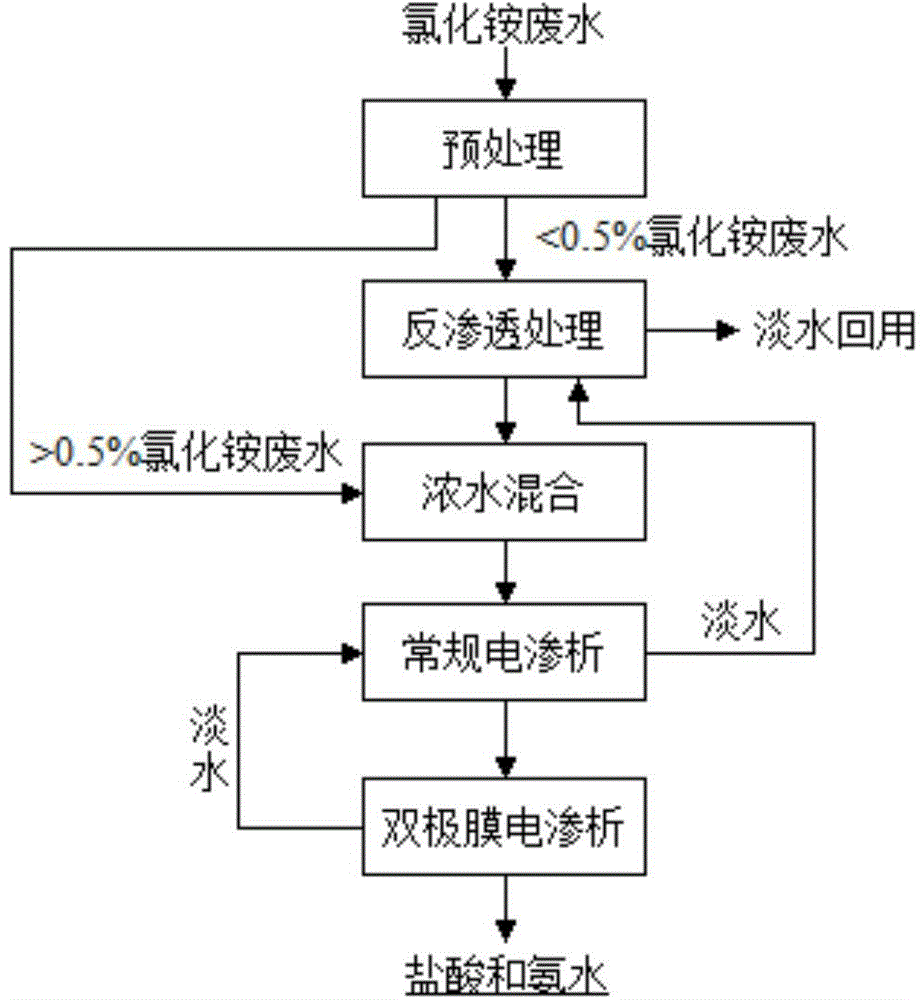
Method for resourceful treatment of ammonia chloride wastewaters
A ammonium chloride and recycling technology, applied in the field of resource recycling, can solve problems such as high energy consumption and equipment corrosion, and achieve the effects of zero emissions, increased concentration, and reduced energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1 Ammonium chloride wastewater electrodialysis desalination and concentration
[0037] Ammonium chloride wastewater was desalted and concentrated by conventional electrodialysis technology, and the effect of electrodialysis desalination and concentration of ammonium chloride wastewater with different initial concentrations was investigated. Prepare ammonium chloride wastewater with a salt content of 0.5%, 1%, 1.5%, 2% and 5%, and treat them with conventional electrodialysis technology. Studies have shown that with the increase of the initial concentration of ammonium chloride wastewater, the longer it takes for the salt content of electrodialysis fresh water to drop below 0.5% under constant pressure conditions, the more stages of electrodialysis membrane stacks are required. As the salt content of fresh water decreases, its resistance increases, which can lead to a decrease in current density. At the same time, it can be found that with the increase of the ...
Embodiment 2
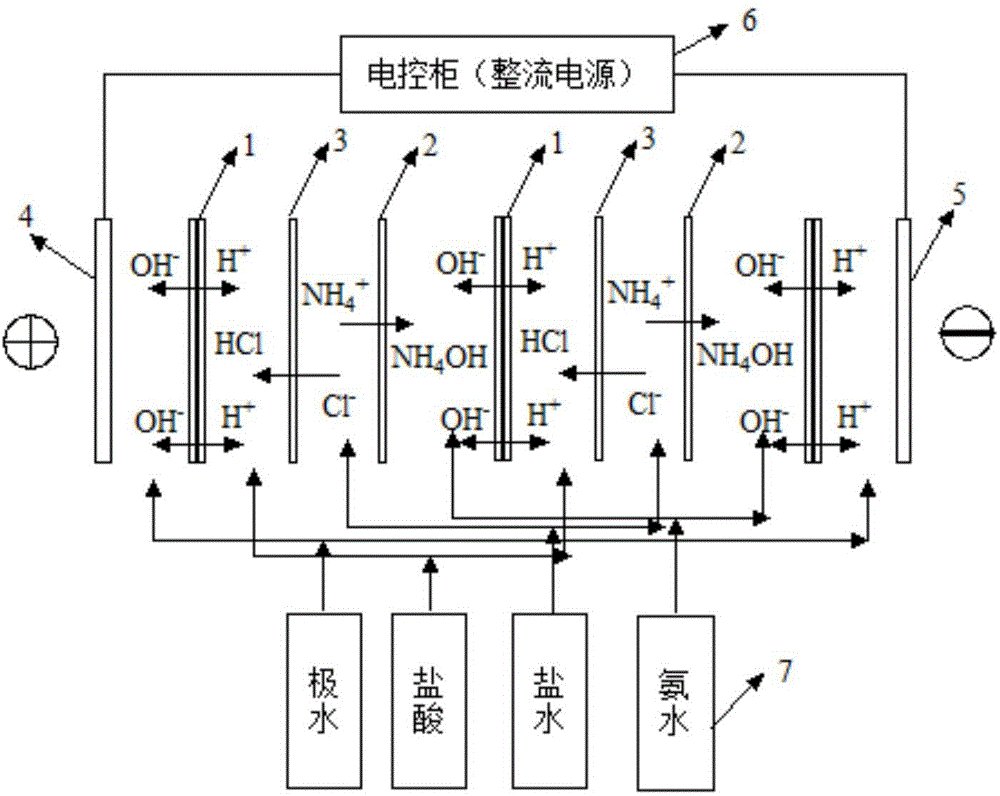
[0038] Example 2 High-concentration ammonium chloride bipolar membrane electrodialysis acid-base regeneration
[0039] Such as figure 2 As shown, the schematic diagram of the principle of bipolar membrane electrodialysis acid-base regeneration adopted in the present invention. The membrane stack structure includes bipolar membrane 1, cation exchange membrane 2, anion exchange membrane 3, separator, liquid storage tank (including polar water tank, brine tank, acid tank, lye tank) 7, electrodes including anode 4, cathode 5 and electric control cabinet (including rectifier power supply), and clamping device, etc. The principle of bipolar membrane electrodialysis acid-base regeneration is that water molecules enter the interface layer of bipolar membrane through diffusion and dissociate into H under the action of polarization potential. + and OH - ions to form an acid chamber and an alkali chamber respectively. At the same time, high-concentration ammonium chloride wastewater ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com