Method for preparing non-woven fabric with moisture absorption and transferability by using short fiber spinning method
A transfer and spinning technology, which is applied in the direction of non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, can solve the problems affecting the water absorption or air permeability of non-woven fabrics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
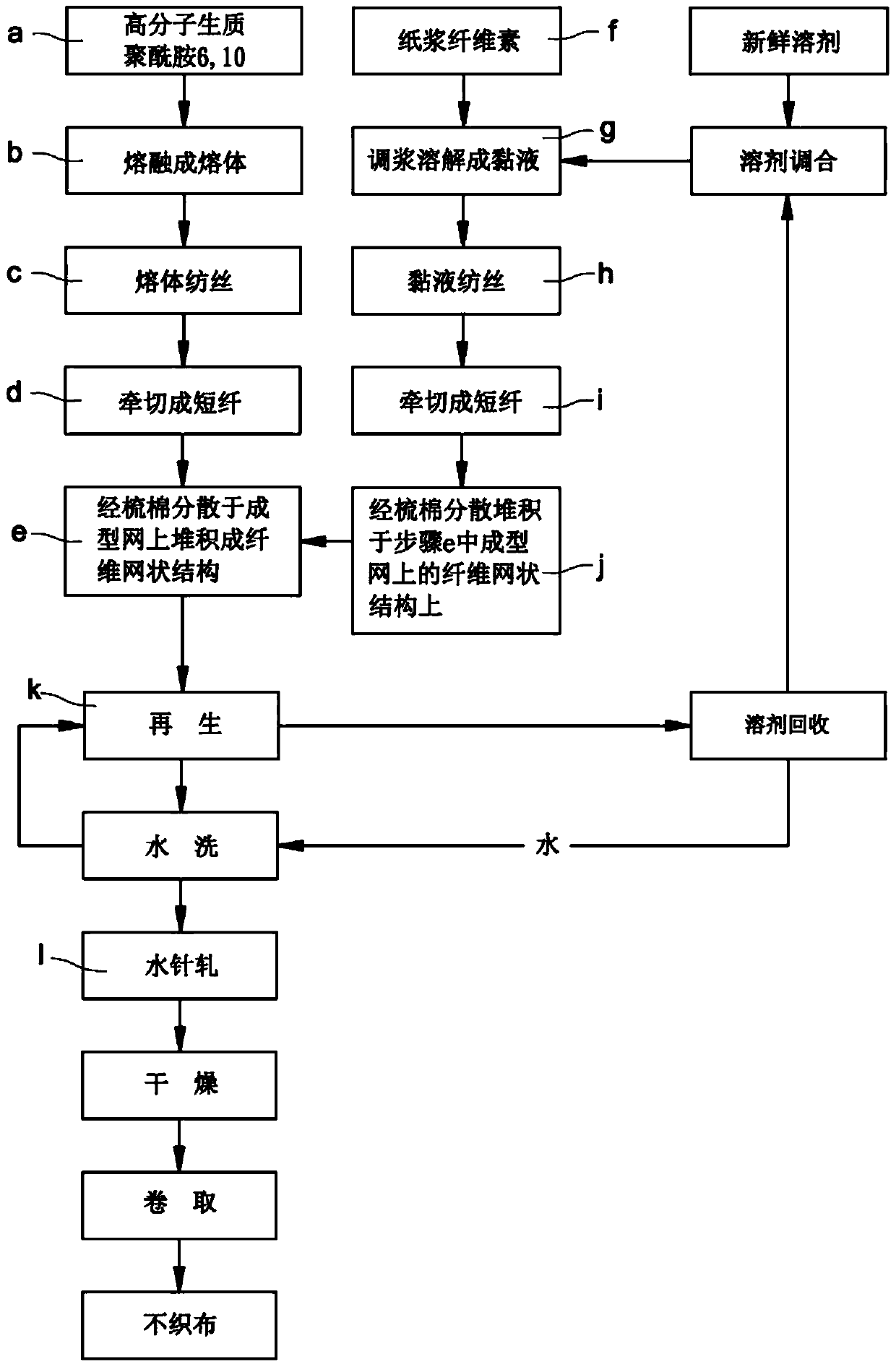
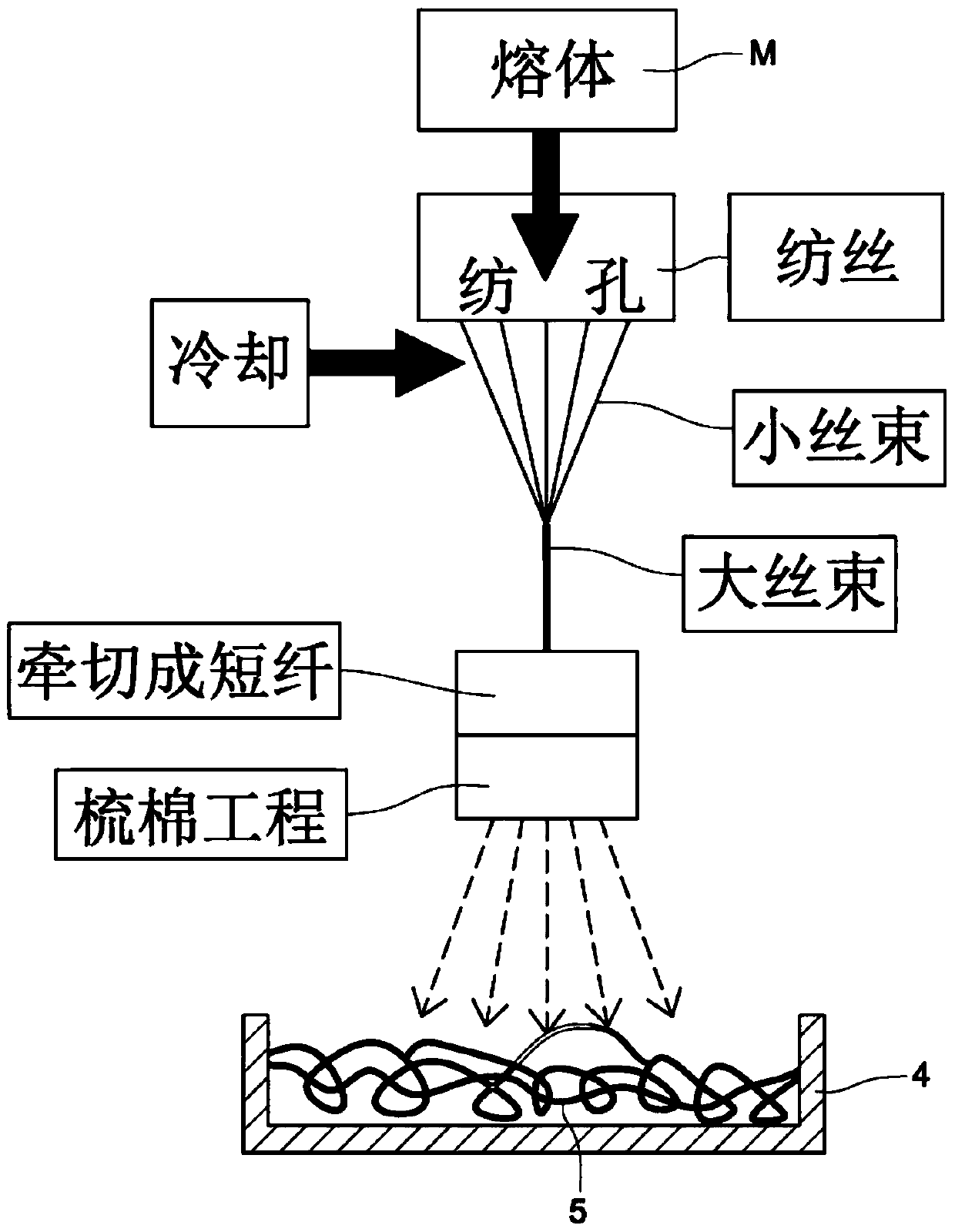
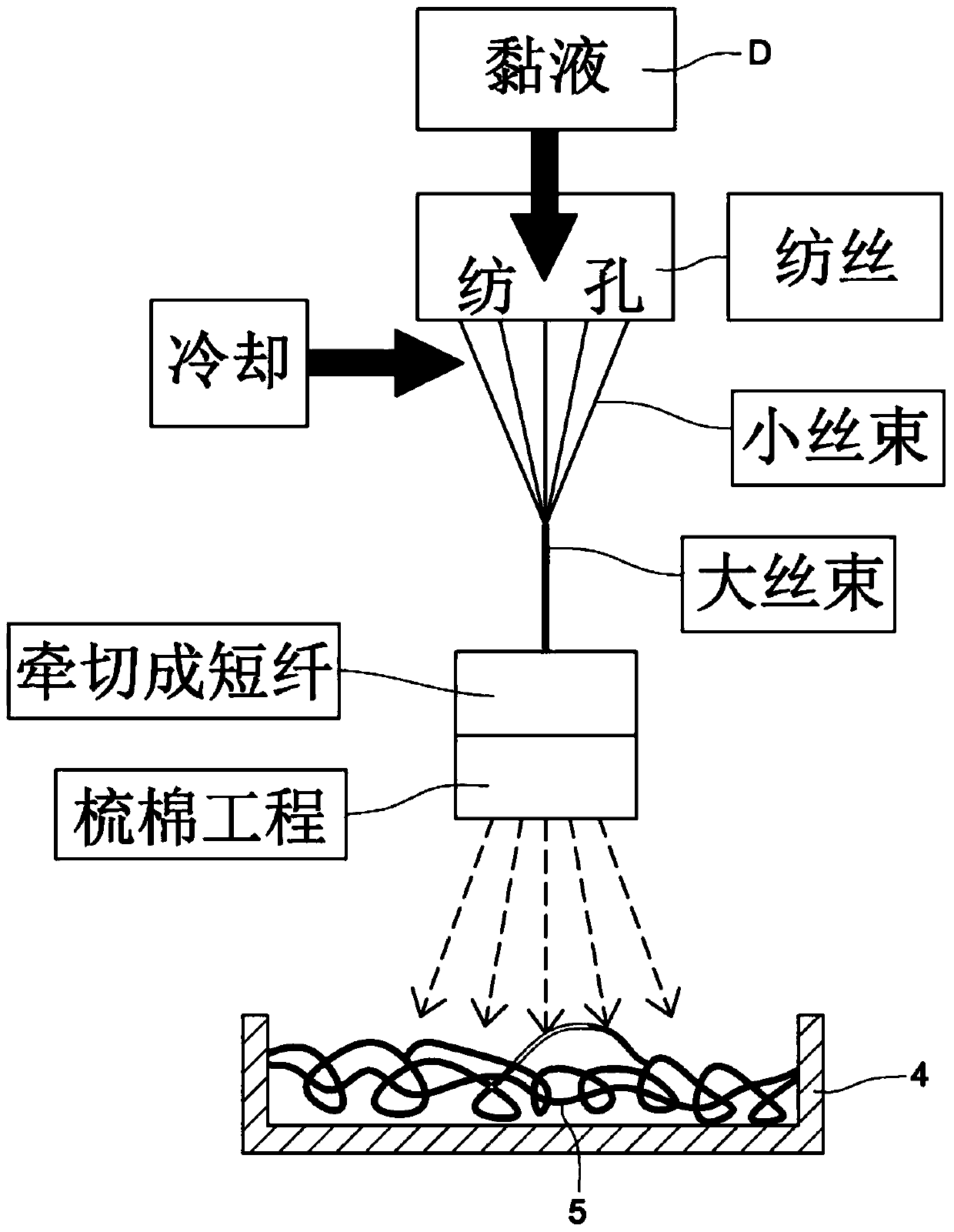
[0054] First, the raw material of raw material polyamide 6 and 10 is melted into a melt at a high temperature of 280°C, and the extrusion rate of the extruder is 300c.c. / min, and the melt is extruded from the spinning hole by spinning to form a raw material. High-quality polyamide 6, 10 fiber small tow, and after cooling with 20 ℃ cold wind outside the spinning hole, collect it into a large tow, after stretching process to make the fiber fineness reach 10um, cut it into staple fiber (Staple), Then, through the carding process, the short-fiber biopolyamide 6,10 fibers are dispersed on the conveyor belt, and accumulated on the conveyor belt to form a biomass polyamide 6,10 fiber network structure; The