Production method of methyl glycolate
A technology of methyl glycolate and dimethyl oxalate, applied in the preparation of carboxylate, chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, etc., can solve the problem of low selectivity of methyl glycolate and low conversion rate of dimethyl oxalate and other problems to achieve the effect of avoiding difficult separation, reducing energy consumption, and low heat utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
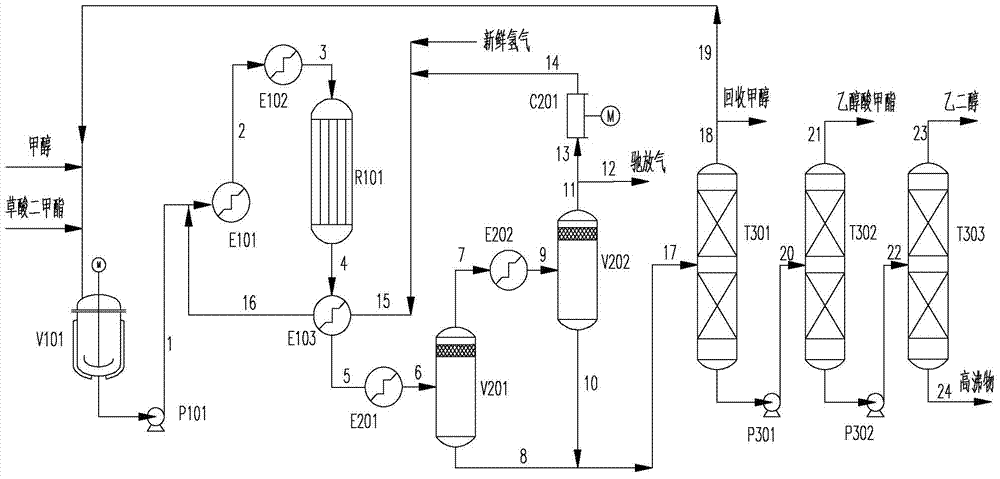
[0042] like figure 1 Shown, the method that the present invention produces methyl glycolate comprises the steps:
[0043] 1) Fresh methanol and dimethyl oxalate are stirred and dissolved in the dimethyl oxalate dissolution kettle V101 at a mass ratio of 1:1 to obtain a methanol solution of dimethyl oxalate. ~0.5MPa, the liquid coming out from the bottom of V101 is pressurized to the reaction pressure by the liquid-phase feed pump P101, the reaction pressure is 1.5MPa in terms of gauge pressure, the outlet stream 1 of the liquid-phase feed pump P101 (that is, dimethyl oxalate methanol solution) and the hydrogen in the raw material gas containing hydrogen (wherein the hydrogen gas fraction is 90%) are mixed in a molar ratio of 1:8 to obtain a mixed feed, which then enters the vaporizer E101, and the outlet stream 2 of the vaporizer E101 goes to the front of the reactor The preheater E102 heats up to the reaction temperature of 188°C and enters the isothermal fixed-bed reactor R...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The hydrogen ester molar ratio in the isothermal fixed-bed reactor R101 is 20, and the rest are the same as in Example 1. The conversion rate of dimethyl oxalate is 98.02%, the selectivity of methyl glycolate is 88.75%, and the selectivity of ethylene glycol is 9.32%. The content of methyl glycolate at the top of the methyl glycolate removal tower was 97.8wt%.
Embodiment 3
[0054] The hydrogen ester molar ratio in the isothermal fixed-bed reactor R101 is 40, and the rest are the same as in Example 1. The conversion rate of dimethyl oxalate is 96.88%, the selectivity of methyl glycolate is 91.32%, and the selectivity of ethylene glycol is 6.84%. The content of methyl glycolate at the top of the methyl glycolate removal tower was 94.4wt%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com