Method for removing lead and zinc in contaminated soil by leaching with biologic materials
A technology of biomass materials and polluted soil, which is applied in the field of removing lead and zinc in contaminated soil by leaching with biomass materials, which can solve the problems of soil matrix damage to nutrients, easy residue, and secondary pollution of soil, etc., and achieves obvious leaching effect , Easy to operate, wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Phytoleaching to remediate polluted soil in a lead-zinc mining area in Hanyuan
[0023] (1) Preparation of eluent
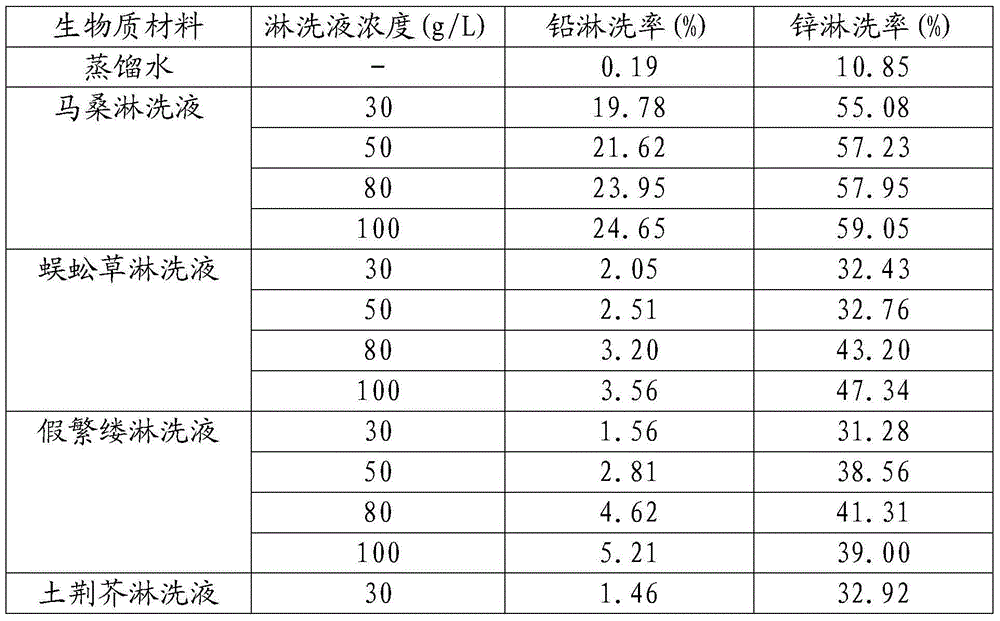
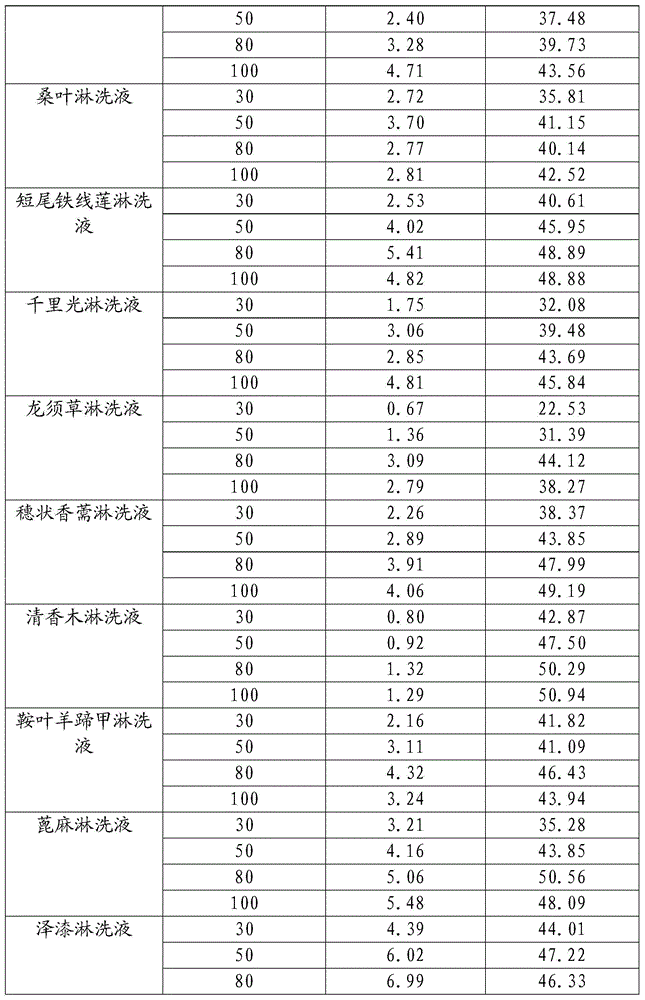
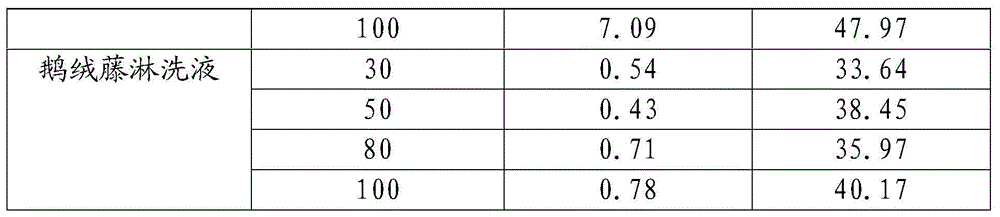
[0024] Sangria mulberry, centipede grass, false chickweed, nepeta, mulberry leaf, clematis, senecio, asparagus, fenugreek, fenugreek, saddle leaf beetle, castor plant, lacquer and goose down The vines were washed with distilled water and placed in a naturally ventilated place to air-dry, and were ground through a 2mm sieve using a pulverizer.
[0025] Add 6g, 10g, 16g and 20g of each plant powder into 200mL distilled water respectively, at 200r / min -1 Shake at constant temperature for 24 hours, and filter to obtain eluents with 4 concentrations of 30g / L, 50g / L, 80g / L and 100g / L.
[0026] (2) Oscillating leaching of contaminated soil
[0027] Take 4 different concentrations of the above 14 kinds of plant eluents and 20ml of distilled water for a total of 57 treatments, and add them to 1.00g of contaminated soil at a soil-to-liquid ratio of 1:20. The pH ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: Lead-zinc leaching efficiency under different leaching time
