R-Fe-B type sintered magnet manufacturing method
A technology of sintered magnets and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the manufacture of permanent magnets, inductors/transformers/magnets, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of oxidation and shedding of heavy rare earth layers, difficult control, and difficulty in swinging materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] A vacuum melting furnace is used to smelt the configured raw materials under the protection of inert gas to form scales with a thickness of 0.1-0.5 mm. The metallographic grain boundaries of the R-Fe-B alloy scales are clear. The alloy scales are crushed mechanically, and jet milled after hydrogen explosion to crush the SMD to 3.4μm. The magnetic field orientation press molding of 15KOe is used to make a compact, and the density of the compact is 3.95g / cm3. The compact is vacuum sintered in a sintering furnace, firstly at 1080°C for 330min. Then perform aging treatment, aging at 480° C. for 240 minutes to obtain a green body. The green body is multi-wire cut into a magnetic sheet of the final product size. The size of the magnetic sheet: 27mm*15mm*5mm, tolerance: ±0.05mm.
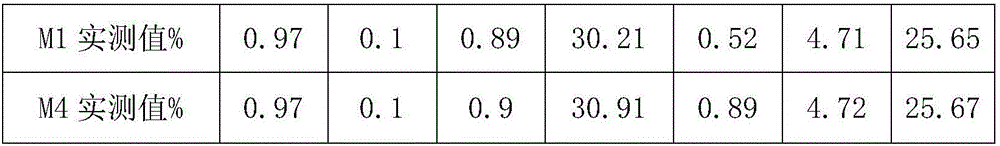
[0020] The surface of the magnetic sheet was washed with acid solution and deionized water, and dried to obtain the treated magnet M1. The composition of M1 is shown in Table 2. First, a layer of ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] A vacuum melting furnace is used to smelt the configured raw materials under the protection of inert gas to form scales with a thickness of 0.1-0.5 mm. The metallographic grain boundaries of the R-Fe-B alloy scales are clear. The alloy scales are crushed mechanically, and jet milled after hydrogen explosion to crush the SMD to 3.4μm. The magnetic field orientation press molding of 15KOe is used to make a compact, and the density of the compact is 3.95g / cm3. The compact is vacuum sintered in a sintering furnace, firstly at 1080°C for 330min. Then perform aging treatment, aging at 480° C. for 240 minutes to obtain a green body. The green body is multi-wire cut into a magnetic sheet of the final product size. The size of the magnetic sheet: 27mm*15mm*5mm, tolerance: ±0.05mm.
[0028] The surface of the magnetic sheet was washed with acid solution and deionized water, and dried to obtain the treated magnet M1. The composition of M1 is shown in Table 3. First, a layer of ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] A vacuum melting furnace is used to smelt the configured raw materials under the protection of inert gas to form scales with a thickness of 0.1-0.5 mm. The metallographic grain boundaries of the R-Fe-B alloy scales are clear. The alloy scales are crushed mechanically, and jet milled after hydrogen explosion to crush the SMD to 3.4μm. The magnetic field orientation press molding of 15KOe is used to make a compact, and the density of the compact is 3.95g / cm3. The compact is vacuum sintered in a sintering furnace, firstly at 1080°C for 330min. Then perform aging treatment, aging at 480° C. for 240 minutes to obtain a green body. The green body is multi-wire cut into a magnetic sheet of the final product size. The size of the magnetic sheet: 27mm*15mm*5mm, tolerance: ±0.05mm.
[0036] The surface of the magnetic sheet was washed with acid solution and deionized water, and dried to obtain the treated magnet M1. The composition of M1 is shown in Table 2. First, a layer of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com