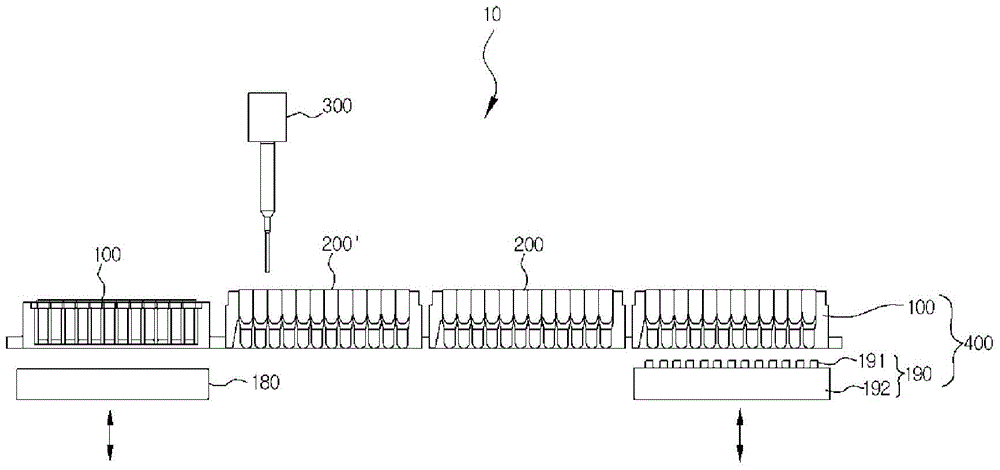
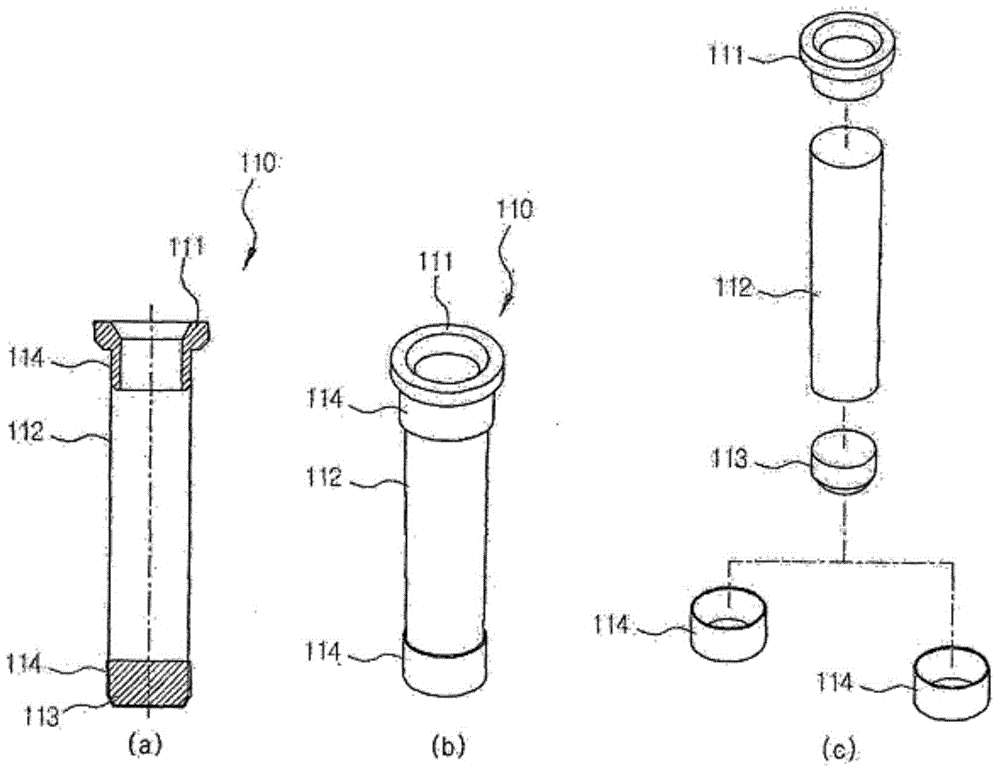
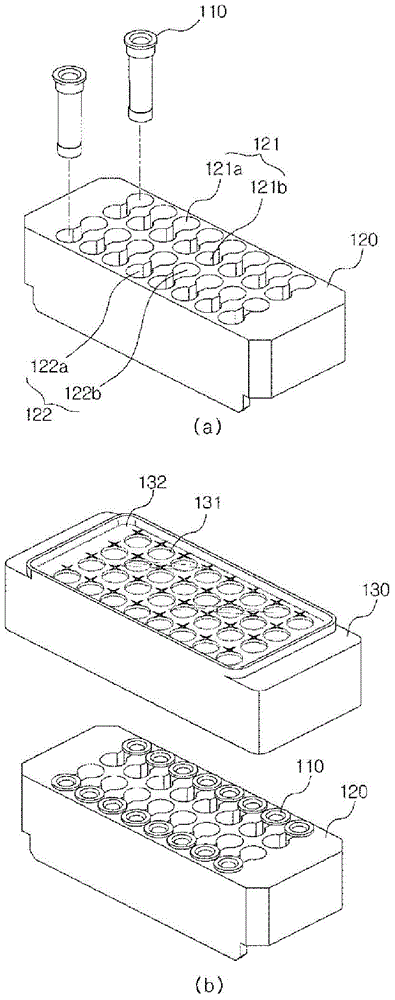
Apparatus for automatically preparing cell-free proteins and method for preparing proteins using same
A protein and cell-free technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, peptide preparation methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of low protein expression efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0159] Embodiment 1: the preparation of template DNA
[0160] 1-1: Preparation of plasmid DNA
[0161] In the present invention, AcGFP, CAT, RFP and TEV-AcGFP genes are used for cell-free protein production. These genes are used to confirm whether the protein is produced by the cell-free protein production system, and it is obvious to those skilled in the art that the present invention is applicable to any protein produced by the cell-free protein production method.
[0162] Each gene was synthesized by a gene synthesis method (NBiochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 248, 200-203). Each synthesized gene was treated with restriction enzymes and then cloned into the histidine-tagged cell-free expression vector pBIVT (Bioneer, Korea). Meanwhile, TEV-AcGFP was constructed to include a sequence (Glu-Asn-Leu-Tyr-Phe-Gln↓Gly) located between the histidine tag and the target protein, which is cleaved by TEV.
[0163] Examples of expression vectors that can be used in the present inve...
Embodiment 2
[0172] Embodiment 2: the preparation of cell lysate
