Lead-zinc smelting wastewater treatment method
A wastewater treatment, lead-zinc technology, applied in the direction of gaseous effluent wastewater treatment, water/sewage treatment, neutralized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems affecting the cleaning cycle and life of microfiltration and nanofiltration equipment, microfiltration, nanofiltration Serious pollution of filtration equipment, microfiltration and nanofiltration effects are not obvious, etc., to achieve obvious removal effect, convenient management, and reduce the degree of corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Processing scale: 400m 3 / d.
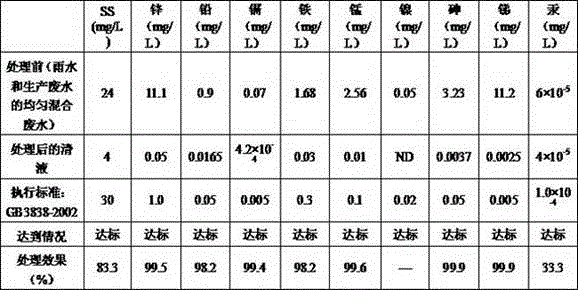
[0030] Wastewater from a lead-zinc beneficiation plant contains harmful pollutants such as SS, zinc, lead, cadmium, iron, manganese, nickel, arsenic, antimony, mercury, etc. The wastewater is acidic, and the total discharge of initial rainwater and production wastewater is about 400m per day 3 / d, according to the requirements of the environmental protection department, it needs to be treated to the Class III water quality standard of the "Surface Water Environmental Quality Standard" (GB3838-2002).
[0031] The processing method includes the following steps:
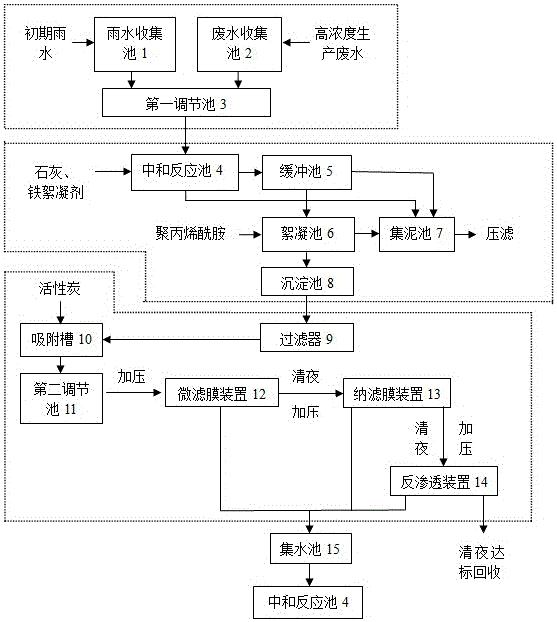
[0032] A. Initial treatment of influent water: The total amount of high-concentration production wastewater collected in a lead-zinc beneficiation plant's rainwater collection tank 1 in one day and high-concentration production wastewater in a day is about 400m 3 , the rainwater and the production waste water are slowly flowed into the first regulating pond 3 together, and at the ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Processing scale: 310m 3 / d.
[0043] Wastewater from a lead-zinc beneficiation plant contains harmful pollutants such as SS, zinc, lead, cadmium, iron, manganese, nickel, arsenic, antimony, mercury, etc. The wastewater is acidic, and the total discharge of initial rainwater and production wastewater is about 310m per day 3 / d, according to the requirements of the environmental protection department, it needs to be treated to the Class III water quality standard of the "Surface Water Environmental Quality Standard" (GB3838-2002).
[0044] The processing method includes the following steps:
[0045] A. Primary treatment of influent water: The total amount of initial rainwater collected in one day by the rainwater collection tank 1 of a lead-zinc beneficiation plant and the high-concentration production wastewater collected by the waste water collection tank 2 by one day is about 310m 3 , the rainwater and the production waste water are slowly flowed into the first regu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com