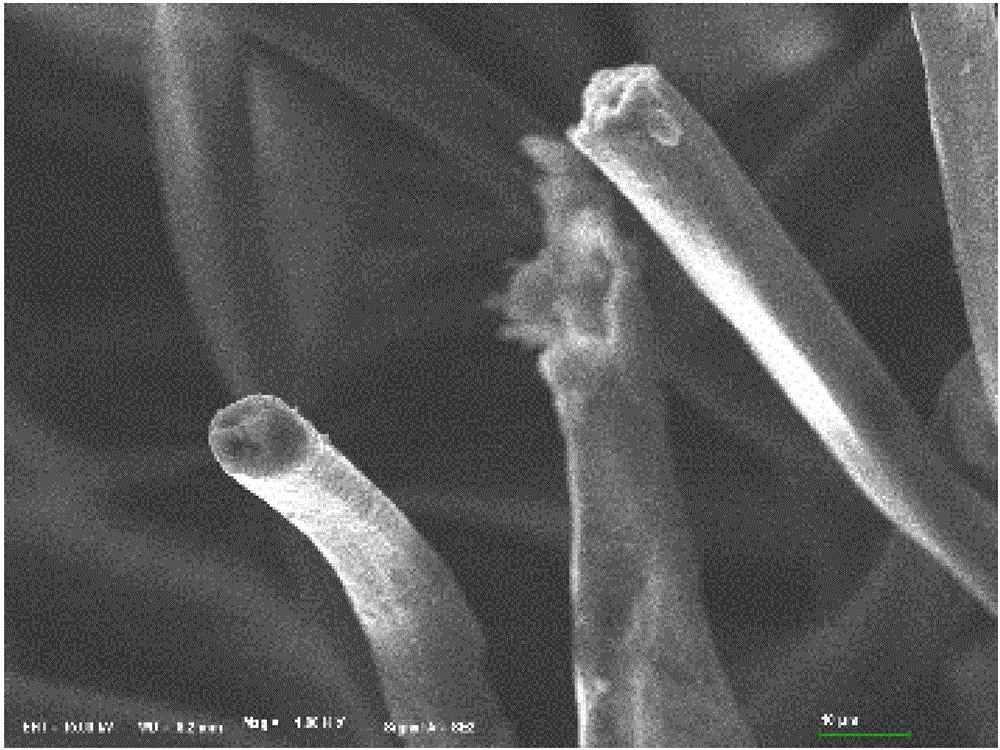
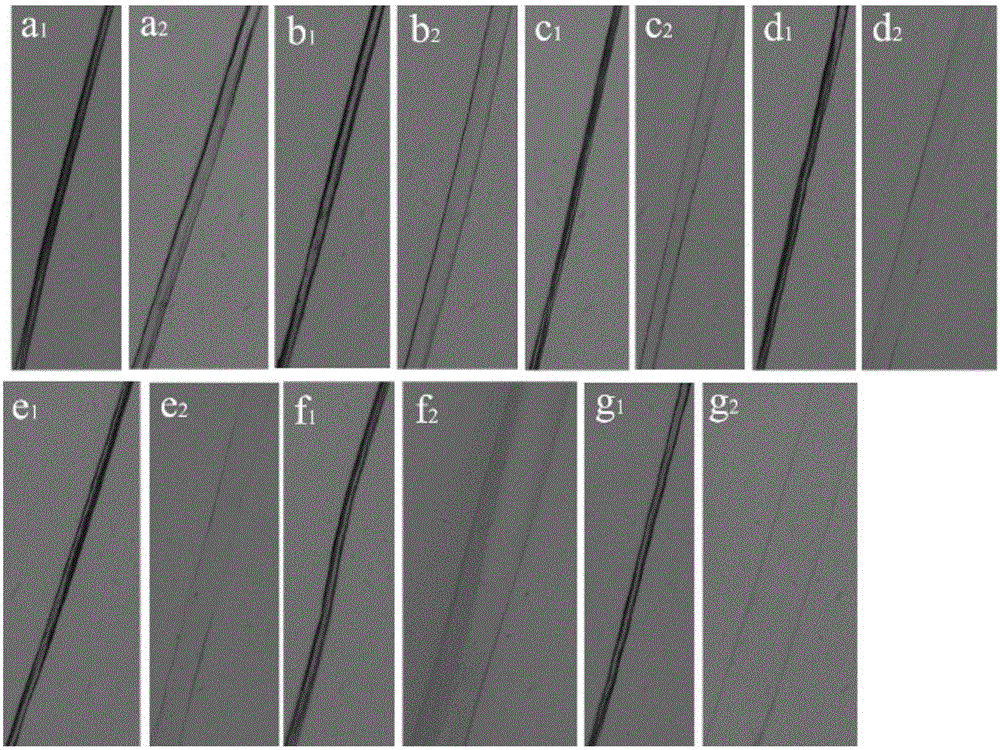
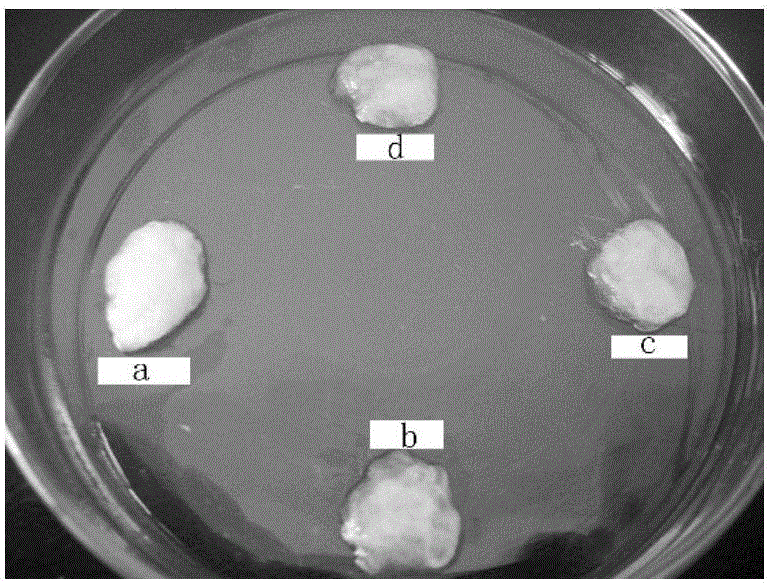
Hemostatic material
A hemostatic material and fiber technology, applied in the field of hemostatic materials, can solve the problems of insufficient fiber absorption, no antibacterial performance, harsh reaction conditions, etc., and achieve good liquid absorption performance and antibacterial performance, good vertical absorption performance, and reaction conditions mild effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0112] Weigh 5 g of chitin fibers with a length of 6 cm and a p / (m+n+p) of 0.25, disperse them in 50 mL of isopropanol, add 2.54 g of 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate, and shake evenly at room temperature. React in a constant temperature water bath for 48 hours under the same conditions, separate the reacted chitin fibers from the reaction mixture, wash twice with 80% (v / v) methanol aqueous solution, take out the fibers, dry them, and disperse them in 80% (v / v) v) Add 30% (w / v) potassium hydroxide aqueous solution dropwise to methanol aqueous solution, adjust the pH of methanol and potassium hydroxide aqueous solution mixture to 11.0, soak for 1 hour, and then separate the soaked fiber from the mixture , washed 3 times with 80% (v / v) methanol aqueous solution, dehydrated, and dried at 40°C to obtain a liquid-absorbent fiber with a viscosity-average molecular weight (Mη) of 3 million and a degree of substitution of acryl group total substance of 0.17.
[0113] Dissolve absorbent fibers ...
Embodiment 2
