Surface enhanced Raman scattering substrate and manufacturing method thereof
A surface-enhanced Raman and substrate technology, applied in Raman scattering, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in forming abundant nano-scale particle gaps, limited SERS enhancement performance, and difficulty in ensuring repeatability, and achieve equipment The effect of low requirements, reduced requirements, and simple and easy process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate, using physical deposition and electrostatic interaction to assemble a nanoparticle film on a substrate that has been cleaned and surface charge modified, the substrate is a silicon chip, and the material of the film layer is gold nanoparticles .
[0034] The physical deposition method of the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate includes the following steps:
[0035] In step 1, ethanol with a volume fraction of 99.7% was used as the first cleaning solution, acetone with a volume fraction of 99.5% was used as the second cleaning solution, and ultrapure water with a resistivity of 18.2 MΩ·cm was used as the third cleaning solution.
[0036] Step 2, the preparation mass fraction is 9.8% aminosilylating reagent ethanol solution, mass fraction is 3% 4-styrene sulfonate sodium aqueous solution, mass fraction is 2% polydiallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride For the aqueous solution, the original solution can be diluted t...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Steps 1-5 of this embodiment are the same as in Embodiment 1, and step 7 repeats the operation of step 6, specifically:
[0043] Step 6: Co-cultivate 20 μL of gold nanoparticle colloid with the substrate in a wet box, then put the wet box at 4°C and let it grow for 15 h, remove the gold nanoparticle sol with a liquid gun, and dry it in an oven.
[0044] Step 7, co-cultivate 20 μL of gold nanoparticle colloid with the substrate dried in step 6 in a wet box, then put the wet box at 4°C and let it grow for 15 h, then remove the gold nanoparticle sol with a liquid gun, and place in an oven. Medium-dried surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Steps 1-6 of this embodiment are the same as in Embodiment 2, and step 7 repeats the operation of step 6 twice.
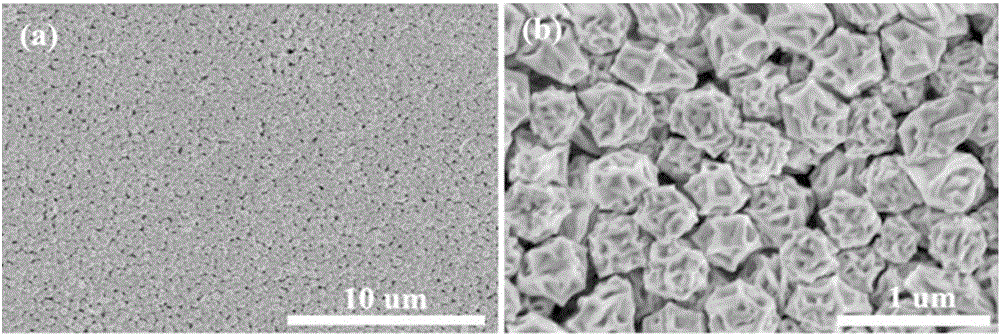
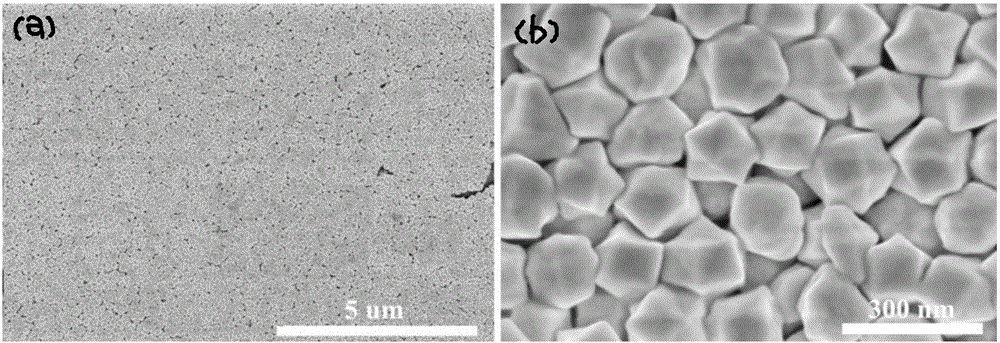
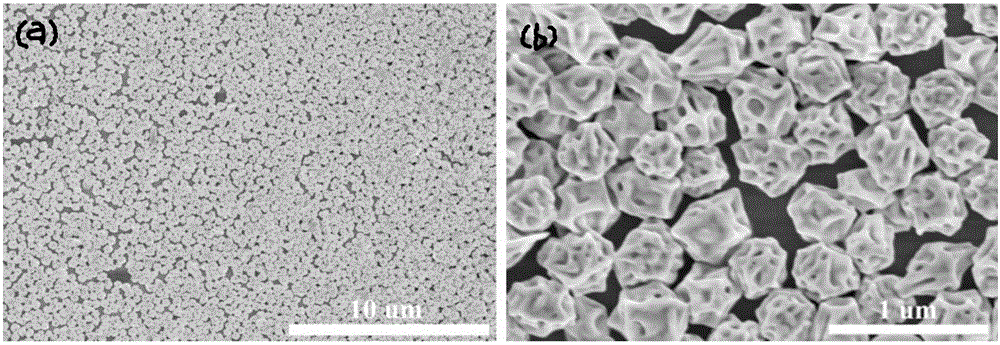
[0047] Examples 1 to 3 are surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates prepared by forming a film once, forming a film twice and forming a film three times respectively. The scanning electron microscope photos are as follows: figure 2 shown, from figure 2 It can be seen that the SERS enhancement and gold nanoparticle density can be regulated by different film-forming times. By changing the film-forming times, the density of gold nanoparticles on the substrate surface and the SERS enhancement can be adjusted. In the limited contact area and gold nanoparticle sol Under the premise of this, a single film formation cannot guarantee uniform nanoparticle film formation in all areas, and repeated deposition operations can solve this problem well.
[0048] The SERS spectrum obtained by scanning the Raman molecule 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA) on the surface-enh...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com