cellulose pulp (plup) was added with N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO for short), and mixed at 60°C, and then heated at 120°C using a vacuum thin film evaporator, within 5 minutes Evaporated, dissolved, and mixed water is removed to 5-13% to form mucus, and the extruder is extruded...
Embodiment 2
[0056] First, the raw material of raw material polyamide 6,10 is melted into a melt at a high temperature of 280°C, and the extrusion rate of the extruder is 250c.c. / min, and the melt is extruded from the spinning hole by spinning to form a raw material. High-quality polyamide 6, 10 fiber small tow, and after cooling with 20 ℃ cold wind outside the spinning hole, collect it into a large tow, after stretching process to make the fiber fineness reach 10um, cut it into staple fiber (Staple), Then, through the carding process, the short-fiber biopolyamide 6,10 fibers are dispersed on the conveyor belt, and accumulated on the conveyor belt to form a biomass polyamide 6,10 fiber network structure; The cellulose pulp (plup) was added with N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO for short), and mixed at 60°C, and then heated at 120°C using a vacuum thin film evaporator, within 5 minutes Evaporated, dissolved, and mixed water is removed to 5-13% to form mucus, and the extruder is extruded at ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] First, the raw material of raw material polyamide 6 and 10 is melted into a melt at 280°C, and the extruder is extruded at a rate of 225 c.c. / min to extrude the melt from the spinning hole to form a raw material. High-quality polyamide 6, 10 fiber small tow, and after cooling with 20 ℃ cold wind outside the spinning hole, collect it into a large tow, after stretching process to make the fiber fineness reach 10um, cut it into staple fiber (Staple), Then, through the carding process, the short-fiber biopolyamide 6,10 fibers are dispersed on the conveyor belt, and accumulated on the conveyor belt to form a biomass polyamide 6,10 fiber network structure; The cellulose pulp (plup) was added with N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMMO for short), and mixed at 60°C, and then heated at 120°C using a vacuum thin film evaporator, within 5 minutes Evaporated, dissolved, and mixed water is removed to 5-13% to form mucus, and the extruder is extruded at a rate of 375 c.c. / min to extrude t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com