Slow-release pharmaceutical preparation of long-acting follicle-stimulating hormone
A technology of follicle-stimulating hormone and slow-release drugs, which is applied to medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, drug combinations, etc., and can solve problems such as high labor costs, affecting effects, and disturbing animals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Preparation of gene recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone:
[0028] The CHO cells with stable and high expression of FSH were inserted into shake flasks and gradually expanded to a density of 1×10 6 / ml, recorded as the first day of culture. After 14 consecutive days, the cell culture fluid was taken to purify the expression product.
[0029] The CHO cell culture medium was centrifuged at 9000 g at a low temperature of 4° C. for 20 min, and the culture supernatant was collected. The membrane ultrafiltration with a molecular weight cut-off of 10 kDa was used to collect the ultrafiltration concentrate. Purify the concentrated solution with ProteinA affinity chromatography column to obtain high-purity FSH protein with a purity of about 98% and a specific activity of 12000 IU / mg. Store at 2-8°C for later use.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Preparation of pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone long-acting injection:
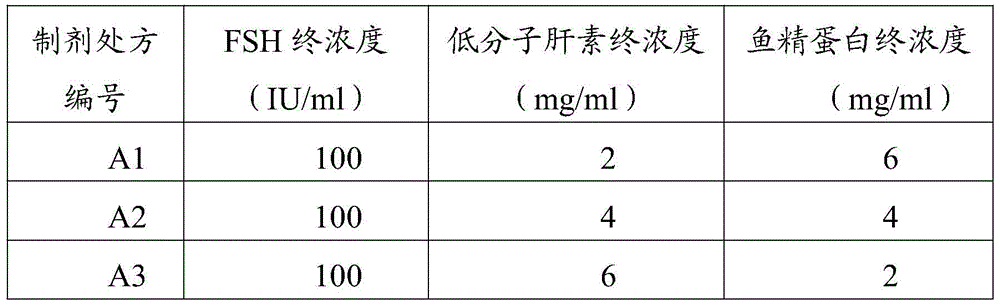
[0032] Take 100,000 IU of pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone (purchased from Ningbo No. 2 Hormone Factory), and dissolve it in 200 ml of sodium citrate-citrate buffer solution (pH 6.8-7.2). Every 1 ml of sodium citrate-citric acid buffer (pH6.8-7.2) contains 30 mg of sodium citrate and 0.6 mg of citric acid. Take a low molecular weight heparin (molecular weight 5000) solution (200, or 400, or 600 ml) with a concentration of 10 mg / ml, and mix it with the pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone solution. Then take a protamine solution (600, or 400, or 200 ml) with a concentration of 10 mg / ml, and mix it with the above-mentioned solution of pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and low molecular weight heparin. Add sodium citrate-citrate buffer to 1000ml. All preparation processes must be carried out in a class 100 sterile area. All solutions were sterile filtered before use. Under stirr...
Embodiment 3
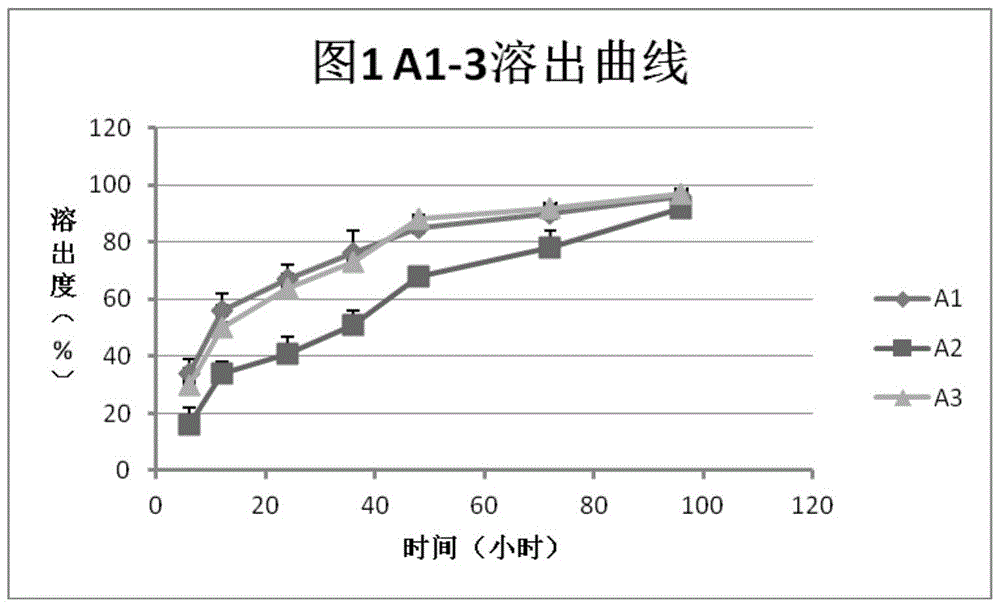
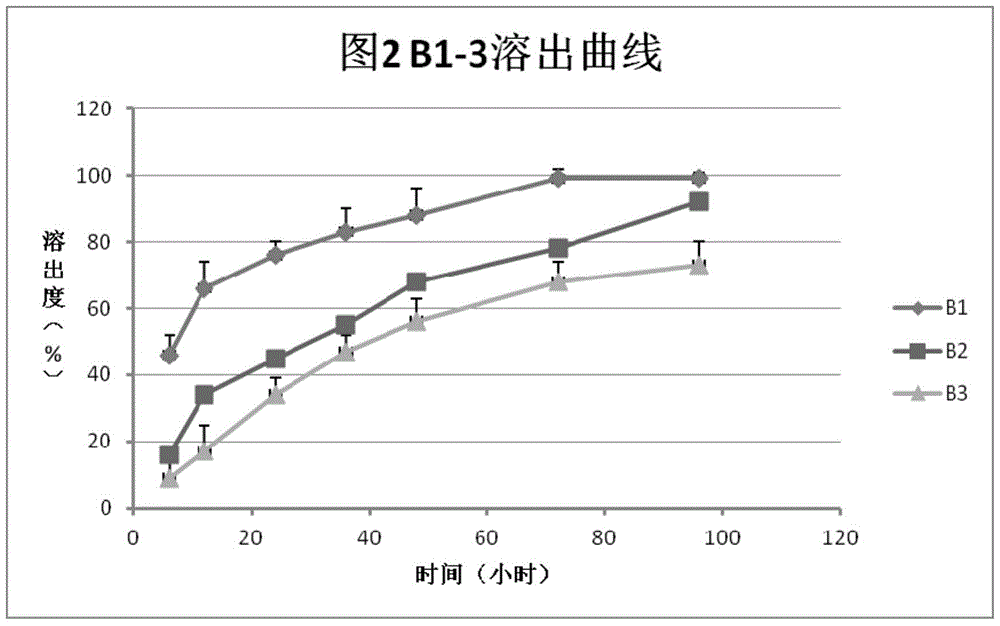
[0037] In vitro dissolution test:
[0038] Take the preparations A1-3 obtained in Example 2, put them in 10ml centrifuge tubes, place them in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C, and centrifuge (3000rpm) at the 6th, 12th, 24th, 36th, 48th, 72nd, and 96th hours, and take the Clear 200 microliters, and measure FSH concentration by ELISA method. After each sampling, 200 μl of sodium citrate-citrate buffer (pH 6.8-7.2) was added to the centrifuge tube. According to the measurement results, the dissolution curve is obtained, such as figure 1 shown. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the dissolution rate of formulation A2 (the ratio of heparin to protamine is 1:1) is significantly slower than that of the other two, and is closer to the zero-order release rate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com