Method for comprehensively recovering rare and dispersed noble metal from refining furnace slag
A technology of rare precious metals and slag, applied in the field of comprehensive recovery of scattered rare precious metals, can solve the problems of low direct recovery rate, large equipment investment, high toxic and harmful content, etc., and achieve the effect of simple process equipment, low energy consumption, and less three wastes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The chemical composition of typical smelting slag is shown in Table 1.
[0033] Table 1 Chemical composition of typical smelting slag
[0034] element
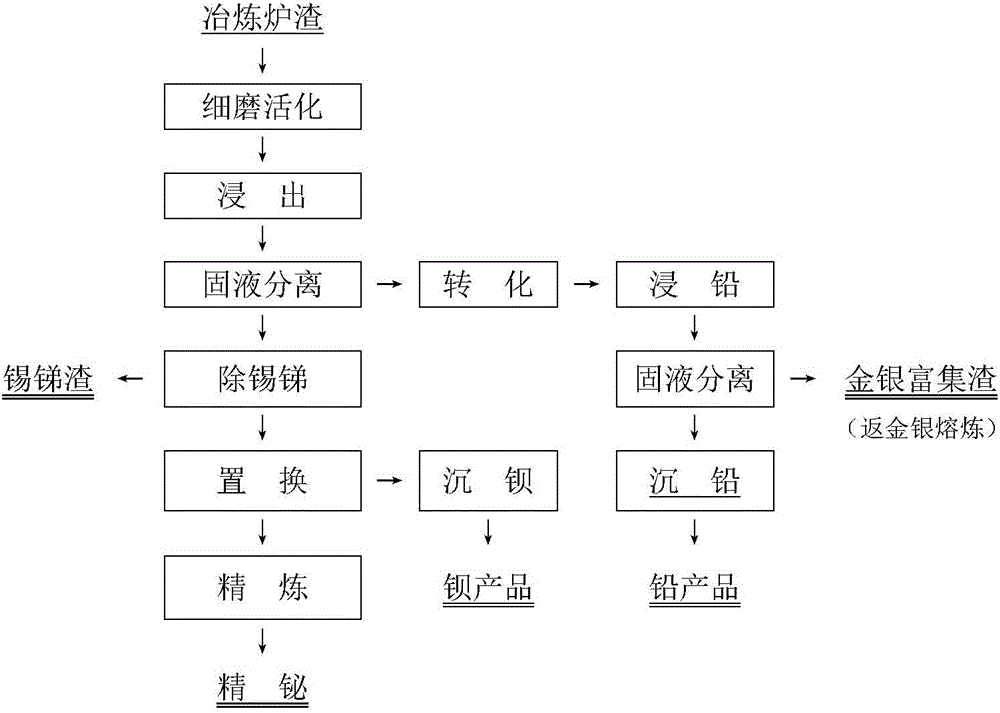
[0035] Finely grind the smelting slag to 50% less than 0.1mm, use HCl concentration of 1mol / L, FeCl 2 The concentration is 4mol / L, the liquid-solid ratio is 3:1, and the leaching temperature is 60°C for 3h; the leachate is 10g / L Fe(OH) at 20°C 2 Precipitate for 4 hours to obtain tin and antimony enrichment; after removing tin and antimony, replace bismuth with 1 times the theoretical amount of iron powder to obtain crude bismuth; After conversion at a ratio of 6:1, the concentration of nitric acid is 3mol / L, the temperature is 20°C, the time is 3h, and the liquid-solid ratio is 2:1 for leaching, so that lead enters the solution, and rare and precious metals such as gold and silver are further enriched in the slag. After analysis, the enrichment ratio of tin and antimony reached 14 times, and the precipitatio...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Finely grind the smelting slag to 50% less than 0.1mm, use HCl concentration of 1.5mol / L, ZnCl 2 The concentration is 3mol / L, the liquid-solid ratio is 4:1, and the leaching temperature is 100°C for 4 hours; the leachate is 20g / L Zn(OH) at 40°C 2 Precipitate for 3 hours to obtain tin-antimony enrichment; after removing tin and antimony, replace bismuth with 1.2 times the theoretical amount of zinc powder in the liquid to obtain crude bismuth; After conversion with a solid ratio of 2:1, the concentration of nitric acid is 1mol / L, the temperature is 80°C, the time is 0.5h, and the liquid-solid ratio is 6:1 for leaching, so that lead enters the solution, and rare and precious metals such as gold and silver are further enriched in the slag. After analysis, the enrichment ratio of tin and antimony reached 14.2 times, and the precipitation rate reached 99.9%; the leaching rate of bismuth was 99.7%, and the direct recovery rate was 95.3%; the enrichment ratio of gold and silve...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Finely grind the smelting slag until more than 50% is less than 0.1mm, using HCl concentration of 4.0mol / L, ZnCl 2 The concentration is 0.5mol / L, the liquid-solid ratio is 6:1, and the leaching temperature is 90°C for 1h; the leachate is 100g / L Zn(OH) at 20°C 2 Precipitate for 8 hours to obtain tin-antimony enrichment; after removing tin and antimony, replace bismuth with twice the theoretical amount of zinc powder to obtain crude bismuth; After conversion with a solid ratio of 3:1, the concentration of nitric acid is 1.5mol / L, the temperature is 40°C, the time is 1h, and the liquid-solid ratio is 4:1 for leaching, so that lead enters the solution, and rare and precious metals such as gold and silver are further enriched in the slag . After analysis, the enrichment ratio of tin and antimony reached 14 times, and the precipitation rate reached 99.9%; the leaching rate of bismuth was 99.8%, and the direct recovery rate was 95.0%; the enrichment ratio of gold and silver w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com