Detection method and detection reagent of fluoroquinolone antibiotics
A fluoroquinolone and detection method technology, applied in the field of antibiotic analysis and detection, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, complicated electrode preparation process, etc., and achieve the effects of high sensitivity, simple preparation process, and simple and fast test method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A detection reagent for fluoroquinolone antibiotics containing divalent heavy metal ions 10 -2 The acetic acid buffer solution of mol / L; Its pH value is 3.6; Described divalent heavy metal ion is copper ion.
[0040] With described fluoroquinolone antibiotic detection reagent, detect ofloxacin, the steps are as follows:
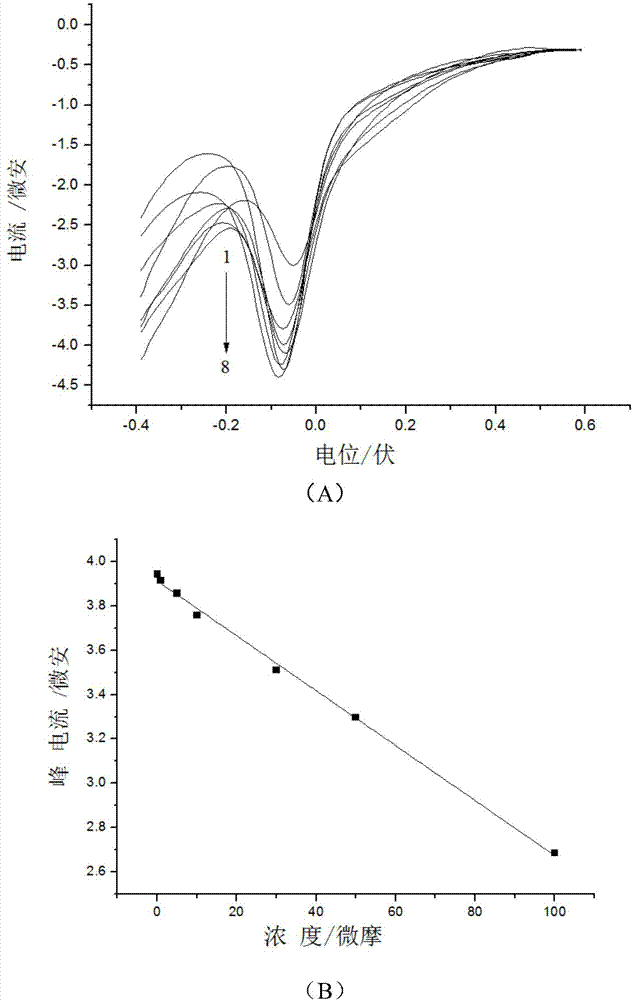
[0041] (1) Add the fluoroquinolone antibiotic detection reagent to the sample to be tested, mix evenly, react for 10 minutes, adjust the pH value to 3.6, and obtain the antibiotic-heavy metal complex solution, wherein the concentration of the divalent heavy metal ion is 10 -4 mol / L. The sample to be tested is a chicken feed sample obtained by the standard recovery method, wherein the concentration of the standard ofloxacin added is 5 × 10 -6 mol / L.
[0042] (2) Select the glassy carbon electrode as the working electrode, the calomel electrode as the reference electrode, and the platinum electrode as the auxiliary electrode, and use the electrochemic...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A detection reagent for fluoroquinolone antibiotics containing divalent heavy metal ions 10 -2 mol / L acetate buffer solution; its pH value is 3.6; the divalent heavy metal ion is cadmium ion.
