A two-dimensional light scattering static cytometer method and device
A light scattering and cytometer technology, applied in the fields of biotechnology, medical devices, environment and safety, and biomedicine. Sophisticated, broadly applicable effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
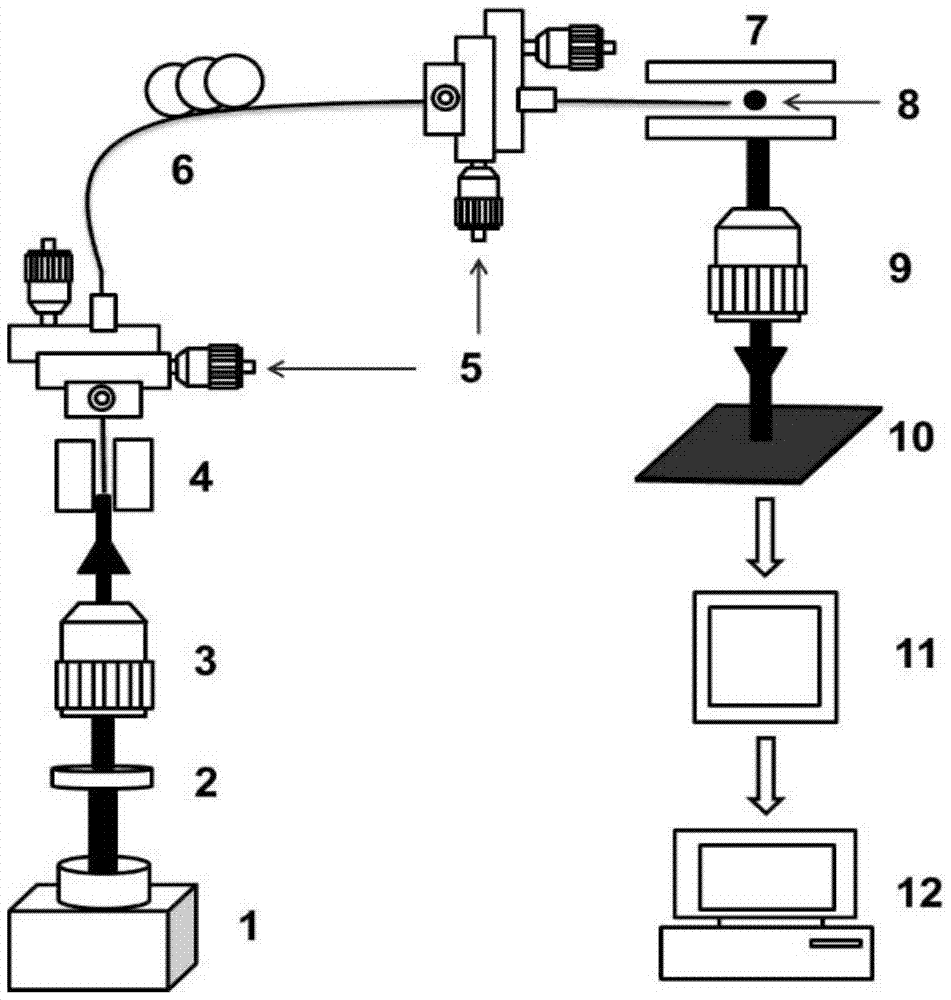
[0063] The structural principle of the device of the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, yeast cells were selected as the tested samples for nanoscale analysis of cell size.
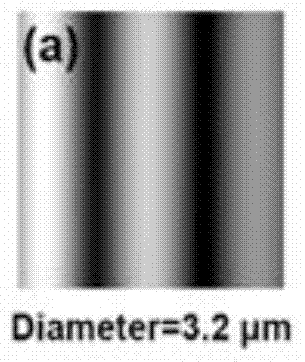
[0064] According to the Mie scattering theory, yeast cells are assumed to have spherical particles with different diameters, the refractive index of the cells is 1.42, the incident light wavelength is 532nm, and the refractive index of the surrounding medium and aqueous solution is 1.334. The nanometer resolution single cells and particles provided by the present invention The angle range of the scattering pattern detected in the analyzed two-dimensional light scattering static cytometer device is 79-101 degrees, so the theoretical simulation also selects the same angle range, and then simulates the two-dimensional light scattering of a large number of yeast cell models with known diameters Pattern 11, such as Figure 3(a)-Figure 3(j) shown.
