Kit for detecting shiga-toxigenic escherichia coli in food
A technology for producing Shiga toxin and Escherichia coli, applied in measurement devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of long detection period, many false positives, low sensitivity, etc., and achieve short detection time, short research and development period, and simple operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] The preparation of embodiment 1 Shiga toxin-producing escherichia coli STEC bacterium liquid
[0061] Take the clinically isolated Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC O157:H7 strain, put it in an LB liquid medium test tube, shake it overnight at 37 degrees Celsius and 180 r / min, and set aside.
Embodiment 2
[0062] The acquisition of embodiment 2 aptamers
[0063] 1. The random single-stranded DNA library and primers were synthesized by Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd.
[0064] Random single-stranded DNA library: 5'-TTGGACAGTGGACGTGAAGC(N36)GACCAAGTGACAGTGACGAG-3' (Note: n36 represents 36 sets of any one of 36 A, T, C, and G bases).
[0065] Primer Ⅰ: 5’–TTGGACAGTGGACGTGAAGC-3’
[0066] Primer Ⅱ: 5'-CTCGTCACTGTCACTTGGTC-3'
[0067] Primer III: 5’-Digoxigenin–TTGGACAGTGGACGTGAAGC-3’
[0068] Primer IV: 5'-biotin-CTCGTCACTGTCACTTGGTC-3'.
[0069] 2. SELEX screening to obtain Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC-specific oligonucleotide aptamers
[0070] 1) SELEX screening process:
[0071] a. For the first round of screening, take 10 μg of synthetic random single-stranded DNA and add it to 400ul 1×binding buffer, denature at 95°C for 5 minutes, and then quickly place it on ice for 10 minutes;
[0072] b. Add 1 mL of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli STEC suspensio...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Embodiment 3 Combination characteristic verification
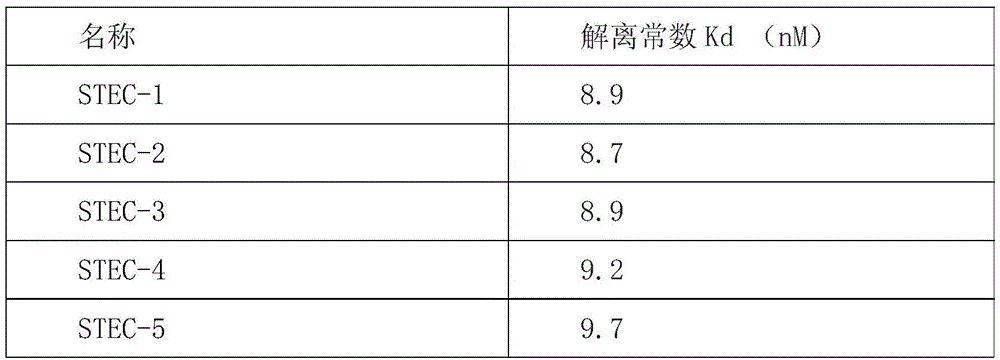
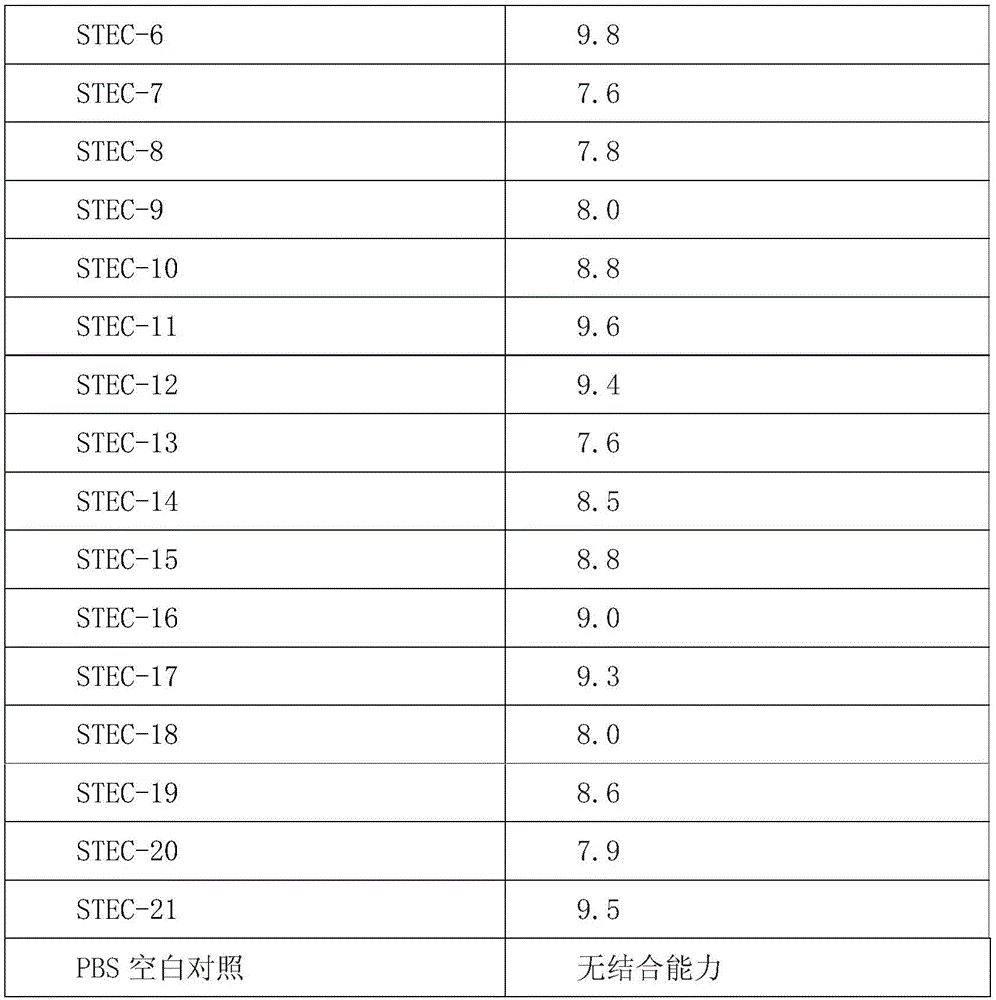
[0087] Take 1.5 μg of aptamers, digest them with calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIP) at 37°C for 1 h, purify and recover the dephosphorylated DNA; label [γ-32P]ATP on the dephosphorylated DNA by T4 polynucleotide kinase The end of a DNA molecule. 10nmol of radioactively labeled DNA aptamers were incubated with bacteria of different concentrations at 37°C for 30min, the reaction solution of each group was filtered through a nitrocellulose membrane, the filter membrane was washed, dried, and the residual amount on the filter membrane was measured by a liquid scintillation counter. For radiation dose, the same sample was measured twice in parallel. Calculate the dissociation constant of each aptamer and bacteria. The result is as follows:
[0088]
[0089]
[0090] It can be seen from the above results that the 21 aptamers of the present invention have very strong binding properties, and there are no ap...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com