Cyanobacteria dewatering and composting treatment method
A treatment method and composting technology, applied in dehydration/drying/concentrated sludge treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, sludge treatment, etc., can solve problems such as secondary pollution, high water content of cyanobacteria, and unfavorable follow-up disposal , to achieve the effect of reducing transportation costs, high degree of automation, and improving resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
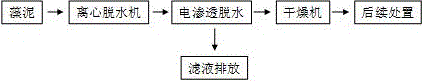
[0019] Embodiment 1: A kind of blue-green algae dehydration composting processing method, comprises the following steps: the blue-green algae collected salvage is centrifuged and dehydrated and then dehydrated with an electroosmotic dehydration device, and then the algae mud is mixed with the engineering composite functional bacterial agent for composting, and the thickness of the composting is 20~30cm, aeration pipes are inserted in the compost mixing pile, the pH value of the decomposed cyanobacteria compost is 8.05, the organic matter content is 32.62%, the total nitrogen content is 1.59%, the total phosphorus (P2O5) content is 0.99%, the total The content of potassium (K2O) is 1.5%, and the content of total nutrients (nitrogen + phosphorus pentoxide + potassium oxide) reaches 4%. Centrifugal dehydration uses a centrifuge for the first step of dehydration, and the moisture content drops from 95%-99% to about 85%. The engineering compound functional bacterial agent includes ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: Reference Example 1: The engineered compound functional bacterial agent includes 2% by mass of the engineered compound functional bacterial species, and the rest is culture medium. Engineering compound functional strains include, in terms of mass percentage: 10% Bacillus subtilis (AJ276351), 15% Thermosaccharococcus thermophiles (X70430), 5% high-temperature lignin-degrading bacteria (AF067651), 14% Thermoglucosidase soil spores Bacillus (AY608981), 13% Denitrophilic Bacillus (AY608961), 15% Geobacillus stearothermophilus (AB271757), 8% Geobacillus (AJ564616), 10% YMO81 (AB250968), 5% YMO722 (AB308475 ), 5% high temperature actinomycetes (AB088361).
Embodiment 3
[0022] Example 3, with reference to Example 1, the engineered compound functional bacterial agent includes 0.5% by mass of the engineered compound functional bacterial strain, and the rest is a culture medium. The engineering compound functional strains include, by mass percentage: 5% Bacillus subtilis (AJ276351), 20% Thermosaccharococcus thermophiles (X70430), 5% high-temperature lignin-degrading bacteria (AF067651), 17% thermoglucosidase soil spores Bacillus (AY608981), 7% Denitrophilic Bacillus (AY608961), 21% Geobacillus stearothermophilus (AB271757), 18% Geobacillus (AJ564616), 5% YMO722 (AB308475), 2% high temperature ray bacteria (AB088361).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com