Mineralization guided tissue regeneration membrane and preparation method and application thereof
A technology to guide tissue regeneration and mineralize collagen, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve problems such as poor regeneration function, and achieve good tissue compatibility, moderate thickness, and low immunogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
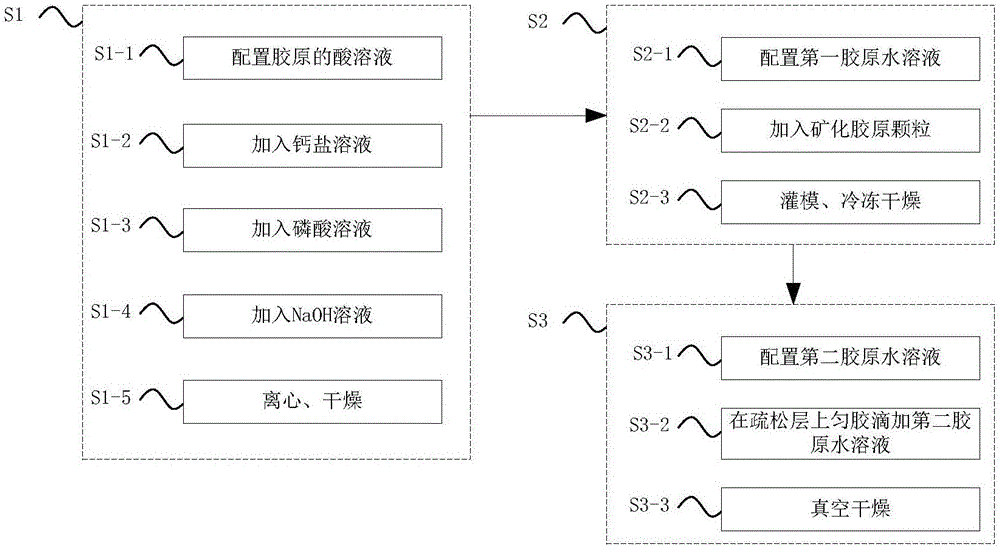
[0055] see figure 1 , is a flowchart of a method for preparing a mineralization-guided tissue regeneration membrane according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 1 Shown, this preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0056] Step S1, preparation of mineralized collagen particles, specifically includes:
[0057] Step S1-1, dissolving collagen in any one of hydrochloric acid, nitric acid or acetic acid to prepare an acid solution of collagen, wherein the concentration of collagen is 0.01-0.5 g / ml (for example, 0.01, 0.1, 0.2 or 0.5 g / ml) . The collagens used in the present invention are all type I collagens.
[0058] Step S1-2, adding calcium salt solution dropwise to the collagen acid solution, wherein the amount of calcium ions added is 0.1-2 mol (eg 0.1, 0.5, 1, 1.5 or 2 mol) of calcium ions per gram of collagen. More preferably, 1-2 mol of calcium ions are added per gram of collagen.
[0059] Step S1-3, adding phosphoric acid so...
Embodiment 1
[0092] (1) Dissolving type Ⅰ collagen in acetic acid with a concentration of 0.5M to form an acid solution of collagen, wherein the concentration of type Ⅰ collagen is 0.01g / ml;
[0093] (2) adding a calcium salt solution dropwise to the acid solution of the collagen, wherein the amount of calcium ions added is 1 mol of calcium ions corresponding to each gram of collagen;
[0094] (3) Add phosphoric acid solution dropwise in the solution obtained in step 2, wherein the molar ratio of the amount of phosphate ions added to the amount of calcium ions added in step S1-2 is Ca / P=1.5 / 1;
[0095] (4) NaOH solution is added dropwise in the solution obtained in step 3 to form a mixed solution, and the pH value is adjusted to be 8;
[0096] (5) After the mixed solution obtained in step 4 was left to stand for 4 hours, the precipitate was centrifuged at a speed of 3000 r / min and then air-dried at 50° C. for 24 hours to obtain mineralized collagen particles.
[0097] (6) dissolving colla...
Embodiment 2 to 14
[0105] Except for the contents of Table 1 and Table 2 below, it was carried out in substantially the same manner as in Example 1.
