Method for preparing bacterial cellulose compounded amnion extracellular matrix material containing collagen
A technology of bacterial cellulose and collagen, applied in catheters, medical science, prostheses, etc., can solve problems such as easy wrinkling and tearing, poor biomechanical properties, and difficult-to-refold tissue, and achieve a good three-dimensional network structure and preparation The process is simple and easy, and the effect of biocompatibility is good
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
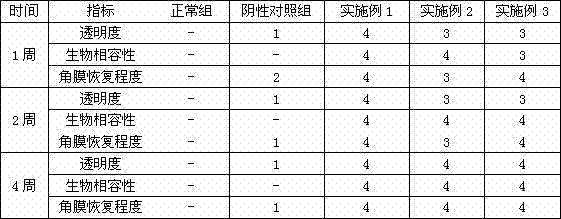
[0024]Acetobacter xylinum, which can secrete bacterial cellulose, was selected to prepare seed mash with a strain concentration of 30%. The collagen was dissolved in 1wt% acetic acid aqueous solution and mixed with the medium to obtain a fermentation medium containing 0.5wt% collagen. Mix the seed mash with the collagen-containing fermentation medium and place it in a culture container. The liquid level of the mixed solution in the culture container is 0.5 cm, and culture it for 1 day to obtain hydrogel-like bacterial fibers with a film thickness of 0.5 cm. Vein / Collagen Membrane.
[0025] The amniotic membrane extracellular matrix material is taken from a safe source, processed to remove cells, fat and soluble antigens, and dried and sterilized, soaked in the culture medium, and spread on the upper surface of the bacterial cellulose / collagen membrane after it is completely wet. Wherein, the sponge layer of the amnion extracellular matrix material is in contact with the upper...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Rhizobia and Pseudomonas, which can secrete bacterial cellulose, were selected and activated to prepare seed mash with a strain concentration of 40wt%. The collagen was dissolved in 1.5wt% acetic acid aqueous solution and mixed with the medium to obtain a fermentation medium containing 1wt% collagen. Mix the seed mash with the collagen-containing fermentation medium and place it in a culture container. The height of the mixed solution in the culture container is 1 cm, and culture it for 2 days to obtain hydrogel-like bacterial cellulose with a film thickness of 0.6 cm. / collagen membrane.
[0028] The amniotic membrane extracellular matrix material is taken from a safe source, processed to remove cells, fat and soluble antigens, and dried and sterilized, soaked in the culture medium, and spread on the upper surface of the bacterial cellulose / collagen membrane after it is completely wet. Wherein, the sponge layer of the amnion extracellular matrix material is in contact...
Embodiment 3
[0030] The seed mash with a strain concentration of 50wt% was prepared by activation of Sarcina and Alcaligenes that could secrete bacterial cellulose. The collagen was dissolved in 2wt% acetic acid aqueous solution and mixed with the medium to obtain a fermentation medium containing 2wt% collagen. After the seed mash is mixed with the fermentation medium containing collagen, it is placed in a culture container, the liquid level of the mixed solution in the culture container is 2 cm, and the hydrogel-like bacterial cellulose / Collagen membrane.
[0031] The amniotic membrane extracellular matrix material is taken from a safe source, processed to remove cells, fat and soluble antigens, and dried and sterilized, soaked in the culture medium, and spread on the upper surface of the bacterial cellulose / collagen membrane after it is completely wet. Wherein, the sponge layer of the amnion extracellular matrix material is in contact with the upper surface of the bacterial cellulose / c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com