Nickel hydrogenation catalyst
A catalyst and nickel source technology, applied in the field of hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty materials, can solve the problems of limiting the total amount of nickel, unfavorable catalyst metal dispersion and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1 (reference): Nickel catalyst: 59.1 wt% Ni supported on silica
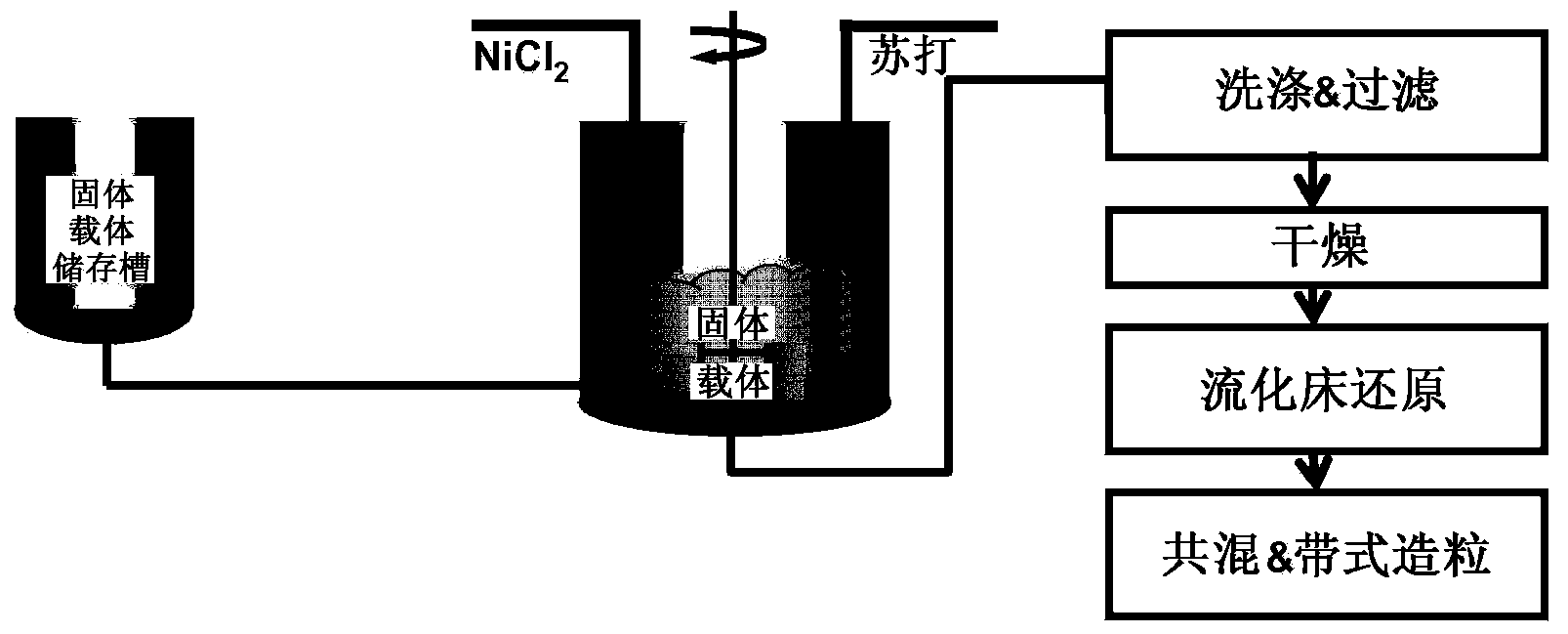
[0053] At a temperature of 90°C, simultaneously and at the same rate, 1000ml of an aqueous solution of nickel chloride (95g / l nickel) and magnesium chloride (7.4g magnesium / liter) and 1000ml of sodium metasilicate (47.6g / lNa 2 SiO 3 ·5H 2 O) solution and sodium carbonate (209 g / liter) were pumped into a stirred 4-liter settling vessel. The initial volume of water in the precipitation vessel was 1725 ml and contained 75 ml of sodium aluminate solution (50.9 g / l Al 2 o 3 ). The pH of the slurry was 7.5 and precipitation was complete after about 1 hour.