[0106]
[0107]
[0108]
[0109] Note: The collagen concentration in the second collagen aqueous solution represents the mass concentration of collagen.
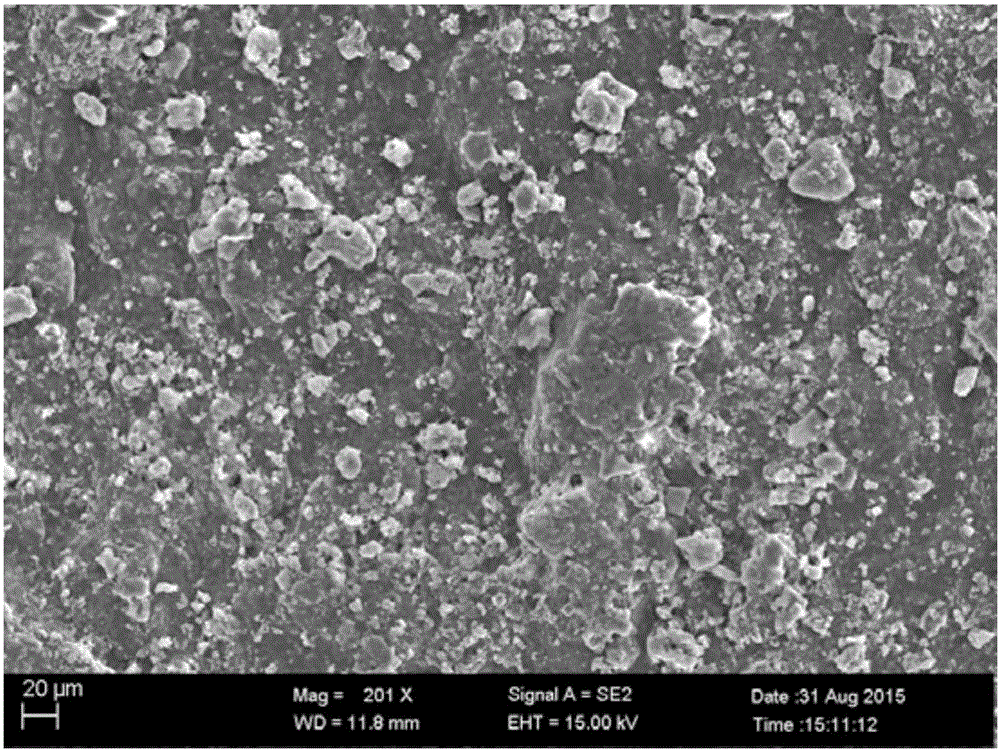
[0110] SEM result observation
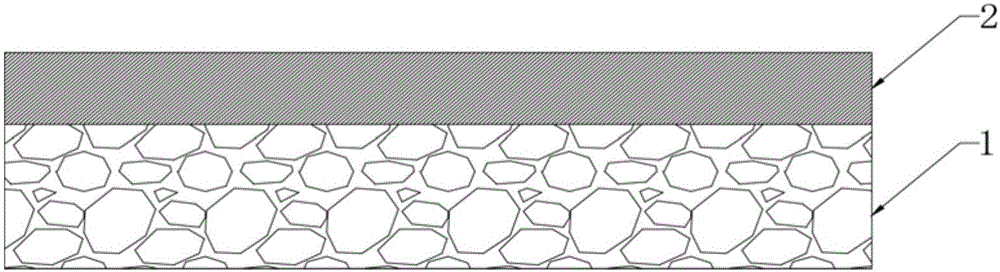
[0111] The mineralization-guided tissue regeneration membrane prepared in Example 1 was observed by a scanning electron microscope (SEM). see image 3 is the SEM result map of the loose layer, Figure 4 is the SEM result map of the dense layer, Figure 5 It is the SEM result picture of the section of the mineralization-guided tissue regeneration membrane. As shown in the figure, the loose layer has a porous structure, while the dense layer has a smooth surface. From the cross-sectional views of the two, it can be seen that the dense layer is composed of type I collagen fiber bundles closely arranged, and the loose layer is compounded with nano-hydrox...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com