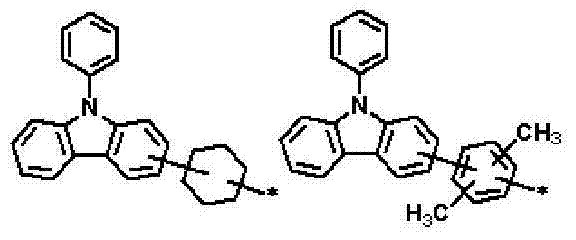
Novel compounds for organic electronic material and organic electroluminescent device using the same
A compound and heteroatom technology, applied in the field of organic electroluminescent devices, can solve the problems of low glass transition temperature difference thermal stability, short working life of organic EL devices, high driving voltage, etc., to achieve improved current characteristics, low driving voltage, the effect of improving power efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation Embodiment 1
[0070] Preparation Example 1: Preparation of compound C-16
[0071]
[0072] Preparation of compound 1-1
[0073] Combine 2,4-dichloroquinazoline (30 g, 151 mmol), 9-phenyl-9H-carbazol-3-ylboronic acid (15.6 g, 75.3 mmol), Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 (2.6 g, 2.3 mmol) and Na 2 CO 3 After dissolving (16 g, 150 mmol) in a mixture of toluene (300 ml) and distilled water (75 ml), the reaction mixture was stirred at 90°C for 2 hours. The obtained organic layer was distilled under reduced pressure and then ground with MeOH. The obtained solid was dissolved in dichloromethane (MC), filtered through silica, and then triturated with MC and hexane to obtain compound 1-1 (9.3 g, 51.4%).
[0074] Preparation of compound 1-2
[0075] Combine dibenzo[b,d]furan-4-ylboronic acid (30 g, 142 mmol), 1-bromo-2-nitrobenzene (23.8 g, 118 mmol), K 2 CO 3 (39.1 g, 283 mmol) and Pd (PPh 3 ) 4 After (6.8 g, 5.8 mmol) was dissolved in a mixture of toluene (600 mL), EtOH (150 mL) and purified water (150 mL), the reaction mi...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0081] Preparation Example 2: Preparation of Compound C-32
[0082]
[0083] Preparation of compound 2-1
[0084] After dissolving 2,4-dichloroquinazoline (50g, 251mmol) and dibenzo[b,d]furan-4-ylboronic acid (53.2g, 251mmol) in a mixture of toluene (1L) and water (200mL) To the reaction mixture was added tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium (14.5g, 12.5mmol) and sodium carbonate (80g, 755mmol). After the reaction mixture was stirred at 80°C for 20 hours, it was cooled to room temperature. After terminating the reaction with 200 mL of ammonium chloride aqueous solution, the reaction mixture was extracted with 1 L of ethyl acetate, and the aqueous layer was extracted with 1 L of dichloromethane. The obtained organic layer was dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the organic solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The resulting solid was filtered through silica gel, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The obtained solid was washed with 100 mL of ethyl...
preparation Embodiment 3
[0092] Preparation Example 3: Preparation of Compound C-51
[0093]
[0094] Preparation of compound C-51
[0095] After compound 2-1 (5.1 g, 15.5 mmol) and compound 1-3 (4.0 g, 15.5 mmol) were suspended in 80 ml of DMF, 60% NaH (930 mg, 23.2 mmol) was added to the mixture at room temperature ), stirring for 12 hours. After adding purified water (1 L), the mixture was filtered under reduced pressure. The obtained solid was ground with MeOH / EA, with DMF, and with EA / THF. It was dissolved in MC, filtered through silica, and then triturated with MeOH / EA to obtain compound C-51 (5.9 g, 69%).
[0096] MS / FAB measured value 552; calculated value 551.59
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com