Novel lactic acid bacterium and method for preparing silage or fermented feed by using the same
A technology for silage and lactic acid bacteria, applied in the field of lactic acid bacteria, can solve the problems of unclear production of bacteriocin, no change, no improvement of fermentation quality, etc., and achieve the effects of good feed intake and high safety for livestock
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Nisin activity in forage boiling juice medium
[0062] The nisin activity of the supernatant of the culture broth when each lactic acid bacteria was cultured in the forage boiling juice medium was measured.
[0063] The forage boiled juice medium is prepared according to the following method. Add 1 liter of distilled water to 100 g of alfalfa pellets, and cook for 30 minutes after the liquid temperature in the boiling water bath reaches 90°C. Filter with gauze, squeeze the residue, centrifuge the filtrate and filter with filter paper. Dilute the filtrate to 1 liter, divide it into test tubes, and sterilize in an autoclave (115°C, 20 minutes).
[0064] The sugar content in the forage cooking juice medium is determined according to the following method. Add 840 μl of acetonitrile to 360 μl of the medium to mix, and let stand at room temperature for 15 minutes. The precipitate was removed by centrifugation (15000 rpm, 15 minutes), and the supernatant was filtered with a 0.2 ...
Embodiment 2
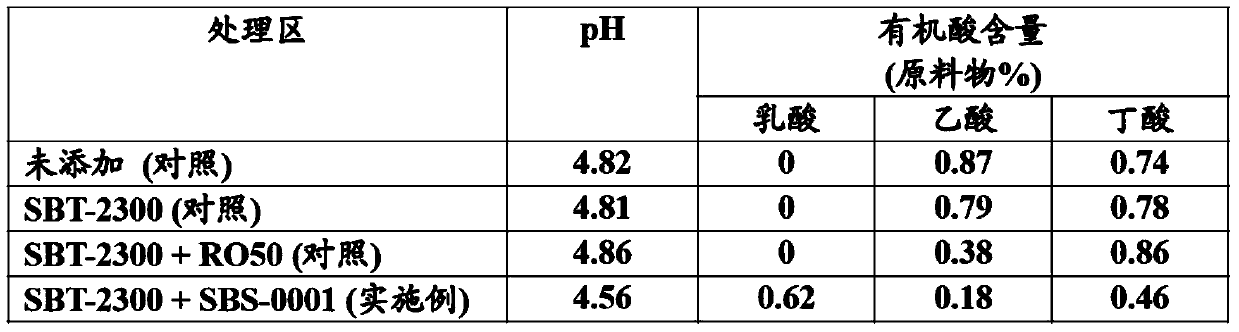
[0084] Silage preparation and fermentation quality
[0085] Each lactic acid bacteria was added to pasture to prepare silage, and the fermentation quality was investigated.
[0086] The lactic acid bacteria, that is, the strains shown in Table 6, were prepared in the following manner. The GYP liquid medium was inoculated with each strain and cultured at 37°C for 24 hours. Centrifuge the culture broth (6500 rpm, 15 minutes), discard the supernatant, add 10% trehalose, 1% sodium glutamate solution to the remaining bacteria to suspend, and dry with a freeze dryer.
[0087] [Table 6]
[0088]
[0089] The silage preparation was carried out according to the following method. Timothy grass, orchardgrass, grass reeds, wheatgrass, Italian ryegrass, and rye were cut at the heading stage, and alfalfa was cut at the flowering stage and cut into a length of about 2 cm. The freeze-dried powder of each lactic acid bacteria was dissolved in water. In the case of only one strain, 1.0×10 per 1g of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com