A bacterial strain that simultaneously utilizes glucose and xylose to produce alcohol fuels and its application
A technology of alcohol fuel and glucose, which is applied in the field of bioengineering to reduce process energy consumption, improve equipment utilization, and improve economic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
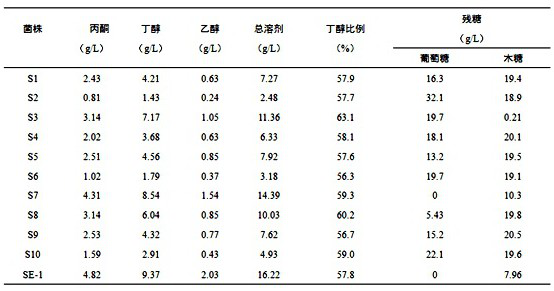
[0027] Example 1: Isolation, screening and identification of a strain of Clostridium beijerinckii capable of synchronously utilizing glucose and xylose to produce butanol and ethanol.
[0028] Step 1: Sampling
[0029] Samples were collected from the sludge of Jinan No. 1 Wastewater Treatment Plant.
[0030] The second step: enrichment culture
[0031] Take 1 g of the collected sample and put it into a 100 mL enrichment medium blue cap bottle, heat shock it at 80 °C for 10 min, cool it with water, place it in a constant temperature incubator at 37 °C for enrichment culture for 3 days, and select the culture with a large number of bubbles. The solution was further enriched in the enrichment medium, and after five passages, samples were taken for gas chromatography analysis. The fermentation broth with butanol production was transferred to the separation medium to continue the fermentation culture.
[0032] Enrichment medium (for culture of anaerobic bacteria): 5 g xylose, 10...
Embodiment 2
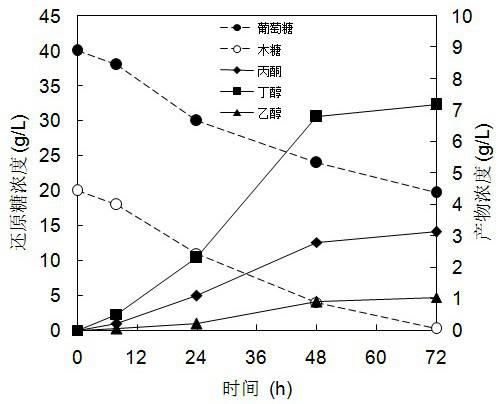
[0053] Production of butanol by batch fermentation of corn cob hydrolyzate by Clostridium beijerinckii SE-2
[0054] 1. Strains:
[0055]Clostridium beijerinckii SE-2, the applicant deposited the strain in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC for short) on August 19, 2014, and its deposit number is: CCTCC No. M2014384.
[0056] 2. Culture medium:
[0057] Corn cob hydrolyzate: total sugar content is 49.2 g / L (including 33.5 g / L glucose and 15.8 g / L xylose)
[0058] Seed medium (TYA medium): glucose 40 g, beef extract 2 g, yeast powder 2 g, peptone 6 g, CH 3 COONH 4 3 g, KH 2 PO 4 0.5 g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2 g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.01 g, distilled water 1000 mL, pH 6.5, autoclave at 121 ℃ for 15 min, blow with sterile nitrogen for 5 min to drive out oxygen.
[0059] Butanol basic fermentation medium (MP2): corncob hydrolyzate, K 2 HPO 4 0.5 g, KH 2 PO4 0.5 g, CH 3 COONH 4 2.2 g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2 g, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.01 g, NaCl 0.01 g, FeSO4 7H 2 ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Production of butanol by batch fermentation of corncob hydrolyzate by Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC824
[0069] 1. The similarities with Embodiment 2 will not be repeated, and the differences will be further explained.
[0070] 2. Strain: Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC824, which is a model strain for butanol production, can utilize glucose and xylose, but there is a "glucose repression effect" in the fermentation process, and xylose can only be utilized after glucose is fully utilized.
[0071] 2. After the fermentation, the concentrations of glucose and xylose in the fermentation broth were 0.5 g / L and 4.2 g / L respectively, and the concentrations of butanol and ethanol were 11.03 g / L and 1.68 g / L respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com