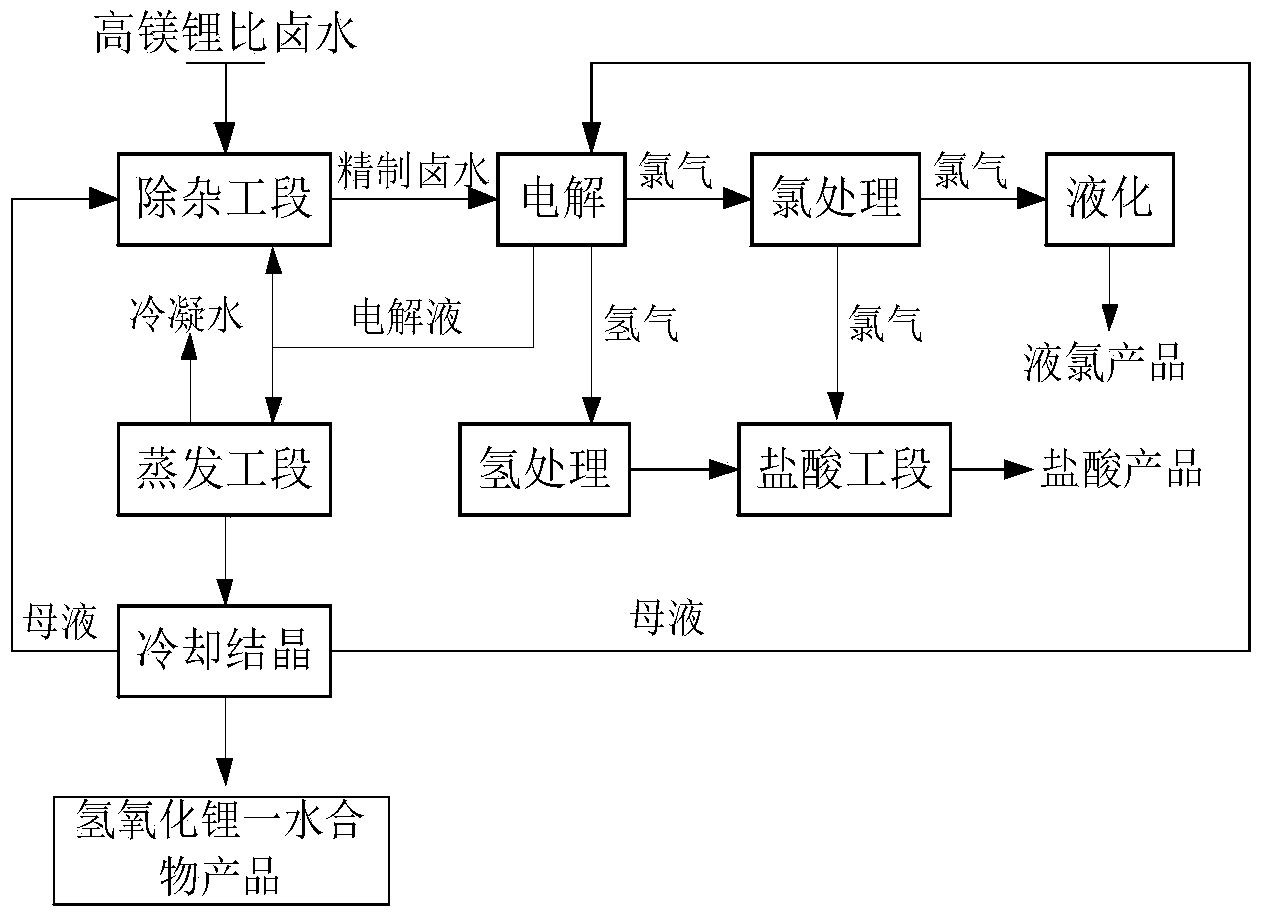
Method for preparing lithium hydroxide through electrolysis of salt lake brine
A lithium hydroxide, salt lake brine technology, applied in the electrolysis process, electrolysis components and other directions, can solve the problems of the product quality is difficult to reach the excellent standard, the brine refining process is complicated, the material flow is large, and the cost is low and the scope of application is wide. , the effect of low impurity content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] (1) Preparation of refined brine
[0045] The saturated magnesium chloride brine obtained by evaporating and concentrating the salt field in the sun is firstly adjusted with hydrochloric acid to keep the pH value at 1.5. Boron in the brine is precipitated as boric acid. After solid-liquid separation, add lime or slaked lime in proportion, fully stir and filter to remove Magnesium and sulfate, to obtain a low-boron, low-sulfur electrolysis raw material solution. Then use a two-step method to remove magnesium at a temperature of 50-70°C. First, adjust the pH of the solution to 8.5 with lithium hydroxide. The generated magnesium hydroxide combines with excess magnesium ions to positively charge and adsorb boron ions in the solution. Solid-liquid Separate and remove most of the magnesium, then adjust the pH of the solution to 11.5 with the mother liquor lithium hydroxide solution and lithium carbonate solution after crystallization separation, remove the remaining magnesium...
Embodiment 2
[0055] (1) Preparation of refined brine
[0056] The saturated magnesium chloride brine obtained by evaporating and concentrating the salt fields in the sun is firstly adjusted with hydrochloric acid to keep the pH value at 2.5, boron in the brine is precipitated as boric acid, after solid-liquid separation, add lime or slaked lime in proportion, fully stir and filter to remove Magnesium and sulfate, to obtain a low-boron, low-sulfur electrolysis raw material solution. Then use a two-step method to remove magnesium at a temperature of 50-70°C. First, adjust the pH of the solution to 9.5 with lithium hydroxide. The generated magnesium hydroxide combines with excess magnesium ions to positively charge and adsorb boron ions in the solution. Solid-liquid Separation and removal of most of the magnesium, and then use the mother liquor lithium hydroxide solution or lithium carbonate solution after crystallization to adjust the pH of the solution to 12.5, remove the remaining magnesiu...
Embodiment 3
[0066] (1) Preparation of refined brine
[0067] The saturated magnesium chloride brine obtained by evaporating and concentrating the salt fields in the sun is firstly adjusted with hydrochloric acid to keep the pH value at 2. Boron in the brine is precipitated with boric acid. After solid-liquid separation, add lime or slaked lime in proportion, fully stir and filter to remove Magnesium and sulfate, to obtain a low-boron, low-sulfur electrolysis raw material solution. Then use a two-step method to remove magnesium at a temperature of 50-70°C. First, adjust the pH of the solution to 9 with lithium hydroxide. The generated magnesium hydroxide combines with excess magnesium ions to positively charge and adsorb boron ions in the solution. Solid-liquid Separate and remove most of the magnesium, then adjust the pH of the solution to 12 with the mother liquor lithium hydroxide solution and lithium carbonate solution after crystallization separation, remove the remaining magnesium, c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com