Bioassay probe for early diagnosis of bacterial infection
A technology of fluorescent probes and fluorescent dyes, applied in the synthesis and application of traceable galactosylated near-infrared fluorescent probes, can solve problems such as poor specificity, inability to target diagnosis, inability to perform in vivo diagnosis, etc., and achieve good applications Foreground effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Synthesis of Gal-MPA
[0034] MPA activation: Dissolve 5.0mg of MPA in 2.0mL of dimethylformamide (DMF), add 4.8mg of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC·HCl) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) 0.6 mg, stirred at room temperature overnight in the dark.
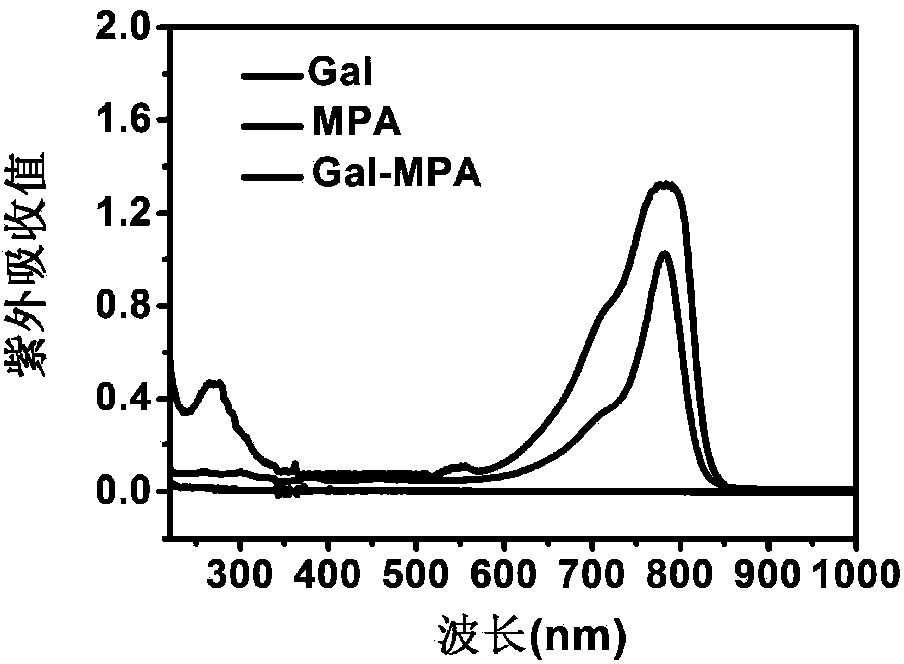
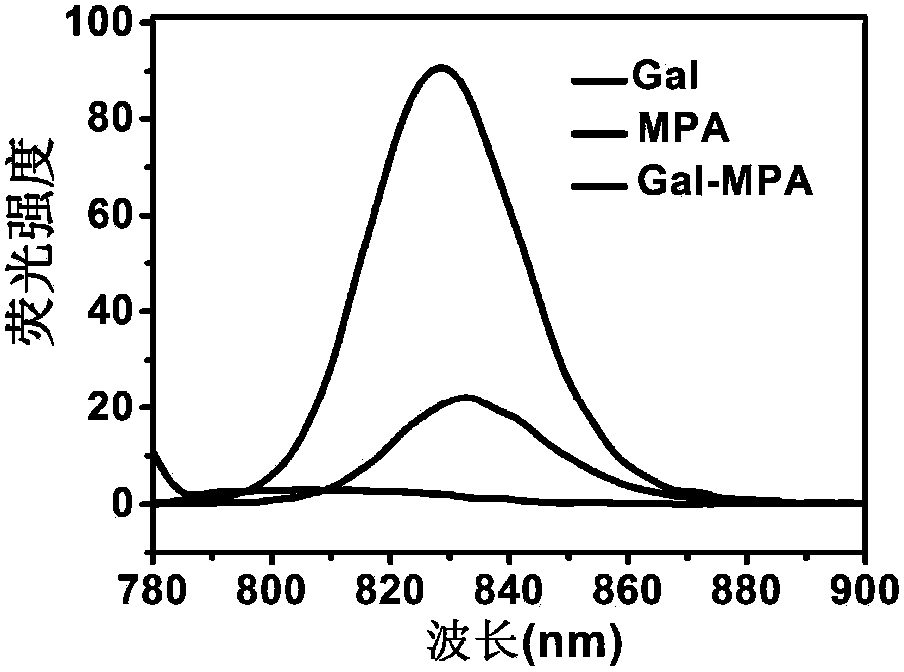
[0035] Synthesis of Gal-MPA: 1.1 mg of galactosamine was dissolved in 2.0 mL of pyridine, added dropwise to the above MPA activation solution, and stirred overnight at room temperature in the dark. Freeze and rotary evaporate to remove pyridine. Preliminary identification of reaction products by thin layer chromatography. The reaction product was dialyzed, purified on Sephadex G10, and freeze-dried to obtain Gal-MPA. A certain amount of Gal-MPA dissolved in distilled water was characterized by ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence emission spectra, which showed that it had stable optical properties. UV absorption spectrum see figure 1 , the fluorescence emission spectrum see figure 2 . ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] cell culture
