Preparation method of large-layer-spacing graphite anode material of sodium-ion battery
A sodium-ion battery, graphite negative electrode technology, applied in battery electrodes, batteries, negative electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of less than 250mAh/g specific capacity, fast capacity decay, easy irreversibility, etc., to achieve increased sodium storage capacity and tap density. The effect of enlargement and simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
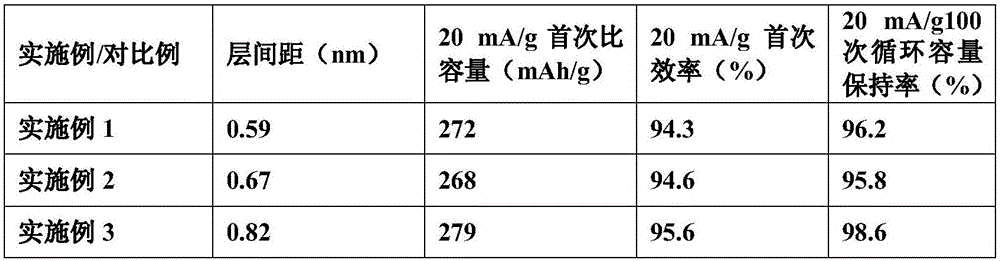
Embodiment 1
[0020] A method for preparing a large interlayer spacing graphite negative electrode material for a sodium ion battery, comprising the steps of:
[0021] (1) Dissolving an appropriate amount of carbon source in a solvent, then adding graphite oxide, stirring at a speed of 50 rpm until evenly mixed, then drying to obtain carbon source-coated graphite oxide;
[0022] The carbon source is coal tar pitch, the solvent is toluene, and the corresponding drying temperature is 200°C.
[0023] The feed ratio of described solvent and carbon source is 25mL:1g; The mass ratio of described carbon source and graphite oxide is 0.2:1;
[0024] (2) Put the carbon source-coated graphite oxide obtained in step 1 into a quartz glass beaker, add liquid nitrogen, the amount of liquid nitrogen is to submerge the carbon source-coated graphite oxide, and then quickly place the quartz glass beaker into the microwave reaction In the device, react under the microwave power of 1000W for 5 minutes, after t...
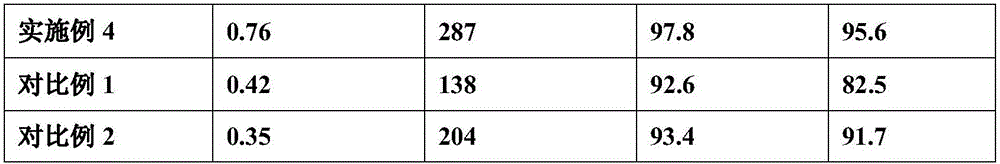
Embodiment 2
[0028] A method for preparing a large interlayer spacing graphite negative electrode material for a sodium ion battery, comprising the steps of:
[0029] (1) Dissolving an appropriate amount of carbon source in a solvent, then adding graphite oxide, stirring at a speed of 20 rpm until evenly mixed, and then drying to obtain carbon source-coated graphite oxide;
[0030] The carbon source is sucrose and glucose, the solvent is deionized water, and the corresponding drying temperature is 100°C.
[0031] The feed ratio of described solvent and carbon source is 5mL:1g; The mass ratio of described carbon source and graphite oxide is 0.01:1;
[0032] (2) Put the carbon source-coated graphite oxide obtained in step 1 into a quartz glass beaker, add liquid nitrogen, the amount of liquid nitrogen is to submerge the carbon source-coated graphite oxide, and then quickly place the quartz glass beaker into the microwave reaction In the device, react under the microwave power of 250W for 20...
Embodiment 3
[0036] A method for preparing a large interlayer spacing graphite negative electrode material for a sodium ion battery, comprising the steps of:
[0037] (1) Dissolving an appropriate amount of carbon source in a solvent, then adding graphite oxide, stirring at a speed of 30 rpm until evenly mixed, and then drying to obtain carbon source-coated graphite oxide;
[0038] The carbon source is coal tar pitch, the solvent is toluene, and the corresponding drying temperature is 100°C.
[0039] The feed ratio of described solvent and carbon source is 15mL:1g; The mass ratio of described carbon source and graphite oxide is 0.1:1;
[0040] (2) Put the carbon source-coated graphite oxide obtained in step 1 into a quartz glass beaker, add liquid nitrogen, the amount of liquid nitrogen is to submerge the carbon source-coated graphite oxide, and then quickly place the quartz glass beaker into the microwave reaction In the device, the reaction was carried out under the microwave power of 8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com