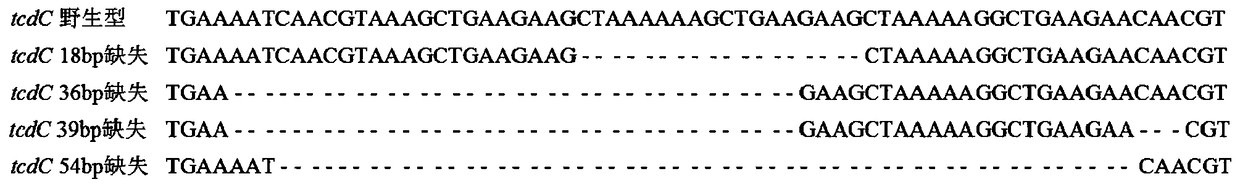Compositions and kits and methods for detecting hypervirulent strains and/or toxin types of Clostridium difficile
A technology for Clostridium difficile and highly virulent Clostridium difficile is applied in the field of compositions for detecting highly virulent strains and/or toxin types of Clostridium difficile, and can solve the problems of tcdC protein truncation and inability to produce functions and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0126] Example 1. Sensitivity detection
[0127] 1. Materials and instruments
[0128] pUC57 plasmid (purchased from GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), dNTPs (purchased from TaKaRa company), Taq enzyme (purchased from TaKaRa company), 10×PCR buffer (purchased from TaKaRa company), Bio-Rad PCR instrument, ABI 3500 PCR machine and so on.
[0129] 2. Design and synthesis of primers and probes
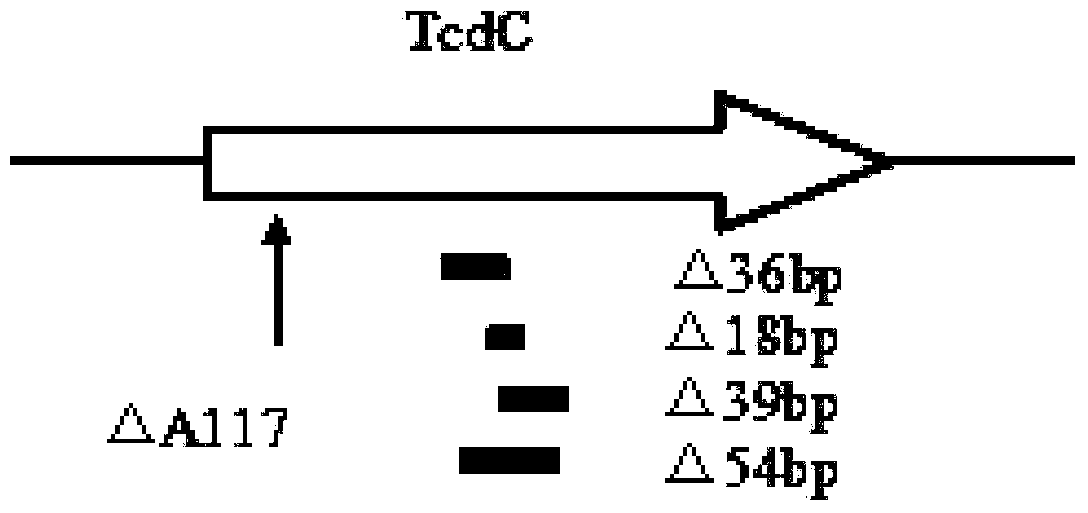
[0130] Targeting the TPI gene, GluD gene, tcdA gene, tcdB gene, cdtA gene, cdtB gene, and tcdC gene of C. difficile high toxic mutations (including 117 site deletion, 18bp deletion, 36bp deletion, 39bp deletion, and 54bp deletion) as targets, Design specific primers and Taqman (including MGBNFQ modified) probes.
