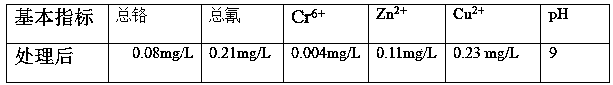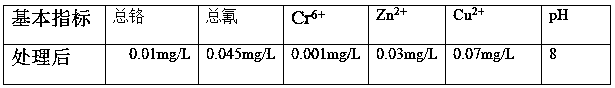A treatment process for electroplating wastewater containing cyanide and chromium
A treatment process and chromium electroplating technology, which is applied in metallurgical wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of difficult treatment of wastewater and increase the difficulty of treatment, so as to strengthen the purification effect and reduce the secondary Pollution, the effect of improving purification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The daily discharge of electroplating wastewater in an electroplating factory is 2,000 tons. Among them, the water quality of the electroplating wastewater containing cyanide and chromium in this electroplating factory is shown in Table 1
[0029] Table 1
[0030]
[0031] This embodiment includes the following steps:
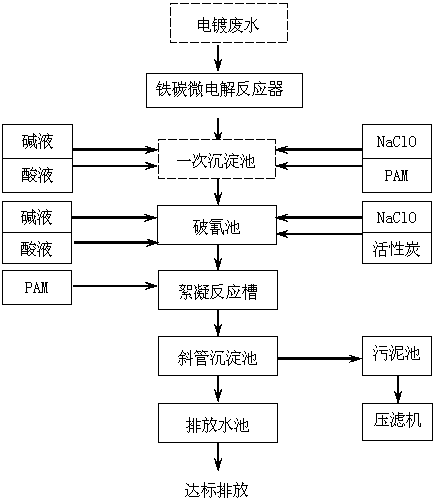
[0032] (1) The above-mentioned cyanide-containing and chromium-containing electroplating wastewater is pretreated through an iron-carbon micro-electrolysis reactor, and the refractory macromolecules and biochemical organic substances are degraded into small molecules by iron-carbon micro-electrolysis method, so as to improve the biodegradability of organic wastewater .
[0033] (2) Discharge the waste water after step (1) into the primary sedimentation tank, and use alkali, such as sodium hydroxide or calcium hydroxide, to adjust the pH to 9~11. Since the wastewater contains a large amount of ferrous ions and some ferrocyanide, ferric ions are need...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The indicators of electroplating wastewater treated in this example are shown in Table 1.
[0041] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0042] (1) Pass the above cyanide-containing and chromium-containing electroplating wastewater through the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis reactor for pretreatment, and use the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis method to degrade the refractory macromolecules and biochemical organics into small molecules, so as to improve the biochemical properties of organic wastewater sex.
[0043] (2) Discharge the waste water after step (1) into the primary sedimentation tank, and use alkali, such as sodium hydroxide or calcium hydroxide, to adjust the pH to 9~11. Since the wastewater contains a large amount of ferrous ions and some ferrocyanide, ferric ions are needed to remove ferrocyanide, so sodium hypochlorite is added to oxidize part of the ferrous iron into ferric iron, so that the wastewater contains ferrous iron at the same time , f...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The indicators of electroplating wastewater treated in this example are shown in Table 1.
[0051] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0052] (1) This step is a pretreatment stage. The above-mentioned cyanide-containing and chromium-containing electroplating wastewater has strong acidity, generally at a pH of about 3. The above-mentioned cyanide-containing and chromium-containing electroplating wastewater is passed through an iron-carbon micro-electrolysis reactor, The electrolysis method degrades the refractory macromolecules and biochemical organics into small molecules, and improves the biodegradability of organic wastewater. This embodiment uses a swirl micro-electrolysis reactor, preferably, a swirl with the patent number ZL201420467908.9 The micro-electrolysis reactor is filled with micro-electrolysis packing, and the waste water is passed through the equipment through the pump, and the residence time is 10~20min. Through the m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com