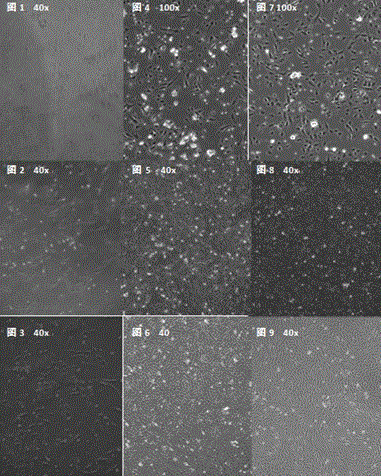
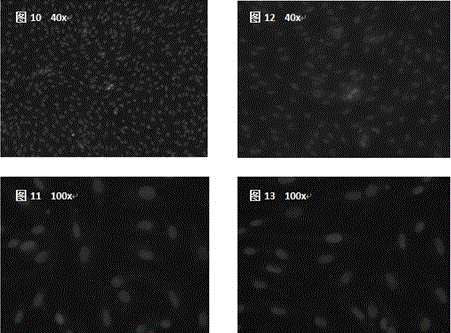
Isolated culture method of piglet myocardial fibroblasts
A fibroblast, isolation and culture technology, applied in the field of porcine myocardial fibroblast isolation and culture, can solve the problem of no piglet myocardial fibroblast isolation and culture, and achieve the effects of improving cell acquisition rate, saving time, and reducing growth impact.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A method for separating and culturing Tibetan pig myocardial fibroblasts, comprising the steps of:
[0036] (1) After 2-day-old piglets were sterilized with 0.1% bromogeramine, the anterior vena cava was exsanguinated quickly, and the piglets were fixed, and the skin of the chest and abdomen were disinfected with 75% alcohol.
[0037] (2) Use a sterile scalpel to incise the skin of the piglet's chest.
[0038] (3) Sterile scissors cut the piglet’s chest cavity forward along the last rib, remove the heart, and immediately put it into a 50mL pre-cooled PBS beaker to wash away blood cells and blood clots.
[0039] (4) Transfer the heart to a sterile plate with sterile tweezers, intercept the ventricular tissue and peel off the pericardium, add an appropriate amount of pre-cooled PBS to rinse, remove blood vessels, fat and connective tissue, and rinse 3 times.
[0040] (5) Ophthalmic scissors cut the tissue into 1mm 3 The left and right fragments were transferred to a 50m...
Embodiment 2
[0048] A method for separating and culturing landrace pig cardiac fibroblasts, comprising the steps of:
[0049] (1) After 3-day-old piglets were sterilized with 0.1% bromogeramine, they were killed by bloodletting from the anterior vena cava, and the piglets were fixed, and the skin of the chest and abdomen were disinfected with 75% alcohol.
[0050] (2) Use a sterile scalpel to incise the skin of the piglet's chest.
[0051] (3) Sterile scissors cut forward along the last rib to open the chest cavity to expose the heart, cut the pericardium with sterile scissors, remove the heart, and immediately put it into a 50mL pre-cooled PBS beaker to wash away blood cells and blood clots .
[0052] (4) Transfer the heart to a plate with sterile tweezers, intercept the ventricular tissue and peel off the myocardium, rinse with an appropriate amount of pre-cooled PBS, remove blood vessels, fat and connective tissue, and rinse 3 times.
[0053] (5) Sterile ophthalmic scissors to cut the...
Embodiment 3
[0062] A method for culturing large white pig cardiac fibroblasts, comprising the steps of:
[0063] (1) The 2-day-old piglets were sterilized with 0.1% bromogeramine, and the anterior vena cava was quickly bled to death. The piglets were fixed, and the skin of the chest and abdomen were disinfected with 75% alcohol.
[0064] (2) Cut the piglet's chest skin with a sterile scalpel.
[0065] (3) Sterile scissors cut the chest cavity forward along the last rib, remove the heart, and immediately put it into a 50mL pre-cooled PBS beaker to wash away blood cells and blood clots.
[0066] (4) Transfer the heart to a sterile plate with sterile tweezers, intercept the ventricular tissue and peel off the myocardium, rinse with an appropriate amount of pre-cooled PBS, remove blood vessels, fat and connective tissue, and rinse 3 times.
[0067] (5) Sterile ophthalmic scissors to cut the tissue into 1mm 3 Left and right fragments were transferred to a 50mL Erlenmeyer flask, rinsed with P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com