Porous nano composite material for fuel cell oxygen reduction catalyst
A nanocomposite, fuel cell technology, applied in nanotechnology for materials and surface science, physical/chemical process catalysts, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the loss of carbon mass, reduction of active sites, affecting the service life of catalysts, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of low cost, easy preparation, and improved ability to catalyze oxygen reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
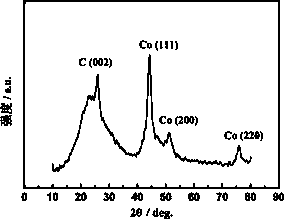
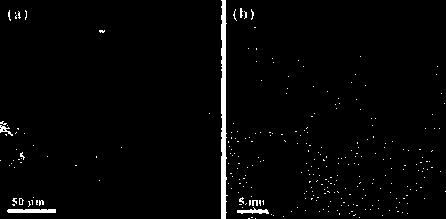
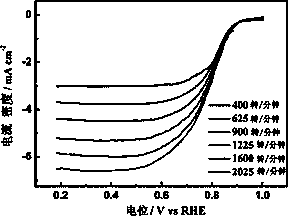
[0030] A porous nanocomposite material used for fuel cell oxygen reduction catalyst, which is uniformly dispersed and embedded in a nitrogen-doped porous carbon support material by small-sized cobalt nanoparticles, wherein the particle size range of cobalt metal nanoparticles is 6- 7 nm, the mass percentage of cobalt metal is 25.8%, and the mass percentage of nitrogen in the porous carbon support is 3.53%.
[0031] The above-mentioned preparation method of the porous nanocomposite material used for fuel cell oxygen reduction catalyst, the steps are as follows:
[0032] 1) Synthesis of Schiff base complexes: bis-salicylaldehyde ethylenediamine acetal and cobalt(Ⅱ)
[0033] 3.5 g Schiff base ligand (salenH 2 ) was dissolved in 30 mL of absolute ethanol, and then 3.5 g of cobalt nitrate was dissolved in 20 mL of absolute ethanol and added dropwise to the three-neck flask under a water bath at 65 °C. Suction filtration under reduced pressure, wash twice with distilled water and ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A porous nanocomposite material used for fuel cell oxygen reduction catalysts, which consists of small-sized iron and iron carbide nanoparticles uniformly dispersed and embedded in a nitrogen-doped porous carbon carrier material, wherein the iron and iron carbide nanoparticles The particle size range is 20-40 nm, the mass percentage of iron metal is 10.2%, and the mass percentage of nitrogen in the porous carbon support is 4.02%.
[0043] The preparation method of the above-mentioned porous nanocomposite material used as an oxygen reduction catalyst for fuel cells is basically the same as in Example 1, except that ferrous nitrate is used instead of cobalt nitrate to prepare a porous iron-nitrogen-carbon nanocomposite material.
[0044] Figure 5 It is the XRD pattern of the porous iron-nitrogen-carbon nanocomposite material, which shows that in addition to the diffraction peak of carbon, the prepared sample contains metallic iron and Fe 3 Phase C.
[0045] Figure 6 ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A porous nanocomposite material for oxygen reduction catalysts, consisting of small-sized nickel nanoparticles uniformly dispersed and embedded in a nitrogen-doped porous carbon support material, wherein the nickel metal nanoparticles have a particle size range of 20-30 nm, the mass percentage of nickel metal is 19.1%, and the mass percentage of nitrogen in the porous carbon support is 3.16%.
[0051] The preparation method of the above-mentioned porous nanocomposite material used as an oxygen reduction catalyst for fuel cells is basically the same as in Example 1, except that nickel nitrate is used instead of cobalt nitrate to prepare a porous nickel-nitrogen-carbon nanocomposite material.
[0052] Figure 8 This is the XRD pattern of the porous nickel-nitrogen-carbon nanocomposite material, which shows that except for the diffraction peak of carbon, all other diffraction peaks can be attributed to metallic nickel.
[0053] Figure 9 This is a TEM photo of the nickel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com