[0051] With described fluoroquinolone antibiotic detection reagent, detect ciprofloxacin, the steps are as follows:
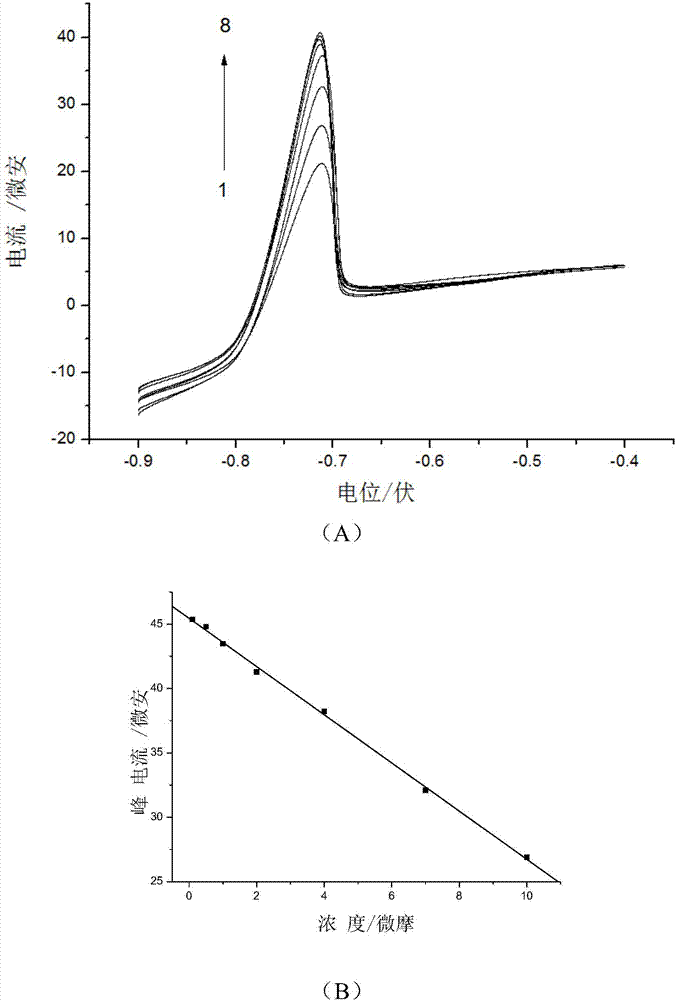
[0052] (1) Add the fluoroquinolone antibiotic detection reagent to the sample to be tested, mix evenly, react for 3 minutes, adjust the pH value to 3.6, and obtain the antibiotic-heavy metal complex solution, wherein the concentration of the divalent heavy metal ion is 10 -4 mol / L. The sample to be tested is ciprofloxacin hydrochloride tablet, the specification is 250mg / tablet.
[0053] (2) Select the glassy carbon electrode modified by nanomaterials as the working electrode, the calomel electrode as the reference electrode, and the platinum electrode as the auxiliary electrode, and use linear sweep voltammetry to perform step (1) in the potential range of -0.9V...
Embodiment 3
[0062] A detection reagent for fluoroquinolone antibiotics containing 5×10 divalent heavy metal ions -3 mol / L acetate buffer solution; its pH value is 5.6; the divalent heavy metal ion is cadmium ion.
[0063] With described fluoroquinolone antibiotic detection reagent, detect ciprofloxacin, the steps are as follows:
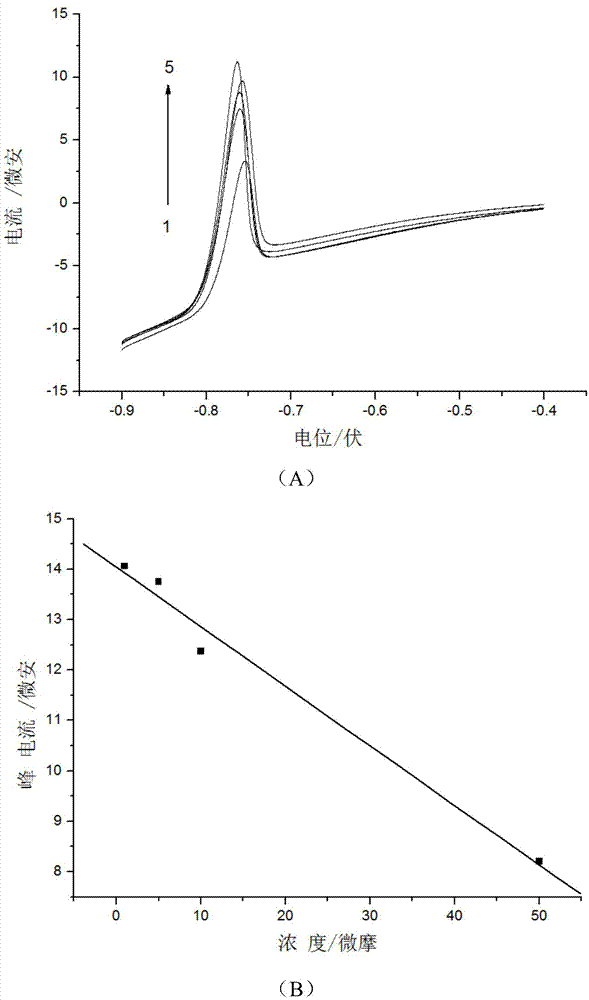
[0064] (1) Add the fluoroquinolone antibiotic detection reagent to the sample to be tested, mix evenly, react for 5 minutes, adjust the pH value to 5.6, and obtain the antibiotic-heavy metal complex solution, wherein the concentration of the divalent heavy metal ion is 5 × 10 -5 mol / L. The sample to be tested is ciprofloxacin hydrochloride tablet, the specification is 250mg / tablet.
[0065] (2) Select the glassy carbon electrode as the working electrode, the calomel electrode as the reference electrode, and the platinum electrode as the auxiliary electrode, and use linear sweep voltammetry to test the antibiotics obtained in step (1) in the potential range of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com