Primer set and kit for detecting mycoplasma, and method for detecting mycoplasma pollution
A mycoplasma and kit technology, which is applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low reliability of research results, insufficient broad-spectrum, insufficient sensitivity, etc., and achieve the effects of easy interpretation, good broad-spectrum and broad application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Design and synthesis of primer sets
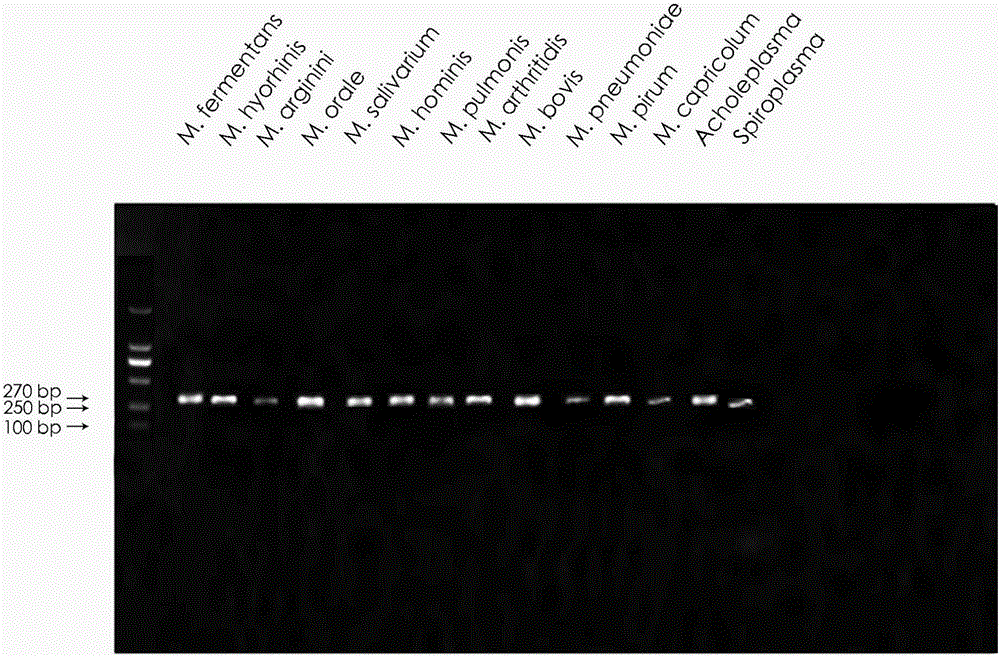
[0035] First, select the mycoplasma species to be detected: According to the most common mycoplasma contamination cases in the cell culture process, 15 common mycoplasma species are selected as the target mycoplasma species to be detected: M.fermentans, M.hyorhinis, M.arginini , M. orale, M. salivarium, M. hominis, M. pulmonis, M. arthritidis, M. bovis, M. pneumoniae, M. pirum, M. capricolum, Acholeplasma or Spiroplasma;
[0036] Then, compare the gene bank: search from the American gene database Genbank, compare the 16S rDNA sequences of the above 15 target mycoplasma species, use xxxx software to analyze and compare homologous sequences, and find a conserved and specific sequence as the target fragment;
[0037] Subsequently, the primers required for the PCR amplification reaction were designed with the above-mentioned target fragments.
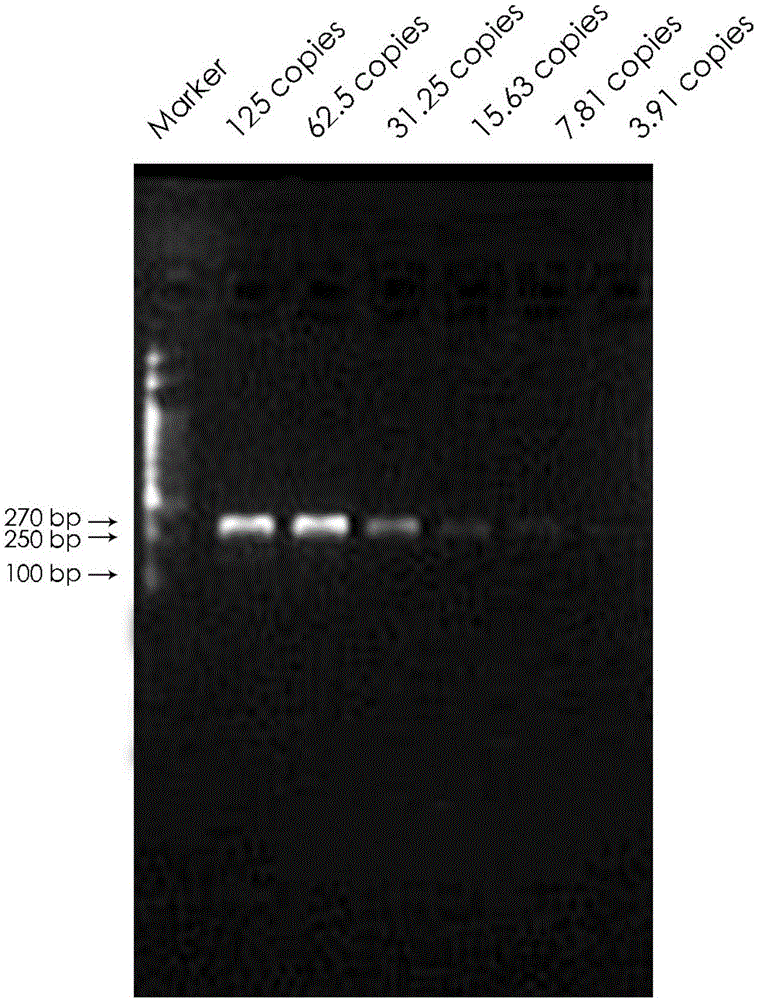
[0038] Finally, test the specificity and sensitivity of the designed primers; i...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: the preparation of kit
[0044] 1) Synthesize the primer set with reference to the above-mentioned Example 1;
[0045] 2) Mycoplasma lysis buffer: mycoplasma lysis reagent (product number 07066) purchased from SIGMA-ALDRICH company;