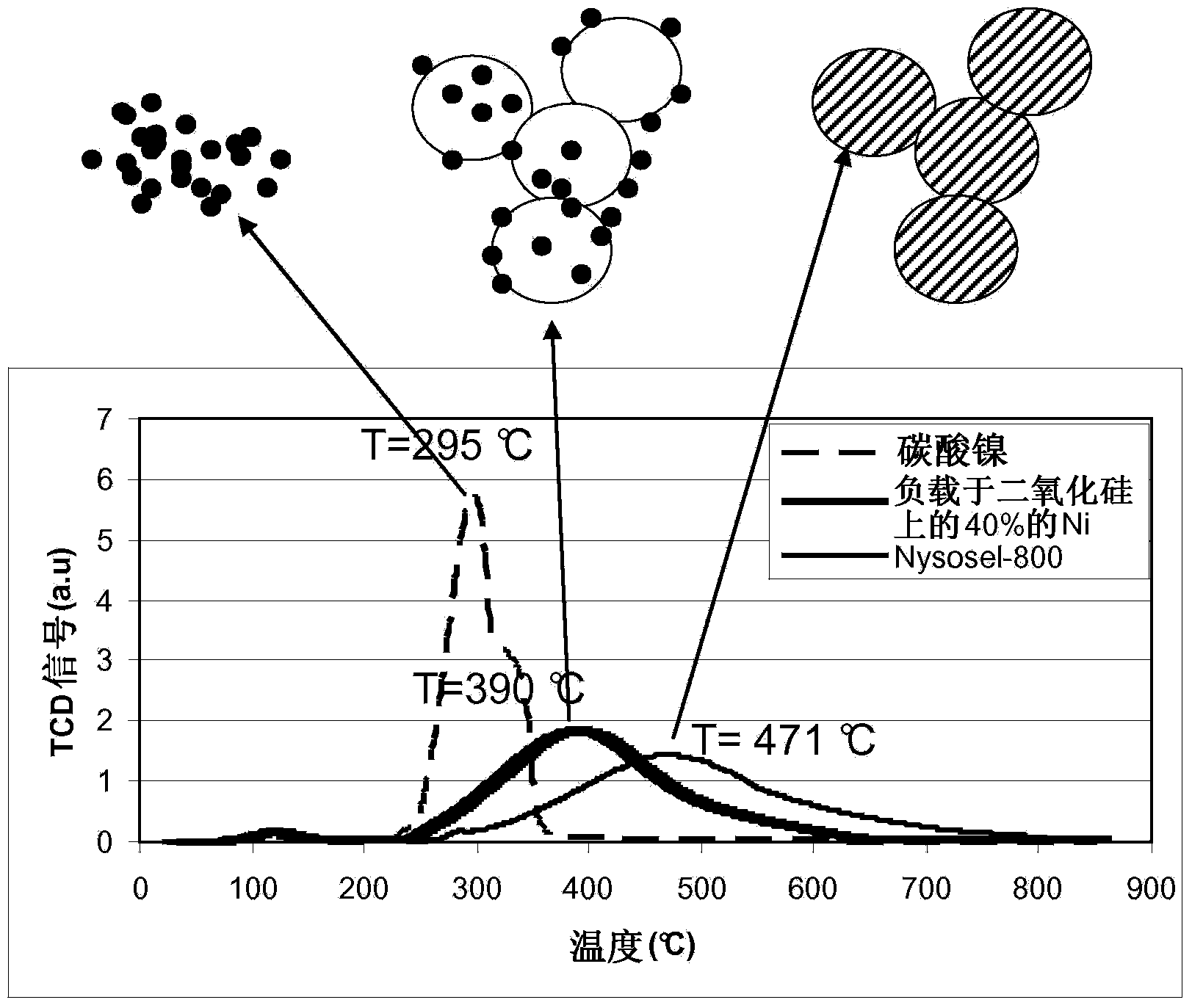
[0054] After washing the precipitate with approximately 30 liters of water, the catalyst precursor formed was filtered and dried in an oven at 110°C. The catalyst was activated with hydrogen at 400°C. The TPR maximum peak and specific pore volume were determined (based on the calcined precursor) to be 471° C. and 0.48 ml / g, respectively.
...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2: 40 wt% Ni supported on silica
[0057]At a temperature of 60° C., 1000 ml of an aqueous solution of nickel chloride (81.6 g / l nickel) and 848 ml of a solution of sodium carbonate (220 g / l) were simultaneously pumped into a stirred 4-liter settling vessel. The initial volume of water in the sedimentation vessel is 2000ml and contains 100 grams with a specific pore volume of 1.72ml / g, 271m 2 / g surface area and Highly porous silica powder with peak porosity. The pH of the slurry was 7.5. Precipitation was complete after about 1 hour.
[0058] After washing the precipitate with about 30 liters of cold water, the catalyst precursor formed was filtered and dried in an oven at 110°C. The catalyst was activated with hydrogen at 400°C. The TPR maximum peak and specific pore volume were determined (based on the calcined precursor) to be 385° C. and 0.52 ml / g, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: (37.5 wt% Ni supported on silica)
[0060] At a temperature of 60° C., 1000 ml of an aqueous nickel chloride (71.7 g / l nickel) solution and 750 ml of a sodium carbonate (220 g / l) solution were simultaneously pumped into a stirred 4-liter settling vessel. The initial volume of water in the precipitation vessel was 2000 ml and contained 100 grams of highly porous silica powder with a specific pore volume of 1.72 ml / g. The pH of the slurry was 7.5 and the precipitation was complete after about 1 hour.
[0061] After washing the precipitate with approximately 30 liters of cold water, the catalyst precursor formed was filtered and dried in an oven at 110°C. The catalyst was activated with hydrogen at 400°C. The TPR maximum peak and specific pore volume were determined (based on the calcined precursor) to be 395° C. and 0.57 ml / g, respectively.
[0062] Based on the weight of the catalyst, the nickel content of the reduced catalyst was 43.2 wt %; the amount of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com