Preparation of molecular imprinting release controlled drug carrier through taking metal and organic gel as pore-foaming agent
An organogel and molecular imprinting technology, which is applied in the field of -BTC) metals, can solve the problems of inability to specifically recognize template molecules and holes without template molecule configurations, and achieve easy operation, simple preparation process, and obvious imprinting effect Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
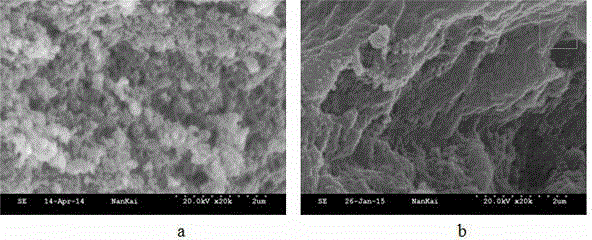
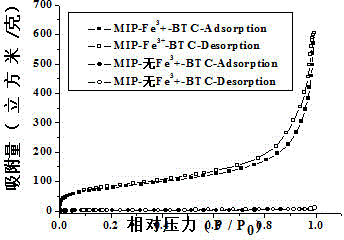
[0025] To confirm that Fe 3+ -The role of BTC metal-organic gels in the synthesis of levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymers. We prepared two levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymers, one based on Fe 3+ - BTC metal-organic gel as porogen levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymer, the other is Fe-free 3+ -BTC metal-organic gel was used as porogen levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymer, and scanning electron microscope analysis was carried out on the two polymers to characterize the morphological characteristics and nitrogen adsorption analysis of the particles. The specific operation steps were as follows:
[0026] with Fe 3+ -BTC metal-organic gel is the porogen levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymer preparation method:
[0027] a. template molecule levofloxacin 0.99% (both mass percent), functional monomer methacrylic acid 1.88%, initiator azobisisobutyronitrile 0.16%, crosslinking agent ethylene glycol dimethacrylate 17.41 %, gel ligand trimesic acid 1.83 ...
Embodiment 2
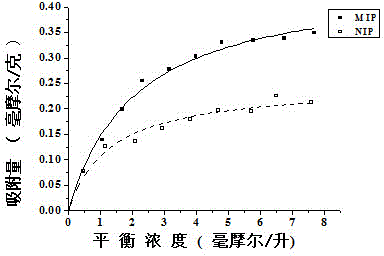
[0037] Experimental study on equilibrium adsorption of levofloxacin with Fe 3+ -Specific adsorption performance of levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymer with BTC metal-organic gel as porogen to imprinted molecule levofloxacin, in order to investigate the specificity of imprinted polymer to levofloxacin To determine the recognition ability, the adsorption isotherms of levofloxacin-imprinted polymers and non-imprinted polymers in the range of 0-10 mmol / L were determined. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0038] a. Synthesize with the above-mentioned method (embodiment 1) with Fe 3+ -BTC metal-organic gel is the levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymer MIP of porogen, and the synthesis of non-imprinted polymer NIP is the same as levofloxacin except that the template molecule levofloxacin is not added. Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers.
[0039] b. Weigh 20.0 mg of dry levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymer and non-imprinted polymer respectivel...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Drug Release Experiments A model for studying the kinetics of drug release from levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymers. In order to investigate the drug release model, the total amount of drug released by levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymers and non-imprinted polymers within a certain period of time was determined. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0047] a. Synthesize with the above-mentioned method (embodiment 1) with Fe 3+ -BTC metal-organic gel is the levofloxacin imprinted polymer MIP of the porogen, and the synthesis of the non-imprinted polymer NIP is the same as the levofloxacin molecule except that the template molecule levofloxacin is not added. Synthesis of imprinted polymers.
[0048] b. Soak the synthesized levofloxacin molecularly imprinted polymer and non-imprinted polymer in pH 7.40 phosphate buffer solution of levofloxacin, then wash twice with double distilled water, and dry at room temperature; Weigh the drug-loaded levoflo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com