Method for preparing spherical aluminum nitride powder under assistance of high atmospheric pressure and fluoride additive
A fluoride and additive technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, nitrogen compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., to achieve the effects of large particle size, convenient operation and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
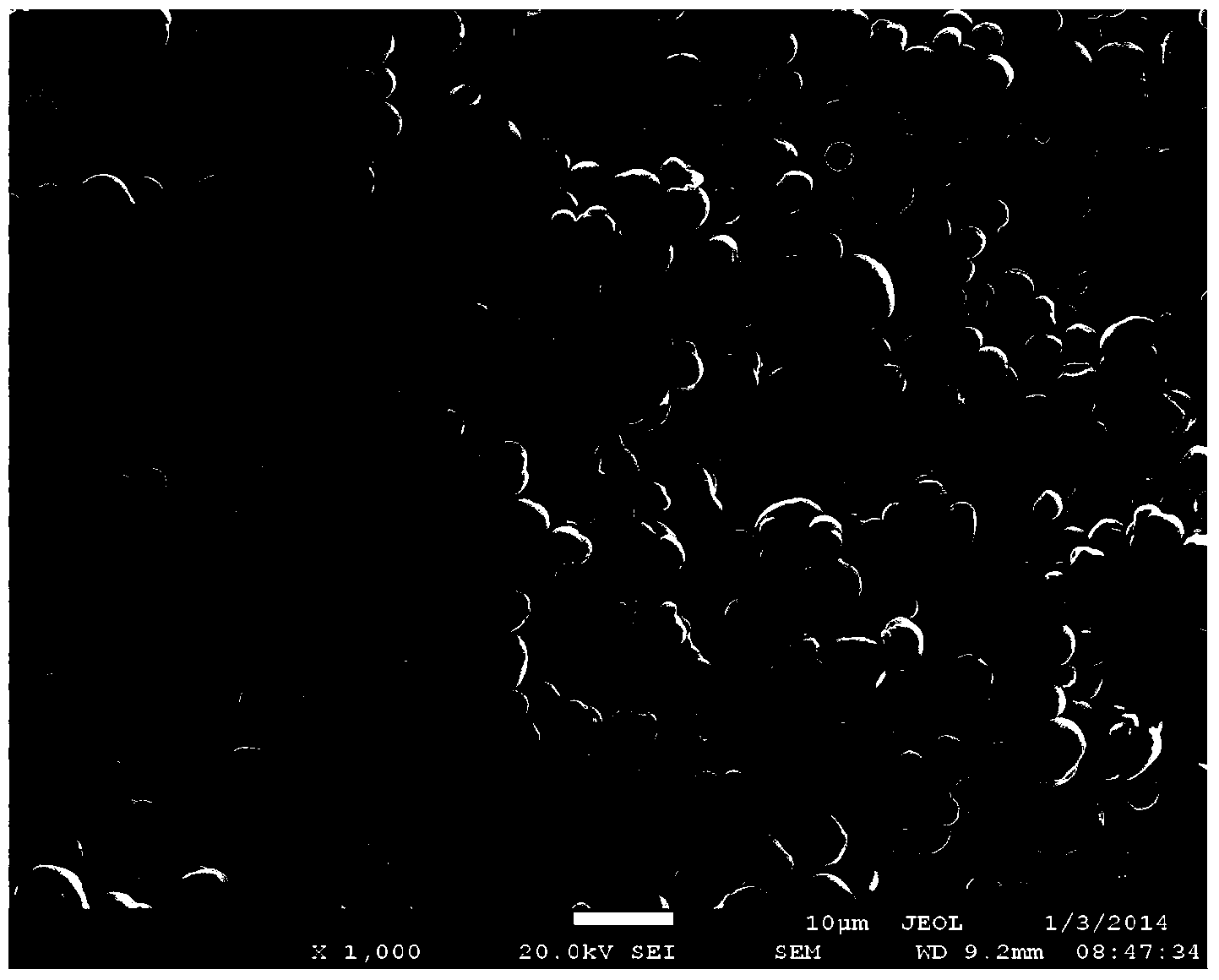
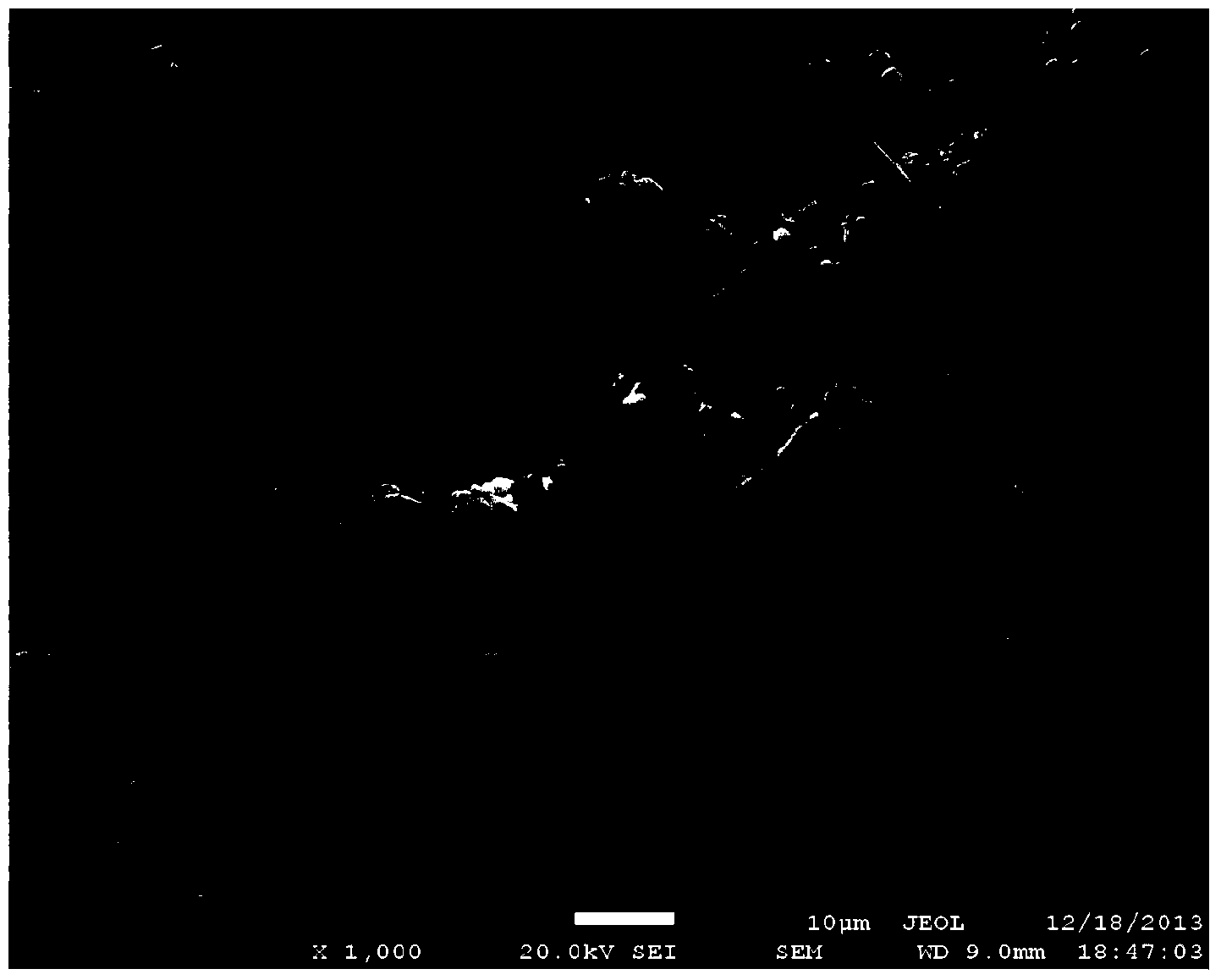
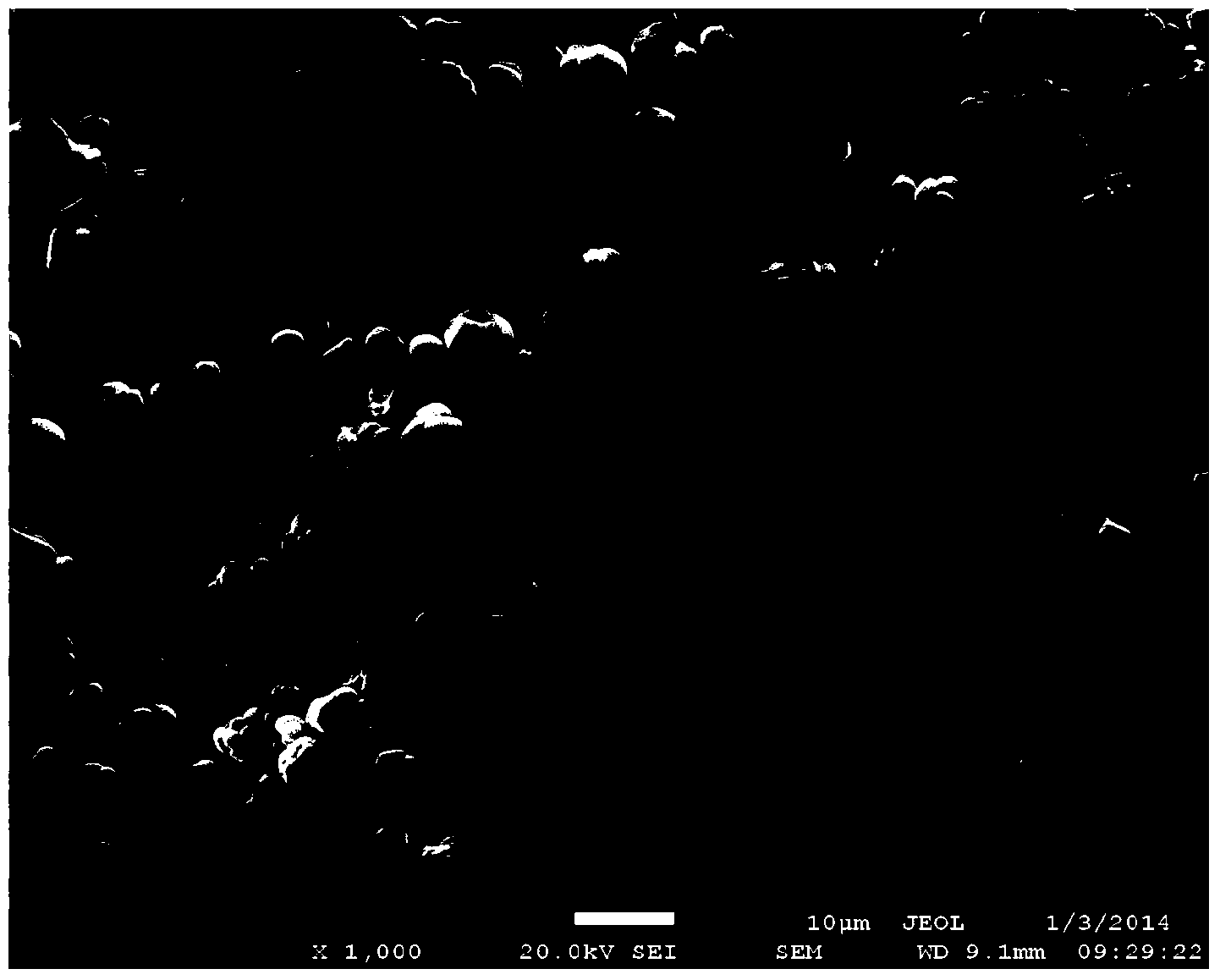
[0028] Add 48.5g of alumina (average particle size 1.1 μm) and 1.5g calcium fluoride into 50 g of deionized water to prepare an aqueous slurry with a solid content of 50 wt%, and add 25 g of carbon black (average particle size of 0.2 μm) into 75 g of water , prepared into aqueous slurries with a solid content of 25%, each ball milled for 24 hours, mixed and then ball milled for 24 hours, then dried and ground. The obtained mixture was placed in a graphite crucible, and transferred to a gas pressure sintering furnace with a nitrogen pressure of 0.9 MPa, and reacted at 1800° C. for 2 h. After the reaction was completed, the obtained product was reacted in a muffle