[0115] Weigh 5 g of chitin fibers with a length of 6 cm and a p / (m+n+p) of 0.10, disperse them in 50 mL of isopropanol, add 7.09 g of 2-hydroxypropyl acrylate, and shake evenly at room temperature. React in a constant temperature water bath for 48 hours under the same conditions, separate the reacted chitin fibers from the reaction mixture, wash twice with 80% (v / v) methanol aqueous solution, take out the fibers, dry them, and disperse them in 80% (v / v) v) Add 30% (w / v) potassium hydroxide aqueous solution dropwise to methanol aqueous solution, adjust the pH of methanol and potassium hydroxide aqueous solution mixture to 11.0, soak for 1 hour, and then separate the soaked fiber from the mixture , washed three times with 80% (v / v) methanol aqueous solution, dehydrated, and dried at 40°C to obtain a liquid-absorbent fiber with a viscosity-average molecular weight of 3 million and a degree of substitution of acryl group total substance of 0.30.
[0116] Dissolve absorbent fibers ...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Weigh 5 g of chitin fibers with a length of 6 cm and a p / (m+n+p) of 0.10, disperse them in 80 mL of isopropanol, add 14.17 g of 2-hydroxypropyl acrylate, and shake evenly at room temperature. React in a constant temperature water bath for 48 hours under the same conditions, separate the reacted chitin fibers from the reaction mixture, wash twice with 80% (v / v) methanol aqueous solution, take out the fibers, dry them, and disperse them in 80% (v / v) v) Add 30% (w / v) potassium hydroxide aqueous solution dropwise to methanol aqueous solution, adjust the pH of methanol and potassium hydroxide aqueous solution mixture to 11.5, soak for 1 hour, and then separate the soaked fiber from the mixture , shake dry, and place in saturated CaCl 2 Soak in the solution for 1 hour, take out the fiber, wash 3 times with 80% (v / v) methanol aqueous solution, and dry at 40°C after dehydration to obtain a viscosity-average molecular weight of 500,000 and a total substitution degree of acryloyl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Gram weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com