Cellulose dissolving agent and application thereof
A cellulose dissolving and regenerated cellulose technology, applied in the direction of single-component cellulose artificial filament, fiber chemical characteristics, spinning solution preparation, etc., can solve the complex dissolution process, high energy consumption, high viscosity and high elasticity of the solution, etc. problems, to achieve the effects of wide adjustable range, shortened process flow, and high solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
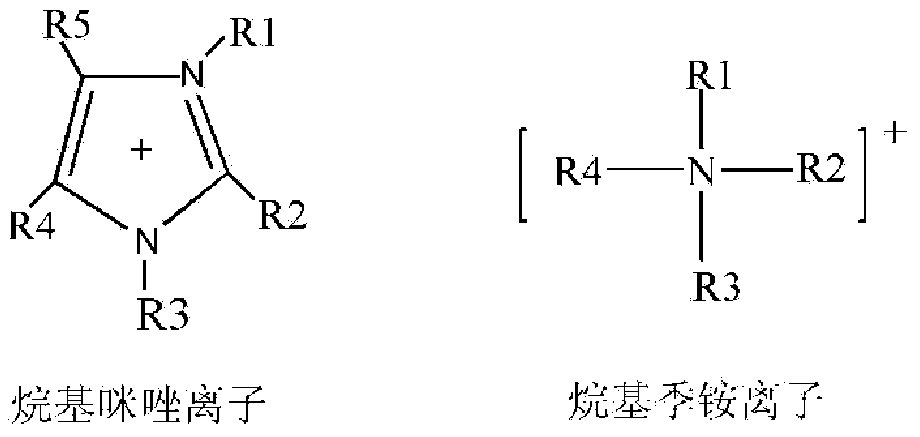
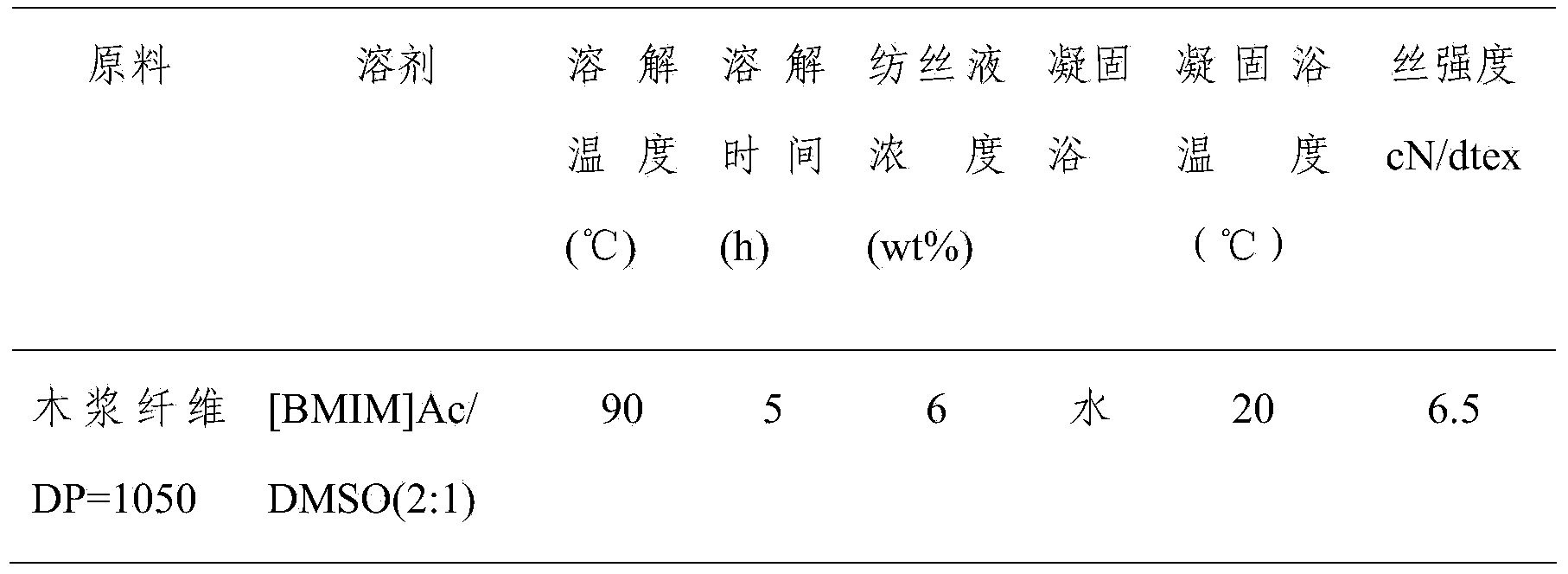
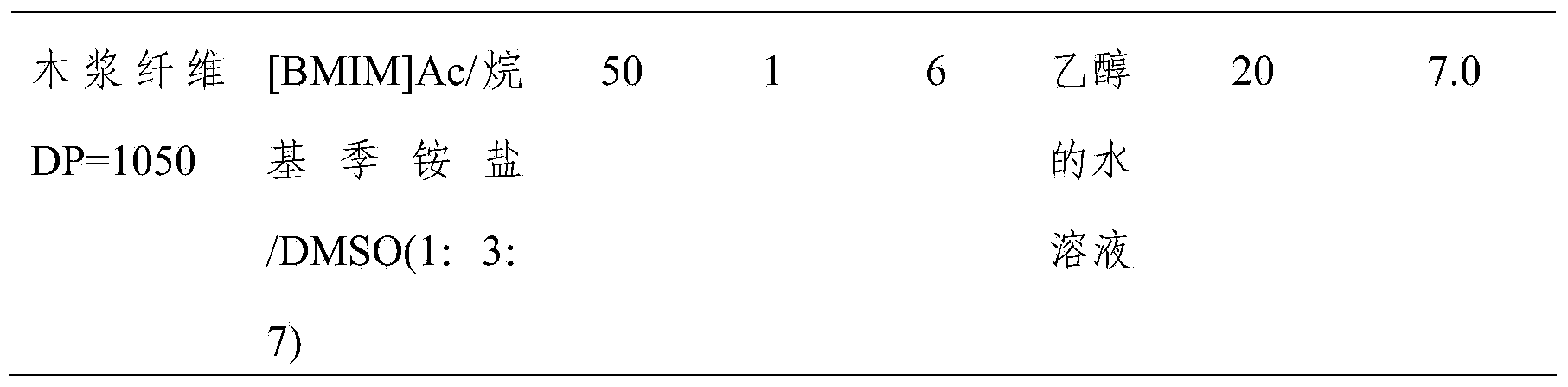
[0027] Add the pulverized wood pulp fibers (DP value of 1050) to 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (【BMIM】Cl) without / adding alkyl quaternary ammonium salt ion solution respectively and dimethyl sulfoxide composition. The ratio of crushed wood pulp fiber to dissolving agent is 3:50.
[0028] The specific data are shown in Table 1:
[0029] Table 1 The effect of alkyl quaternary ammonium salt ion solution on the dissolution rate of wood pulp fiber
[0030]
[0031]
[0032] The experimental results are as follows:
[0033] 1, do not add the wood pulp fiber of alkyl quaternary ammonium salt ion solution, dissolve at 90 ℃ according to prior art record, form uniform, stable, transparent spinning solution through 5 hours, the concentration of spinning solution is 6%. The spinning liquid is filtered and defoamed, then wet-spun, the coagulation bath is water, and the temperature is 20°C. The drawing ratio during spinning is 2, and the cellulose fibers with a strength of ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Add the pulverized cotton linters (DP value of 850) to 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (【BMIM】Ac) without / adding alkyl quaternary ammonium salt ion solution respectively. and dimethyl sulfoxide composition. The ratio of crushed wood pulp fiber to dissolving agent is 1:25. The specific data are shown in Table 2:
[0038] The impact of table 2 alkyl quaternary ammonium salt ion solution on the dissolution rate of cotton linters
[0039]
[0040]
[0041] The experimental results are as follows:
[0042]1, do not add the linter of alkyl quaternary ammonium salt ion solution, dissolve at 90 ℃ according to prior art record, form uniform, stable, transparent spinning solution through 4.5 hours, the concentration of spinning solution is 4%. The spinning liquid is filtered and defoamed, then wet-spun, the coagulation bath is water, and the temperature is 20°C. The drawing ratio during spinning is 2, and the cellulose fibers with a strength of 6 cN / dtex are obtaine...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Add the pulverized microcrystalline cellulose (DP value of 220) to 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate ([BMIM] Ac ) and dimethyl sulfoxide composition. The ratio of crushed wood pulp fiber to dissolving agent is 1:5. The specific data are shown in Table 3:
[0047] The impact of table 3 alkyl quaternary ammonium salt ion solution on the dissolution rate of microcrystalline cellulose
[0048]
[0049] The experimental results are as follows:
[0050] 1. Microcrystalline cellulose without adding alkyl quaternary ammonium salt ion solution, according to prior art records, dissolves at 90°C, and forms a uniform, stable and transparent spinning solution after 4.5 hours, and the concentration of the spinning solution is 20% . The spinning liquid is filtered and defoamed, then wet-spun, the coagulation bath is water, and the temperature is 20°C. The drawing ratio during spinning is 2, and the cellulose fibers with a strength of 2.8cN / dtex are obtained through washing a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com