[0173] First, E. coli cells (BL21(DE3), Novagen, USA) were cultured in a 350 l fermenter (2×YT medium) at 37°C. In absorbance (OD 600 ) is 0.6, add 1mM IPTG to express T7RNA polymerase, and in absorbance (OD 600 ) was 3.0-3.5, the culture was stopped, and the cells were harvested by centrifugation and stored at -50°C.
[0174] Wash 100 g of harvested E.coli cells with 500 ml of washing buffer (10 mM Tris (oAc) pH 8.2, 14 mM Mg (oAc) 2 , 60mM K(OAc), 1mM DTT (dithiothreitol), 0.05% (v / v) 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME)), and then centrifuged (3000RPM, 30min). Repeat this step 4 times.
[0175] After washing, the E.coli cells were weighed and added to a buffer (10mM Tris(oAc) pH 8.2, 14mM Mg(oAc)2, 60mM K(OAc), 1mM DTT (disulfide threitol)) and dispersed. Then, the cells were lysed using a cell homogenizer (Pressure Cell Homogeniser, Stansted Fluid Power) under constant pressure (280 psi).
[0176] The cell lysates were centr...
Embodiment 3
[0177] Example 3: Preparation of expression solution and small molecule expression solution
[0178] By adding 114mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.5), 2.4mM ATP, each of 1.7mM CTP, GTP and UTP, 2mM DTT, 90mM K(Glu), 80mM NH 4 (OAc), 12mM Mg(OAc), 68g / ml folinic acid (L-5-formyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate), 2.5mM amino acid mix, 2% PEG 8000 and 67mM creatine phosphate Mix with each other to prepare expression solution for cell-free protein expression. Alternatively, by mixing expression solution, DEPC DW, and 5% NaN at a ratio of 46.7:52.3:1 3 To prepare small molecule expression solution.
[0179] Store the expression solution and small molecule expression solution at -20°C until use.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com