[0046] 3) Polymerase chain reaction reagents: purchased from the "low background, high sensitivity PCR series" products produced by TaKaRa Biotechnology Company, mainly including: Taq enzyme, PCR reaction buffer, MgCl 2 and dNTPs;
[0047] 4) Positive control: a plasmid containing the conserved sequence of mycoplasma 16S rDNA (270bp);
[0048] 5) Negative control: sterile water.
[0049] The forward sequence and reverse sequence of the above primer set were placed in airtight containers; the positive control and negative control were respectively placed in airtight containers; and then assembled into the kit together with the purchased polymerase chain reaction reagent products.
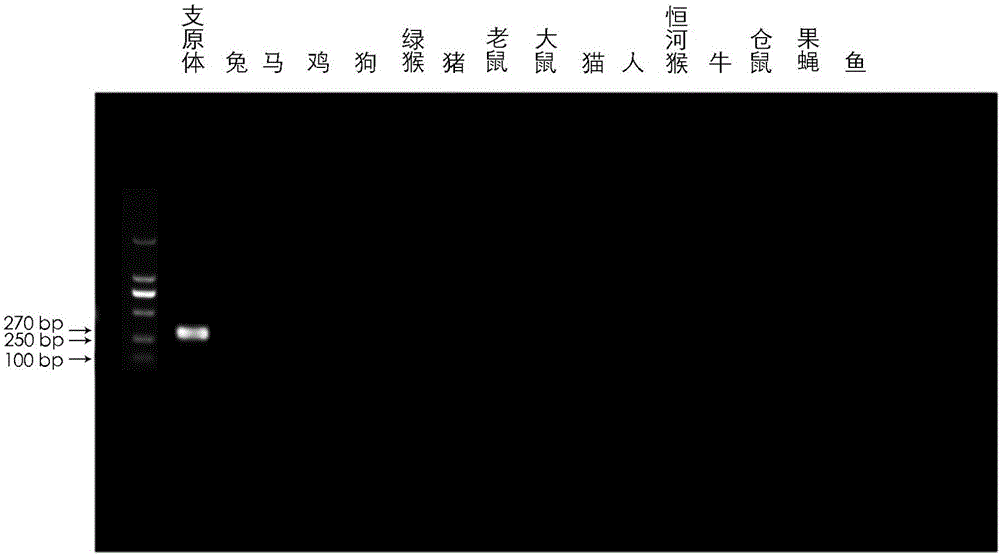
[0050] The specificity evaluation of ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Embodiment 3: detect mycoplasma pollution
[0063] Step 1) Mycoplasma lysis: use the mycoplasma lysis buffer in the kit of Example 2 to process the samples to be tested (samples 1, 2 and 3) to obtain a lysate;
[0064] First, take 0.5-1 ml of the sample to be tested (cell culture supernatant) and add it to a 2 ml centrifuge tube; briefly centrifuge at 500 rpm for 60 seconds to pellet cell debris; transfer the centrifuged supernatant into a new In a sterilized 2 ml centrifuge tube; centrifuge at 20000rpm for 10 minutes to precipitate mycoplasma, then gently aspirate and discard the supernatant; then add 50 microliters of mycoplasma lysis buffer to the centrifuge tube, gently pipette Swipe to mix the precipitate, and heat at 95 degrees Celsius for 3 minutes to obtain a lysate containing mycoplasma DNA;
[0065] Step 2) PCR amplification: mixing the lysate obtained in step 1) with the polymerase chain reaction reagent and the primer set to perform a PCR amplification re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com