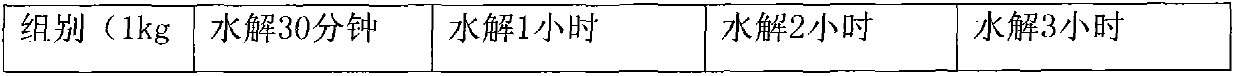Method for extracting chlorogenic acid from honeysuckle
A technology of honeysuckle and chlorogenic acid, applied in the separation/purification of carboxylate, organic chemistry, etc., to achieve the effects of high yield, reduced industrial energy consumption, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] A method for extracting chlorogenic acid from Flos Lonicerae, comprising the steps of:
[0020] 1) Pulverization: put 1 kg of honeysuckle (produced in Pingyi, Shandong) into a pulverizer to pulverize, and then spread it into 1 square meter;
[0021] 2) Ultraviolet irradiation: irradiate under ultraviolet light for 10 minutes, and the ultraviolet intensity is 2000uW / cm 2 ;
[0022] 3) Hydrolysis: use deionized water 8 times the weight of honeysuckle as a solvent, maintain at 0.1 atmosphere, hydrolyze at 75°C for 1 hour, and collect the filtrate;
[0023] 4) concentration: the filtrate is placed in a vacuum concentrator, and vacuum concentrated to one-third of the volume of the filtrate;
[0024] 5) Precipitation: Add the calculated amount of alcohol so that the alcohol content of the concentrated solution reaches 75% (v / v). After standing for 1 hour, the chlorogenic acid is completely precipitated, and the filtrate is collected by filtration for extracting hedera sapon...
Embodiment 2
[0026] A method for extracting chlorogenic acid from Flos Lonicerae, comprising the steps of:
[0027] 1) Pulverization: put 1 kg of honeysuckle (produced in Pingyi, Shandong) into a pulverizer and pulverize it, and spread it into 1 square meter;
[0028] 2) UV irradiation: UV irradiation for 15 minutes, the UV intensity is 2000uW / cm 2 ;
[0029] 3) Hydrolysis: use deionized water 10 times the weight of honeysuckle as a solvent, maintain a state of 0.1 atmosphere, hydrolyze at 75°C for 1 hour, and collect the filtrate;
[0030] 4) concentration: the filtrate is placed in a vacuum concentrator, and vacuum concentrated to one-third of the volume of the filtrate;
[0031] 5) Precipitation: Add the calculated amount of alcohol so that the alcohol content of the concentrated solution reaches 75% (v / v). After standing for 1 hour, the chlorogenic acid is completely precipitated, and the filtrate is collected by filtration for extracting hedera saponin. After vacuum drying at 80°C,...
Embodiment 3
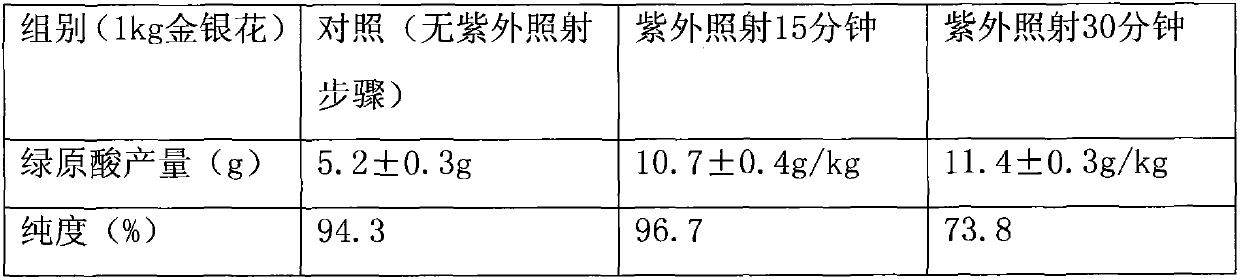
[0033] Effects of Factors on Extraction Efficiency of Chlorogenic Acid
[0034] 1. The influence of ultraviolet irradiation intensity and time, control other conditions unchanged, only change the ultraviolet irradiation parameters, repeat the experiment three times for each group, see Table 1 for specific results
[0035] Table 1
[0036]
[0037] Conclusion: Through analysis, it is found that ultraviolet irradiation can greatly increase the production of chlorogenic acid, but with the increase of time, the purity of chlorogenic acid is greatly reduced, which may be due to the decomposition of chlorogenic acid caused by strong light.
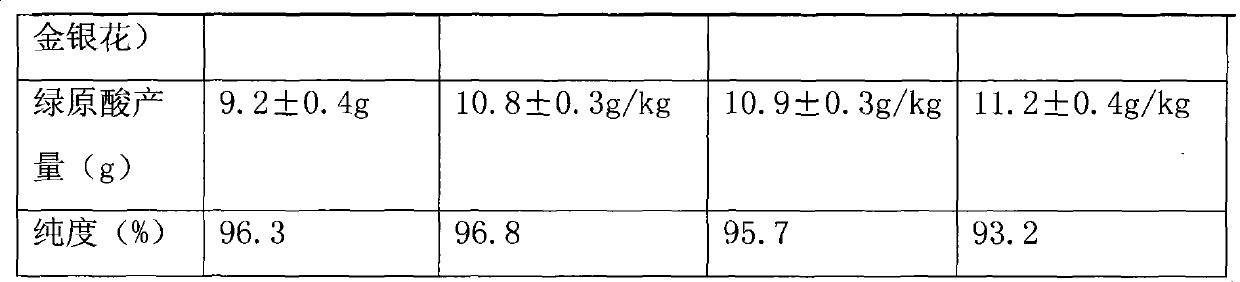
[0038] 2. The effect of hydrolysis time on the yield of chlorogenic acid
[0039] Change the time of hydrolysis, control other conditions unchanged, repeat each group of experiments three times, see Table 2 for specific results
[0040] Table 2
[0041]
[0042]
[0043] Conclusion: Through the analysis, it was found that after one h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com