Preparation method of negative electrode active material for lithium-ion battery
A negative electrode active material and lithium-ion battery technology, applied in the field of materials science, can solve problems such as graphene-like transition metal dichalcogenide layers control crystal integrity, etc., achieve high economic value and application prospects, excellent performance, method green effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
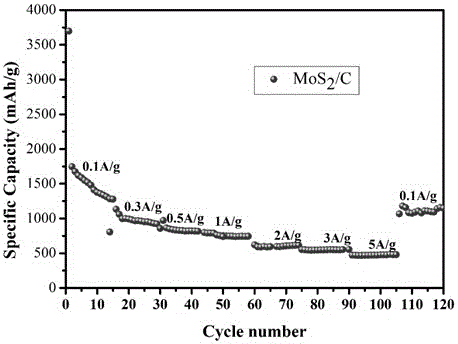
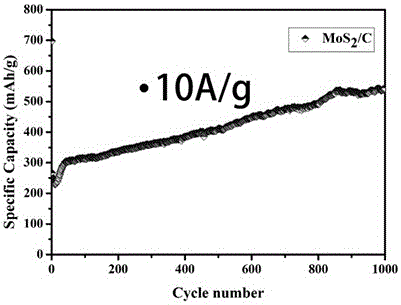
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Preparation of graphene-like transition metal molybdenum disulfide / porous carbon materials
[0023] (1) Chitosan-assisted liquid phase exfoliation of graphene-like transition metal molybdenum disulfide
[0024] Chitosan is added to an aqueous solution of acetic acid with a volume fraction of 0-10%, stirred and dissolved at a temperature of 5-90°C, and configured into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.1-100 mg / mL, and the graphene-like transition metal disulfide Molybdenum is added to the chitosan aqueous solution in a certain proportion, and ultrasonically dispersed for 0.5-200 hours to form a dispersion;
[0025] (2) Preparation of graphene-like transition metal molybdenum disulfide / nonionic polysaccharide porous foam
[0026] Centrifuge the dispersion obtained in step 1 at 1000~20000rpm per minute for 5-60 minutes to remove the bottom precipitate, and freeze the obtained layered metal molybdenum disulfide / nonionic polysaccharide aqueous dispersion at -5~-...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Preparation of graphene-like transition metal tungsten disulfide / porous carbon materials
[0033] (1) Chitosan-assisted liquid phase exfoliation of graphene-like transition metal tungsten disulfide
[0034] Chitosan is added to an aqueous solution of acetic acid with a volume fraction of 0-10%, stirred and dissolved at a temperature of 5-90°C, and configured into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.1-100 mg / mL, and the graphene-like transition metal disulfide Add tungsten into the chitosan aqueous solution in a certain proportion, and ultrasonically disperse for 0.5-200 hours to form a dispersion;
[0035] (2) Preparation of graphene-like transition metal tungsten disulfide / nonionic polysaccharide porous foam
[0036] Centrifuge the dispersion obtained in step 1 at 1000~20000rpm per minute for 5-60 minutes to remove the bottom precipitate, and freeze the obtained layered metal tungsten disulfide / nonionic polysaccharide aqueous dispersion at -5~-196°C After 5...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Graphene-like transition metal MoSe 2 / Preparation of porous carbon materials
[0041] (1) Chitosan-assisted liquid phase exfoliation of graphene-like transition metal MoSe 2
[0042] Chitosan was added to an aqueous solution of acetic acid with a volume fraction of 0-10%, stirred and dissolved at a temperature of 5-90°C, and prepared into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.1-100 mg / mL, and the graphene-like transition metal MoSe 2 Add it into the aqueous solution of chitosan according to a certain proportion, and disperse it ultrasonically for 0.5-200 hours to form a dispersion liquid;
[0043] (2) Graphene-like transition metal MoSe 2 / Preparation of nonionic polysaccharide porous foam
[0044] The dispersion liquid obtained in step 1 is centrifuged at 1000-20000rpm per minute for 5-60 minutes to remove the bottom precipitate, and the obtained layered metal MoSe 2 / The non-ionic polysaccharide aqueous dispersion is frozen at -5 ~ -196 ° C for 5 ~ 150...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com