furnace at 650° C. for 4 hours to remove carbon. Use X-ray diffraction to calculate the nitriding rate of the product; use a laser particle size analyzer to measure the average particle size D50 of the product; use an electron scanning electron microscope to observe the product morphology, and randomly select 50 partic...
Embodiment 2
[0031] 48.5g aluminum oxide (average particle diameter 1.1 μm) and 1.5g yttrium oxide are added in 50g deionized water, are mixed with the aqueous slurry that solid content is 50wt%, 25g carbon black (average particle diameter 0.2 μm) is added in 75g water, Aqueous slurries with a solid content of 25% were prepared, and after ball milling for 24 hours, they were mixed and ball milled for 24 hours before being dried and ground. The obtained mixture was placed in a graphite crucible, and transferred to a gas pressure sintering furnace with a nitrogen pressure of 0.9 MPa, and reacted at 1800° C. for 2 h. After the reaction was completed, the obtained product was reacted in a muffle furnace at 650° C. for 4 h to remove carbon. The nitriding rate, average particle size, morphology, sphericity, etc. of the product were characterized by the same method as in Example 1, which are listed in Table 1. Composite materials were prepared by the same method as in Example 1, and the thermal ...
Embodiment 3
[0033]50g of alumina (average particle size 1.1 μm) was added to 50 g of deionized water to prepare an aqueous slurry with a solid content of 50 wt%, and 25 g of carbon black (average particle size of 0.2 μm) was added to 75 g of water to prepare a solid content of 25 wt%. % water-based slurry, after ball milling for 24 hours respectively, after mixing, continue ball milling for 24 hours and then dry and grind. The obtained mixture was placed in a graphite crucible, and transferred to a gas pressure sintering furnace with a nitrogen pressure of 0.1 MPa at normal pressure, and reacted at 1800° C. for 2 h. After the reaction was completed, the obtained product was reacted in a muffle furnace at 650° C. for 4 h to remove carbon. The nitriding rate, average particle size, morphology, sphericity, etc. of the product were characterized by the same method as in Example 1, which are listed in Table 1. Composite materials were prepared by the same method as in Example 1, and the therm...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com