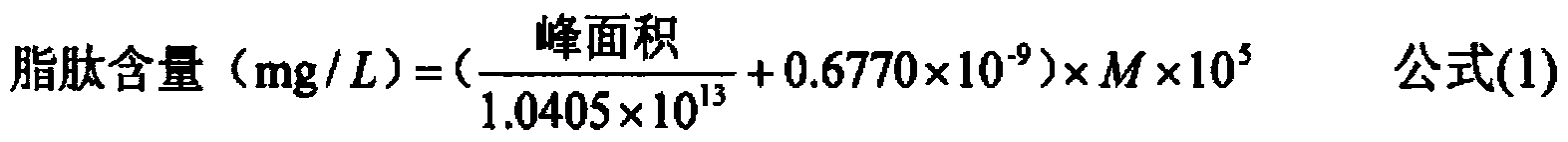Method for quantitatively detecting lipopeptide
A quantitative detection and lipopeptide technology, which is applied in measurement devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of rough quantification, harsh conditions, and complicated steps, and achieve the effects of improving detection sensitivity, mild reaction conditions, and simple and fast methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
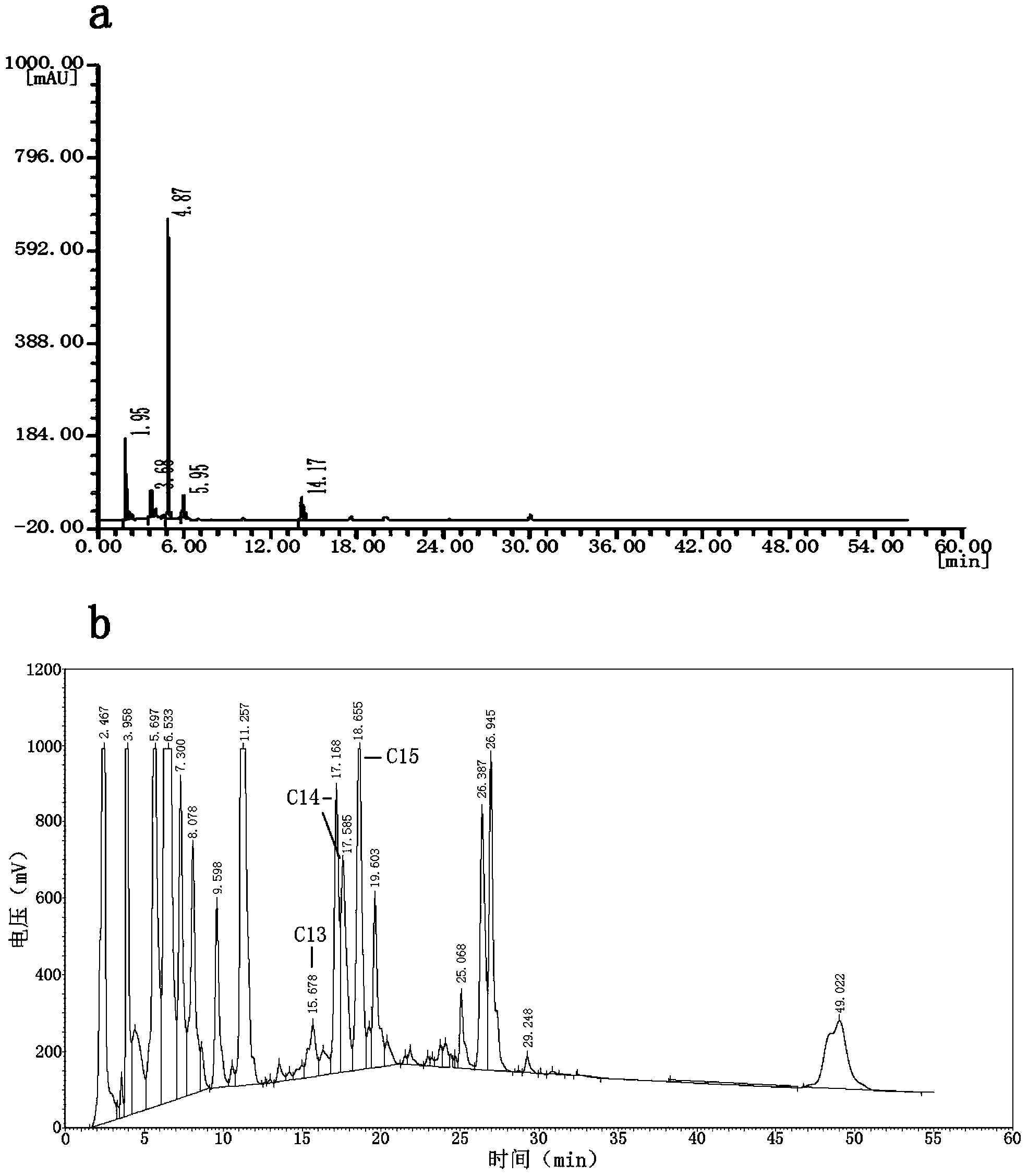
[0026] Add 6M hydrochloric acid to 10mL of microbial fermentation broth to adjust the pH of the solution to 2.0, extract with ether three times, dry the ether to obtain the crude lipopeptide, add 2mg of 4-bromomethyl-7-methoxycoumarin to the crude lipopeptide and 100 μL of triethylamine, add acetonitrile to make up to 1 mL, react at 60°C for 20 min, and perform HPLC analysis after cooling (high performance liquid chromatography: WUFENG-LC100; fluorescence detector: Shimadzu RF-20A), see HPLC results figure 2 , the HPLC fluorescence detector detects that the aliphatic chain length is that the peak area of the lipopeptide homologue with 13 carbons is 11022255 μ V s, and the molecular weight of the lipopeptide homologue is 1007.68, and the concentration of the lipopeptide homologue is calculated according to formula (1) is 107mg / L, and the peak area of the lipopeptide homologue with aliphatic chain length of 14 carbons is 12374905μV s, the molecular weight of this lipopeptide...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Add 6M hydrochloric acid to 10mL of microbial fermentation broth to adjust the pH of the solution to 2.0, extract with ether three times, dry the ether to obtain the crude lipopeptide, add 2mg of 4-bromomethyl-7-methoxycoumarin to the crude lipopeptide and 100 μL triethylamine, add acetonitrile to make it to 1 mL, react at 40°C for 30 min, and perform HPLC analysis after cooling (high performance liquid chromatography: WUFENG-LC100; fluorescence detector: Shimadzu RF-20A), and the HPLC fluorescence detector detects The peak area is 53682755μV·s, and the total amount of lipopeptide calculated according to the formula (1) is 516mg / L.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Add 6M hydrochloric acid to 10mL of microbial fermentation broth to adjust the pH of the solution to 2.0, extract with ether three times, dry the ether to obtain the crude lipopeptide, add 2mg of 4-bromomethyl-7-methoxycoumarin to the crude lipopeptide and 100 μL triethylamine, add acetonitrile to make it to 1 mL, react at 80°C for 10 min, and perform HPLC analysis after cooling (high performance liquid chromatography: WUFENG-LC100; fluorescence detector: Shimadzu RF-20A), and the HPLC fluorescence detector detects The peak area is 52746305μV·s, and the total amount of lipopeptide calculated according to the formula (1) is 507mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com