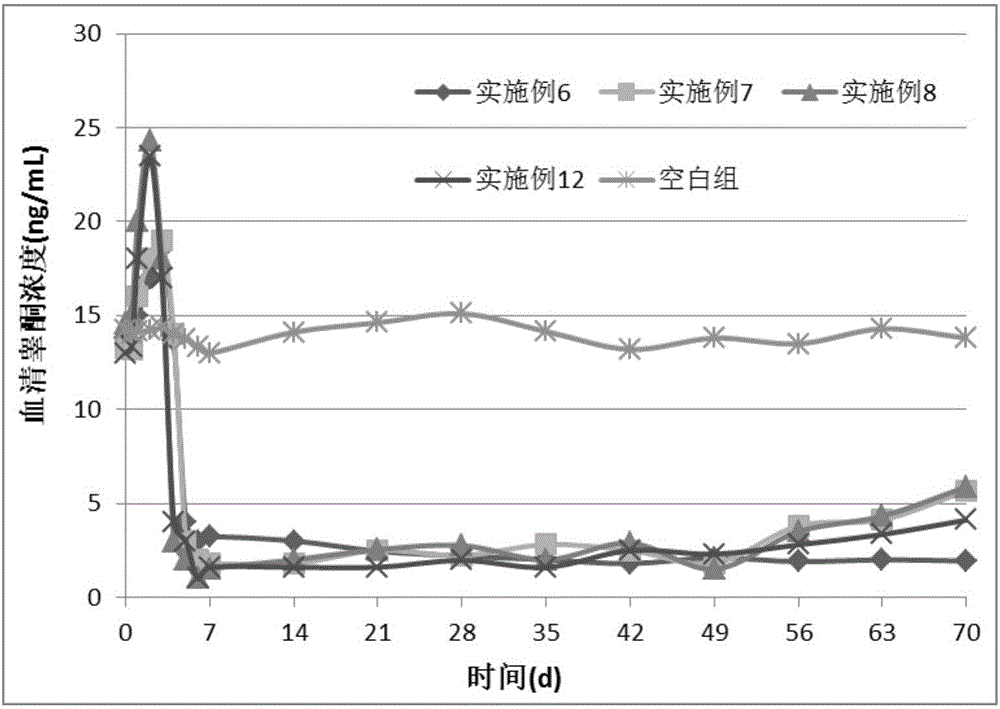
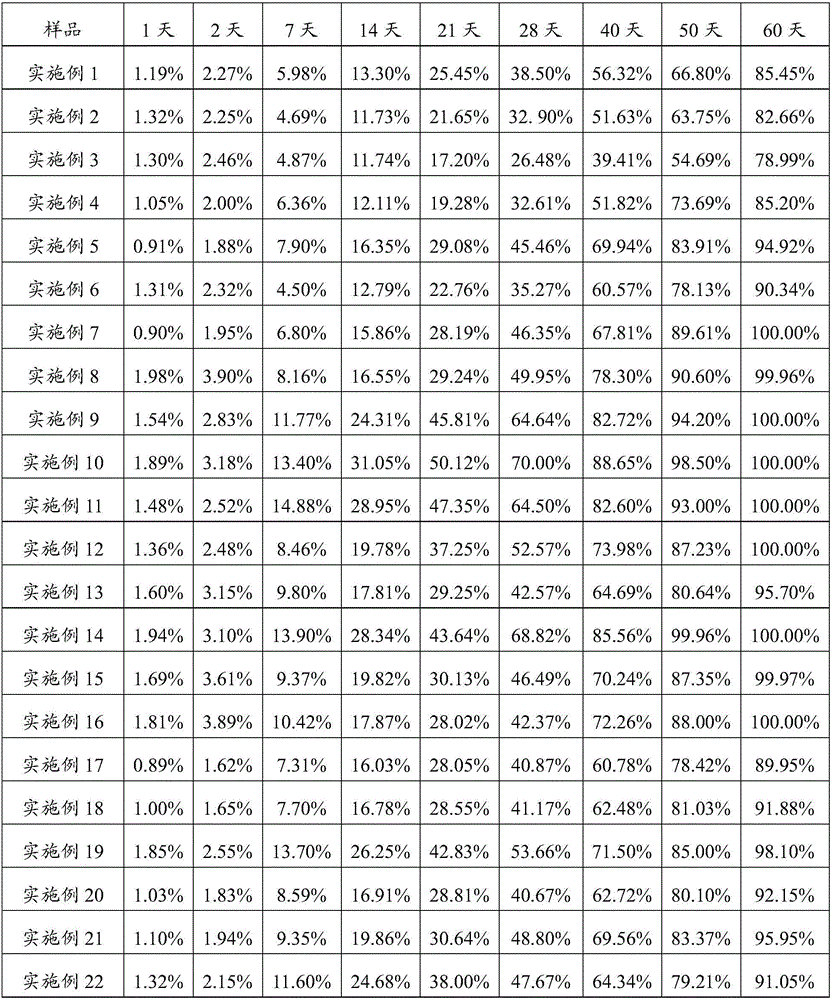
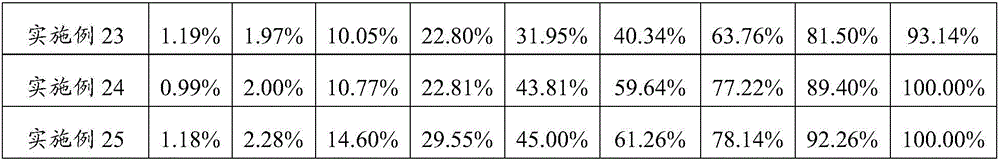
Preparation method of sustained-release microparticles
A technology for slow-release microparticles and microparticles, which can be applied to medical preparations without active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, and pharmaceutical formulations, etc., and can solve the problems of difficulty, disadvantage, and denaturation in the preparation of microparticles.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Example 1: Preparation of Glucagon / PLA Microparticles
[0097] (1) Preparation of solid dispersion
[0098] Dissolve 0.99g PLA (molecular weight 25kDa, terminal ester group) in about 5.50mL glacial acetic acid, then add 0.01g sermorelin acetate, 0.05g xylitol and 0.05g zinc hydroxide, vortex to dissolve, and then slowly Inject into stirred anhydrous diethyl ether (8°C) to produce a white precipitate, collect the white precipitate and extract about 5 times with anhydrous diethyl ether, dry the precipitate in a vacuum oven for 24 hours (10°C) to obtain a solid Dispersions.
[0099] (II) Preparation of microparticles
[0100] Uniformly disperse the solid dispersion obtained in step 1 in about 5.50 g of dichloromethane to obtain an internal oil phase, and then inject the internal oil phase into 210 mL of 0.1% (w / w) polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution that has been pre-heated to about 6°C and emulsifying with a wheel-type homomixer to prepare S / O / W emulsion (running speed ...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Embodiment 2: Preparation of Ziconotide / PLGA microparticles
[0102] (1) Preparation of solid dispersion
