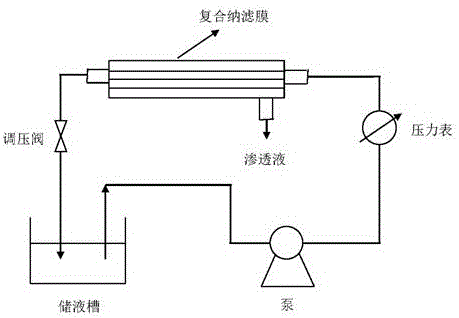
Preparation method of positively-charged hollow polytetrafluoroethylene composite nanofiltration membrane
A technology of polytetrafluoroethylene and composite nanofiltration membrane, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, membranes, membrane technology, etc., can solve the problems of complex nanofiltration membrane structure and complex preparation process, and achieve small footprint and structural details Combined effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] (1) Activation: inject 0.1% mass concentration carboxylated chitosan aqueous solution into the interior of the hydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene hollow fiber membrane with a syringe, fill it up, and stay for 10 min; Obtain active basement membrane;
[0023] (2) Aqueous phase impregnation: inject a 0.2% aqueous solution of hyperbranched polyethyleneimine into the active base membrane with a syringe, fill it up, and stay for 1 min, then suck out the excess solution with a syringe, and dry it in the air to obtain Interlayer 1;
[0024] (3) Oil phase impregnation: use a syringe to inject 0.1% trimesoyl chloride n-hexane solution into the interior of the intermediate film 1, fill it up, stay for 5 s, and then place it in the air to dry to obtain the intermediate film 2;
[0025] (4) Heat treatment: inject deionized water into the interior of the interlayer membrane 2 with a syringe, fill it up, suck it out, and repeat once; then put it in a drying oven at 30°C, stay for 2...
Embodiment 2
[0028] (1) Activation: inject 4.0% mass concentration of carboxylated chitosan aqueous solution into the interior of the hydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene hollow fiber membrane with a syringe, fill it up, and stay for 60 minutes; active basement membrane;
[0029] (2) Aqueous phase impregnation: inject a 2.0% aqueous solution of hyperbranched polyethyleneimine into the active base membrane with a syringe, fill it up, and stay for 30 min, then suck out the excess solution with a syringe, and dry it in the air to obtain Interlayer 1;
[0030] (3) Oil phase impregnation: use a syringe to inject a toluene solution of 5.0% isophthaloyl chloride into the interior of the intermediate film 1, fill it up, stay for 30 minutes, and then dry it in the air to obtain the intermediate film 2;
[0031] (4) Heat treatment: inject deionized water into the interior of the interlayer 2 with a syringe, suck it out, and repeat 5 times; then put it in a drying oven at 100°C, fill it up, stay for ...
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Activation: inject 1.0% mass concentration of carboxylated chitosan aqueous solution into the interior of the hydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene hollow fiber membrane with a syringe, fill it up, and stay for 30 minutes; active basement membrane;
[0035] (2) Aqueous phase impregnation: inject a 0.8% mass concentration hyperbranched polyethyleneimine aqueous solution into the active base membrane with a syringe, fill it up, and stay for 10 min, then suck out the excess solution with a syringe, and dry it in the air to obtain Interlayer 1;
[0036] (3) Oil phase impregnation: use a syringe to inject 4.0% n-octane solution of terephthaloyl chloride into the interior of the intermediate film 1, fill it up, stay for 20 minutes, and then dry it in the air to obtain the intermediate film 2 ;
[0037](4) Heat treatment: use a syringe to inject deionized water into the interior of the interlayer 2, suck it out, and repeat 4 times; then put it in a drying oven at 50°C, fil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com