Cancer promotion activity quantitative determination method and screening method of cancer promoter
A quantitative detection and activity technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of prolonged detection time, time-consuming and laborious, unable to meet the actual detection of fast and large samples, etc., and achieve the effect of quantitative detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
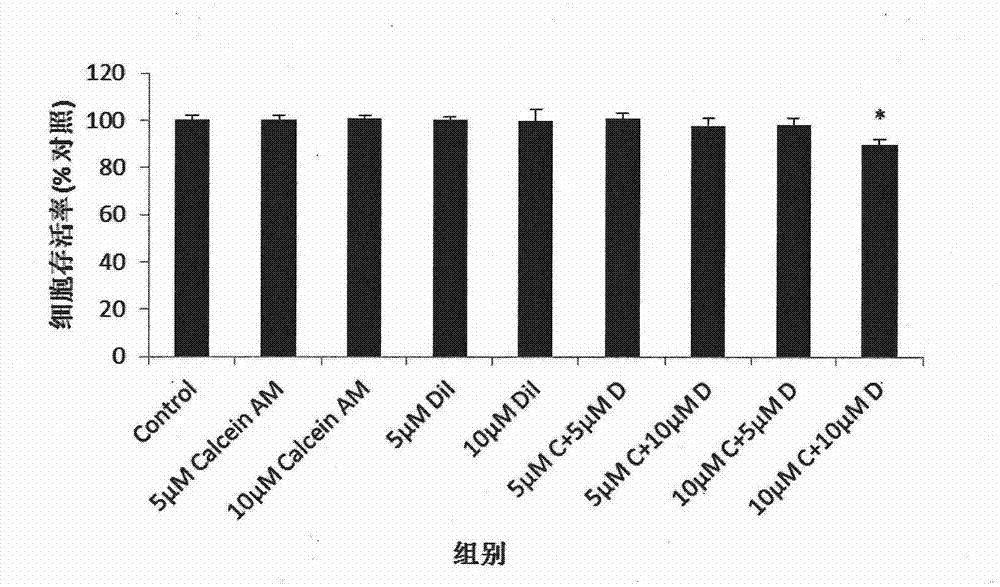
[0062] 1. Establish a stable fluorescent probe-labeled cell model
[0063] 1.1 Cell culture
[0064] Select human immortalized epidermal HaCat cells (CCTCC, China Type Culture Collection Center), use MEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and penicillin-streptomycin double antibody (penicillin 100U / mL; streptomycin 100 μg / mL), At 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultivated under conditions. The cells in the logarithmic growth phase were digested with 0.25% trypsin (containing 0.03% EDTA), and passaged once every 2-3 days.
[0065] 1.2 Fluorescent probe preparation
[0066] Calcein AM (C-3099, Molecular Probes) solution (1 mM) was aliquoted and stored at -20°C in the dark for future use. DiI (D-282, Molecular Probes) powder was prepared into 2mM stock solution with DMSO, and stored at -20°C in the dark for future use after aliquoting.
[0067] Probe diluent: Glucose was dissolved in sterilized double distilled water to prepare a 0.3M glucose use solution, and stored at 4°C for later us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com