[0038] The preparation method of the leaching agent and the leaching steps of the polluted soil are consistent with the conditions in Example 1, only the leaching oscillation time is changed, and the change of the leaching rate is tested under different oscillation times. For specific data, refer to the table 2.
[0039] Table 2 Efficiency of 14 kinds of plant leaching agents to remove lead and zinc from contaminated soil in mining areas under different leaching time
[0040]
[0041]
[0042]
[0043] Note: The eluent concentration is the extraction concentration of 14 kinds of plant powders; each treatment was repeated 3 times, and the data in the table is the average value of 3 repetitions of one leaching.
[0044] It can be seen from Table 2 that under the same conditions, the use of biomass materials such as horse mulberry, centipede grass, false chickweed, nepeta, mulberry leaves...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3: Determination of the leaching efficiency of each biomass to lead and zinc in polluted soil under different pH conditions
[0046] The preparation method of leaching agent and the leaching step to polluted soil are consistent with the conditions in embodiment 1, only change the pH value of mixed solution wherein, test each biomass to the lead-zinc in polluted soil under different pH value conditions. For the variation of the leaching rate, refer to Table 3 for specific data.
[0047] Table 3 Efficiency of 14 plant leaching agents to remove lead and zinc from contaminated soil in mining areas under different pH values
[0048]
[0049]
[0050] Note: The eluent concentration is the extraction concentration of 14 kinds of plant powders; each treatment was repeated 3 times, and the data in the table is the average value of 3 repetitions of one leaching.
[0051] This study tested the leaching rates of lead and zinc under acidic, neutral and alkaline conditio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com