Toxicity reduction and recycling system and treatment method for biotreated effluent in printing and dyeing industry
A tail water and biochemical technology, applied in the direction of biological water/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment, water treatment parameter control, etc., can solve the problems of high operating cost and inability to reduce biological toxicity, achieve low operating cost, and realize comprehensive biological Toxicity, toxicity-reducing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
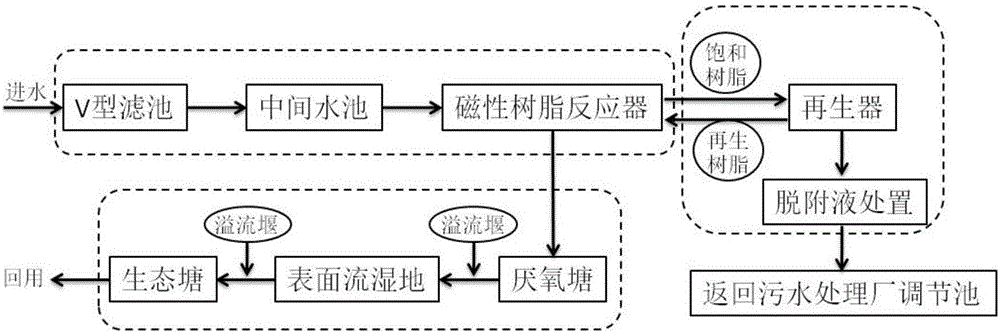
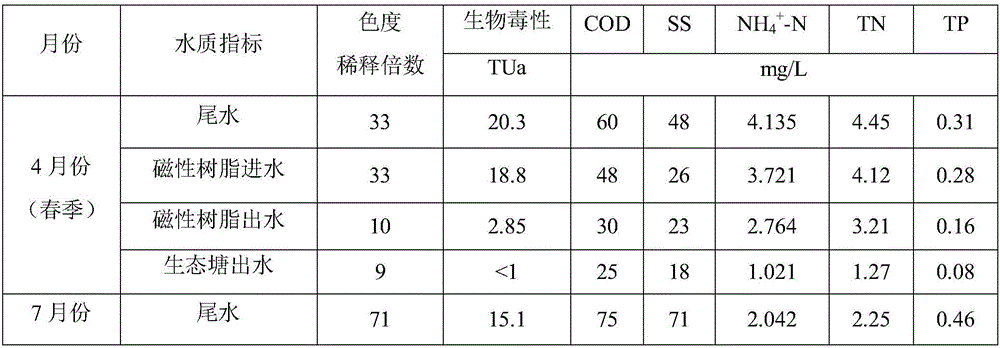
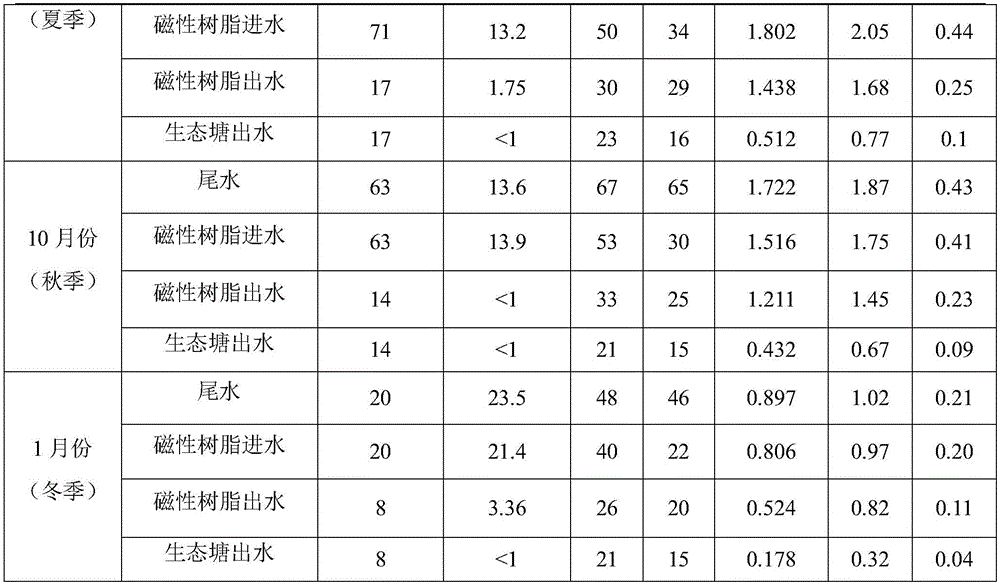
[0038] The wastewater treatment scale of a printing and dyeing textile park is 6,000 tons / day. After the traditional biochemical process, the concentration of COD in the effluent is 80-100mg / L, the concentration of ammonia nitrogen is 3-5mg / L, the concentration of total nitrogen is 1.0-5.0mg / L, and the concentration of total phosphorus is 0.3 -1.0mg / L, such as figure 1 As shown, a biochemical tail water toxicity reduction and reuse system in the printing and dyeing industry is used for advanced treatment of wastewater. The treatment devices used include V-shaped filters (2 sets, length 5.5 meters × width 3.5 meters × height 4.0 meters), Intermediate pool (1, length 11.0m x width 5.5m x height 4.0m), magnetic resin reactor (1, diameter 5.0m x height 8.0m), anaerobic pond (1, length 295m x width 72m × 5 meters high), surface flow wetlands (2, length 180 meters × width 85 meters × height 1.5 meters) and ecological ponds (1 building, length 120 meters × width 60 meters × height 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] A textile printing and dyeing park produces 3,000 tons of sewage per day. After traditional biochemical treatment, the effluent COD concentration is 95-140mg / L, ammonia nitrogen concentration is 2-4mg / L, total nitrogen concentration is 5-10mg / L, and total phosphorus concentration is 0.5-1.5 mg / L. The treatment method steps are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the resin reactor adopted is a hydraulic circulation stirring mode (the magnetic resin reactor provided in Example 1 of Chinese Invention Patent No. ZL201110127627.X), The hydraulic retention time is 40 minutes, and the annual ratio of resin dosage to treated water is 1:300. The treatment devices used include V-shaped filters (2, 4.0 m long x 2.8 m wide x 3.5 m high), an intermediate pool (1, 6.0 m long x 3.5 m wide x 4.0 m high), a magnetic resin reactor ( 1 building, 3.5 meters long × 3.5 meters wide × 7.0 meters high), anaerobic pond (1 building, 208 meters long × 50 meters wide × 5 me...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The daily sewage production of a textile printing and dyeing park is 5,000 tons. After traditional biochemical treatment, the effluent COD concentration is 75-100mg / L, ammonia nitrogen concentration is 2-5mg / L, total nitrogen concentration is 1.0-4.5mg / L, and total phosphorus concentration is 0.5- 1.0mg / L. The steps of the treatment method are basically the same as in Example 1, except that the hydraulic retention time of the resin reactor is 30 minutes, and the ratio of resin dosage to treated water is 1:300. The treatment device used includes a V-shaped filter (1 set, 7.5 meters long × 4.0 meters wide × 4.5 meters high), an intermediate pool (1 set, 10.0 meters long × 4.5 meters wide × 4.5 meters high), a magnetic resin reactor ( 1 building, diameter 6.0 meters x height 6.0 meters), anaerobic pond (1 building, length 252 meters x width 68 meters x height 4.5 meters), surface flow wetland (3 buildings, length 150 meters x width 46 meters x height 2.0 meters ) and ecol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com