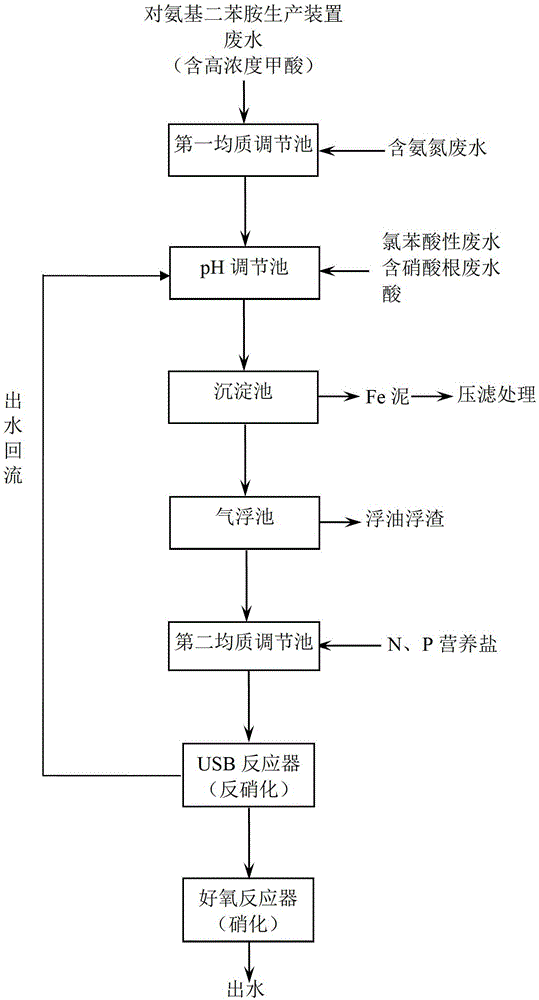
A method for treating waste water from the production of ammonia nitrogen-containing p-aminodiphenylamine
A technology for the production of p-aminodiphenylamine and waste water, which is applied in natural water treatment, chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of COD content failing to meet the national emission standards, chlorine gas leaking into the air, and lack of integrity Effective means and other issues, to achieve the effect of stable treatment effect, reduced wastewater treatment cost, high ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] The flow rate of p-aminodiphenylamine production wastewater in a chemical plant is 110t / d, and the pollutant indicators in the wastewater are: COD of wastewater is 52130mg / L, TOC is 31320mg / L, concentration of formic acid is 115400mg / L; concentration of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen is 212mg / L.
[0080] In the first step, in the first homogeneous regulating tank, p-aminodiphenylamine wastewater (wastewater from the production of p-aminodiphenylamine containing formic acid) is mixed with wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen (wastewater from the production of aniline containing ammonia nitrogen).
[0081] In the second step, in the pH adjustment tank, add chlorobenzene acid wastewater containing high concentration Fe and catalyst industrial wastewater containing nitrate, and add a certain amount of alkaline denitrification reflux water or dilution water to dilute the wastewater and adjust the mixed wastewater. The pH is 6.5. Then the COD i...
Embodiment 2
[0088] The flow rate of p-aminodiphenylamine production wastewater in a chemical plant is 120t / d, and the pollutant indicators in the wastewater are: COD of wastewater is 63500mg / L, TOC is 42600mg / L, concentration of formic acid is 178500mg / L; concentration of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen is 253mg / L.
[0089] In the first step, in the first homogeneous regulating tank, p-aminodiphenylamine wastewater is mixed with ammonia nitrogen-containing wastewater.
[0090] In the second step, in the pH adjustment tank, add chlorobenzene acid wastewater containing high concentration Fe, and catalyst industrial wastewater containing nitrate, and add dilution water or a certain amount of alkaline denitrification reflux water to dilute the wastewater and adjust the mixing The wastewater pH was 7.3. Then the COD in the effluent water of the pH adjustment tank is 1270.0mg / L, the TOC is 852.0mg / L, the formic acid is 3570.0mg / L, the nitrate is 1301.1mg / L, and the a...
Embodiment 3
[0097] The flow rate of p-aminodiphenylamine production wastewater in a chemical plant is 100t / d, and the pollutant indicators in the wastewater are: wastewater COD is 79400mg / L, TOC is 53420mg / L, formic acid concentration is 236400mg / L; ammonia nitrogen concentration in ammonia nitrogen-containing wastewater is 314mg / L.
[0098] In the first step, in the first homogeneous regulating tank, p-aminodiphenylamine wastewater is mixed with ammonia nitrogen-containing wastewater.
[0099] In the second step, in the pH adjustment tank, add chlorobenzene acid wastewater containing high concentration Fe, and catalyst industrial wastewater containing nitrate, and add dilution water or a certain amount of alkaline denitrification reflux water to dilute the wastewater and adjust the mixing The wastewater pH was 7.8. Then the COD in the effluent water of the pH adjustment pool is 1588.0mg / L, the TOC is 1068.4mg / L, the formic acid is 4728.0mg / L, the nitrate is 1278.8mg / L, and the ammonia n...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| chemical oxygen demand (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com