[0103]Dissolve 0.97g PLGA (molecular weight 25kDa, monomer ratio 90 / 10, terminal ester group) in about 5.39mL glacial acetic acid, then add 0.03g ziconotide acetate, 0.05g xylitol and 0.03g zinc chloride, vortex Spin down to dissolve, and then slowly inject into anhydrous ether (6°C) under stirring, resulting in a white precipitate, collect the white precipitate and extract it with anhydrous ether for about 5 times, collect the precipitate and dry it in a vacuum oven for 24 hours (10°C) to obtain a solid dispersion.
[0104] (II) Preparation of microparticles
[0105] Uniformly disperse the solid dispersion obtained in step 1 in about 5.39 g of dichloromethane to obtain an internal oil phase, and then inject the internal oil phase into 290 mL of 0.5% (w / w) polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution that has been pre-heated to about 4°C , and use a high-speed homogenizer...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Example 3: Preparation of Tecoctide / PLGA Microparticles
[0107] (1) Preparation of solid dispersion
[0108] Dissolve 0.95g PLGA (molecular weight 30kDa, monomer ratio 85 / 15, carboxyl-terminated) in about 6.33mL glacial acetic acid / acetonitrile mixture, then add 0.05g tecosetide acetate, vortex to dissolve, and then slowly inject In cyclohexane (6°C) under stirring, a white precipitate is produced. Collect the white precipitate and extract it with cyclohexane for about 5 times. After collecting the precipitate, dry it in a vacuum oven for 24 hours (10°C) to obtain a solid dispersion body.
[0109] (II) Preparation of microparticles
[0110] The solid dispersion obtained in step 1 was uniformly dispersed in about 6.33 g of chloroform to obtain the internal oil phase, and then the internal oil phase was injected into 480 mL of 1% (w / w) hypromellose aqueous solution that had been pre-heated to about 4 °C , and use SPG membrane emulsifier to prepare S / O / W emulsion (memb...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com