A degradable zinc-based microporous drug-loaded stent and its preparation method
A microporous, zinc-based technology, applied in medical science, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of polymer membrane bubbling, fragments entering the blood stream, weak blocking effect, etc., to increase local inflammation, good biocompatibility, Inhibition of restenotic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
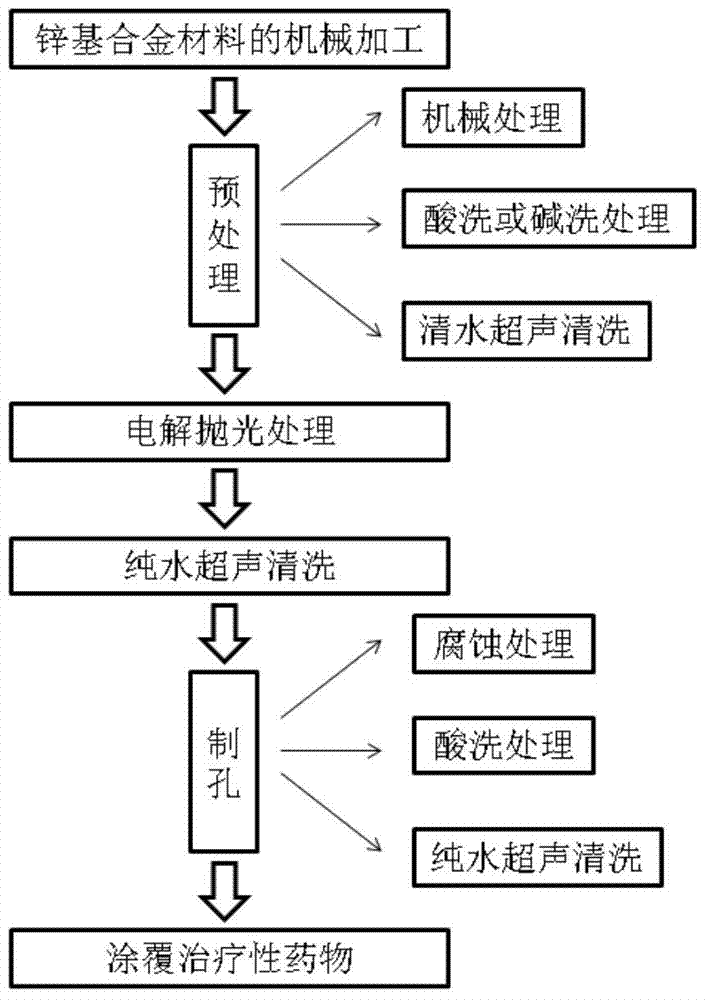
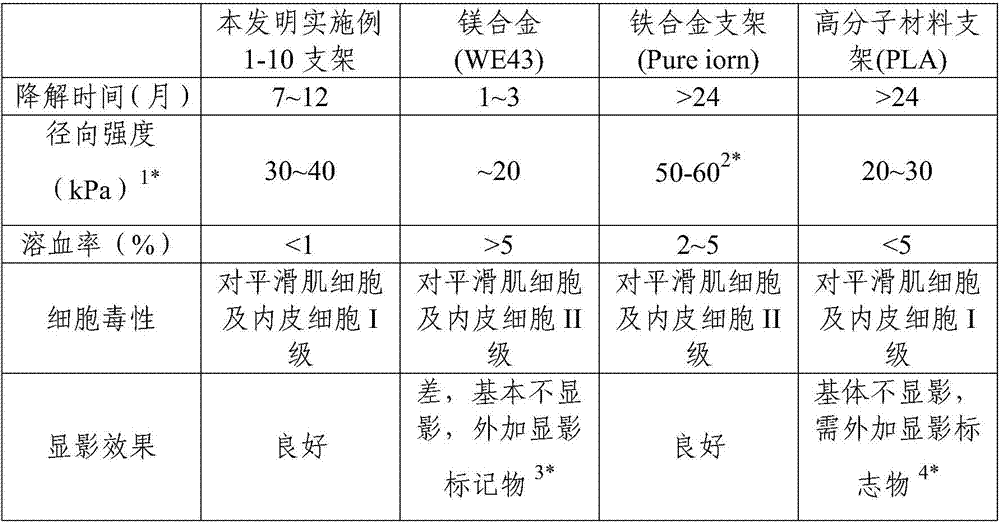
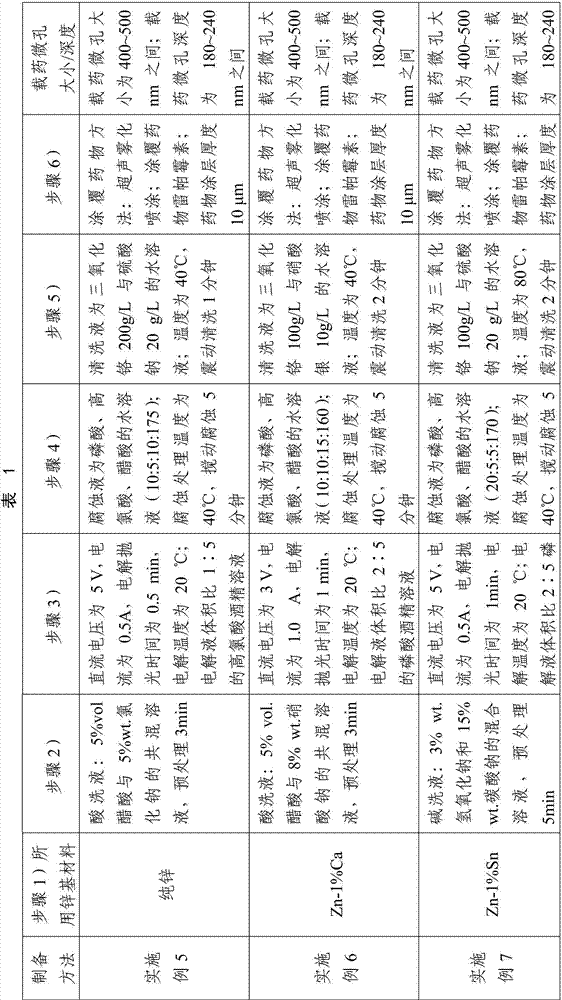
[0038]The present invention unexpectedly finds that when the degradable zinc-based material is selected as Zn-1%Mg alloy or Zn-1%Mg-0.5%Ca alloy, the drug-loaded micropore size is between 400-500nm, and the micropore depth is 180-500nm. 240nm, when the therapeutic drug is rapamycin and the thickness of the drug coating is 1-20 μm (especially 10-20 μm), the stent of the present invention is particularly excellent in terms of degradation speed, biocompatibility and drug sustained release. performance. The flow chart of the preparation method of a degradable zinc-based microporous drug-loaded stent according to the embodiment of the present invention is as follows: figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0039] 1) Process the degradable zinc-based material into a stent matrix; the degradable zinc-based material is composed of pure zinc or zinc alloy material; it can be processed into a vascular stent, a tracheal stent, an esophageal stent, an intestinal stent, a biliary...
Embodiment 1
[0054] A degradable zinc-based microporous drug-loaded stent, comprising a degradable zinc-based material stent matrix, the surface of the stent matrix is provided with uniform drug-loading micropores, and the surface of the stent with uniform drug-loaded micropores is covered with therapeutic drugs-Rapa Mycin coating, the stent matrix is a cylindrical network structure; the degradable zinc-based material is Zn-1%Mg alloy; the drug-loaded micropore size is 400-500nm, and the micropore depth is 180-240nm; coated with drug The thickness of the coating was 10 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0056] A degradable zinc-based microporous drug-loaded stent, comprising a degradable zinc-based material stent matrix, the surface of the stent matrix is provided with uniform drug-loading micropores, and the surface of the stent with uniform drug-loaded micropores is covered with therapeutic drugs-Rapa Mycin coating, the stent matrix is a cylindrical network structure; the degradable zinc-based material is Zn-1%Mg-0.5%Ca alloy; the drug-loaded micropore size is 400-500nm, and the micropore depth is 180-240nm ; The thickness of the drug coating is 10 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com