[0038] Human cell line L02 (normal human hepatocytes) was incubated at 37°C in an incubator containing 5% carbon dioxide. Cultured in RPMI1640 supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 μg / ml penicillin and 100 μg / ml streptomycin.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Cytotoxicity
[0041] 5) Cell proliferation experiments were performed with L02 cells. Cells were seeded into 96-well plates (1×10 4 cells / well) for 24 hours under culture conditions.
[0042] 6) Gal-MPA solution dissolved in phosphate buffered PBS was added to the cells, and the culture was continued for 24 hours, and the sample concentration ranged from 1.5625 to 100 μg / mL.
[0043] 7) Add 10 μl thiazolium blue (MTT) solution (5.0 mg / mL) to each well and incubate for another 4 hours. Carefully remove residual MTT in the medium, and dissolve the purple crystals in 150 μL dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
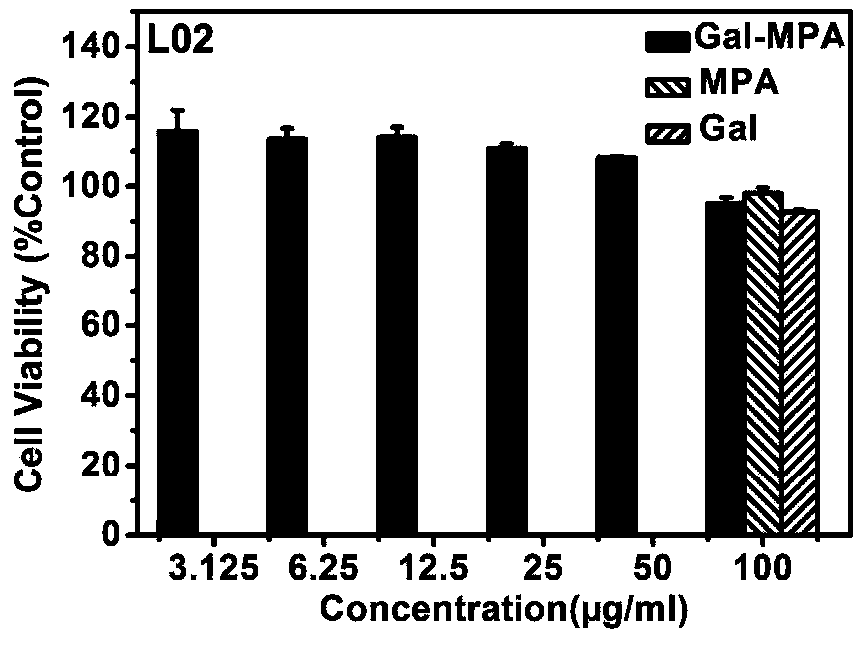
[0044] 8) After shaking and mixing for ten minutes, all test samples were detected by ELIASA, and the cell viability was calculated by the following formula: Cell survival rate = (average absorbance of sample group - average absorbance of medium wells) / (average absorbance of solvent group - medium The average absorbance of the well) × 100%. See image 3 , Gal-MPA wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com