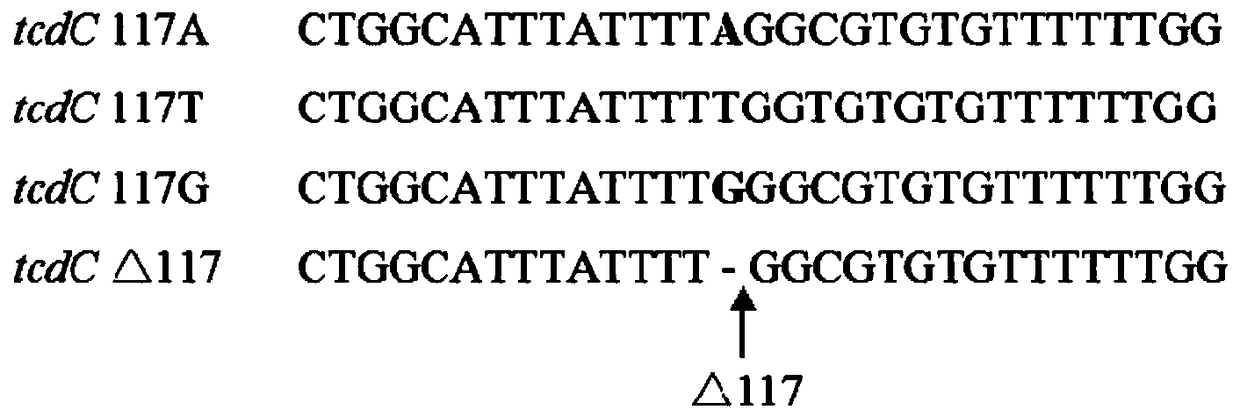
[0131] Among them, the detection primers and probes for the deletion of position 117 of the tcdC gene are:
[0132] Upstream primer of tcdC△117: 5'-TTGCTCTACTGGCATTTATTTGG-3', SEQ ID NO.1,
[0133] Downstream primer of tcdC△117: 5'-ACCATGGTTCAGCATCAGACAA-3', SEQ ID NO. 2,
[0134] tcdC△117...
Embodiment 2
[0185] Example 2: Specific detection
[0186] 1. Strains
[0187] See the table below for strains and numbers:
[0188] Strain
Strain
Clostridium difficile 1
ATCC BAA1804
Clostridium difficile 2
ATCC43598
Clostridium difficile 3
ATCC9689
Clostridium difficile 4
ATCC BAA1805
Escherichia coli
ATCC8739
ATCC6633
Shigella flexneri
CMCC44149
CMCC44149
Enterobacter aerogenes
ATCC13048
CMCC51105
Shigella dysenteriae
CMCC51105
Enterobacter cloacae
CMCC45301
Toxigenic Escherichia coli
CMCC44814
Salmonella typhimurium
CMCC50013
Bacteria vulnificus
CICC10383
Staphylococcus aureus
ATCC25923
Hemorrhagic Escherichia coli
ATCC12900
Enterobacter sakazakii
ATCC29544
[0189] Among them, Clostridium difficile 1-3 (ATCC BAA1804, ATCC43598, ATCC9689) are positive for tcdA and tcdB; Clostridium difficile 4 (ATCC BAA1805) is positive for tcdA, tcdB, cdtA, cdtB and contain...
Embodiment 3
[0220] Example 3: Detection of clinical stool samples by real-time fluorescent PCR
[0221] 1. Specimen source
[0222] Among 48 feces collected from Hubei Provincial Tumor Hospital, the fecal DNA of 8 specimens that confirmed the isolation of Clostridium difficile using the CCFA selective culture method was used in this example. The specific process of the CCFA selective culture method is as follows: the anal swab specimens are mixed with an equal volume of 98% ethanol for 30 minutes to 1 hour, and 0.1 mL of the mixed solution is inoculated on the cycloserine cefoxitin mannitol agar medium, and the medium is placed at 35℃ After anaerobic incubation for 24 hours, the frozen stool is thawed and suspended in a 9-fold capacity anaerobic transport medium. For the colonies detected on the culture medium, C. difficile was determined from the traits and Gram stain.
[0223] 2. Use Tiangen Fecal Genomic DNA Extraction Kit to extract bacterial genomic DNA
[0224] Weigh 200 mg of the stool s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com