[0065] Preparation of the single-cell thin layer of ...
Embodiment 2
[0070] The structural principle of the device of the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, microspheres with average diameters of 3.87 μm (standard error 0.25 μm) and 4.19 μm (standard error 0.27 μm) were selected as the tested samples for submicron level analysis of particle size.
[0071] The refractive index of theoretically simulated microspheres is 1.42, the incident light wavelength is 532um, the refractive index of the surrounding medium and aqueous solution is 1.334, and the angle range is 79-101 degrees. A large number of microsphere models with known diameters are simulated by Mie scattering theory. Dimensional light scattering pattern11.
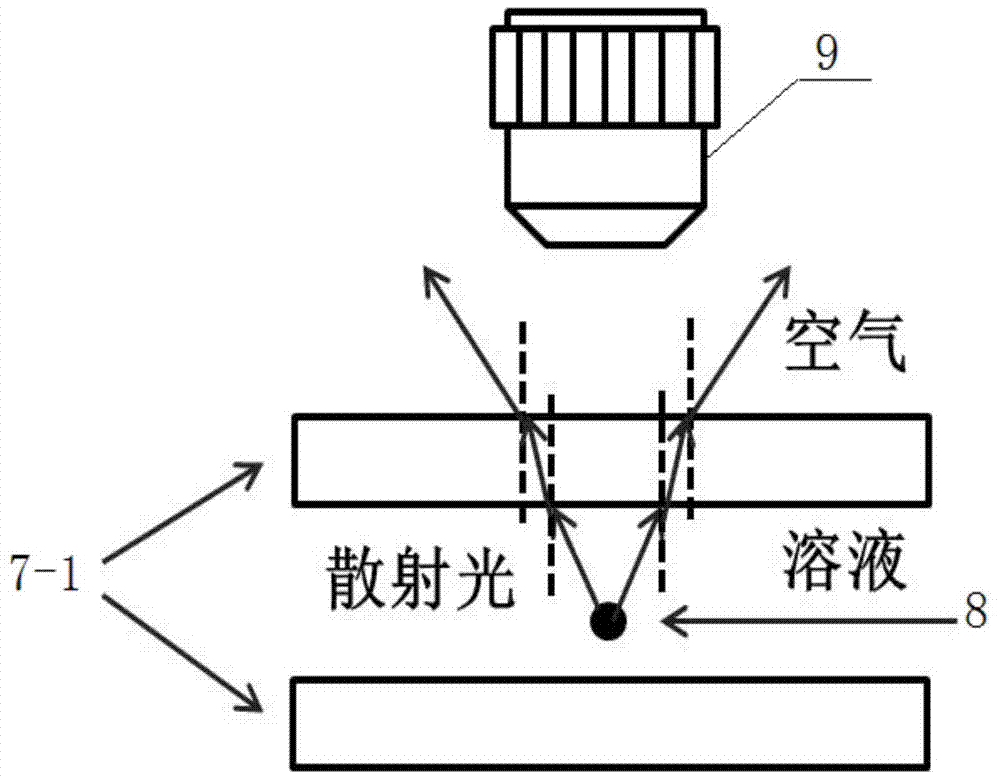
[0072] The measured microsphere solution is diluted to ensure that there is a small amount of free microspheres in the observation field of view of the ten times objective lens 9. Use a pipette to draw a small amount of microsphere solution each time, drop it on the center of slide glass 7-1 with a cover glass placed at each...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The structural principle of the device of the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, yeast cells with a refractive index of 1.42 (incident wavelength of 589 nm) and microspheres with a refractive index of 1.59 (incident wavelength of 589 nm) were selected as tested samples for refractive index analysis.
[0078] According to the Mie scattering theory, 45 two-dimensional light scattering patterns 11 of the yeast model with a refractive index of 1.42, an incident light wavelength of 532nm, a refractive index of the surrounding medium and aqueous solution and different diameters (diameters ranging from 2.8 μm to 7.2 μm) were obtained by simulation. μm, with a step size of 0.1 μm), scan the 45 scattering patterns horizontally to obtain the change curve of the grayscale image; perform FFT on the grayscale curve obtained by scanning, and a typical main peak will appear in the FFT curve, and make statistics on it Analysis, the linear equation of the yeast cell peak frequen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com