Method for producing aminoanisole by solvent-free catalytic hydrogenation
A technology for the catalytic hydrogenation of aminoanisole, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, the preparation of organic compounds, and the preparation of aminohydroxyl compounds, etc., to achieve the effects of saving equipment investment, production safety, and reducing catalyst consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
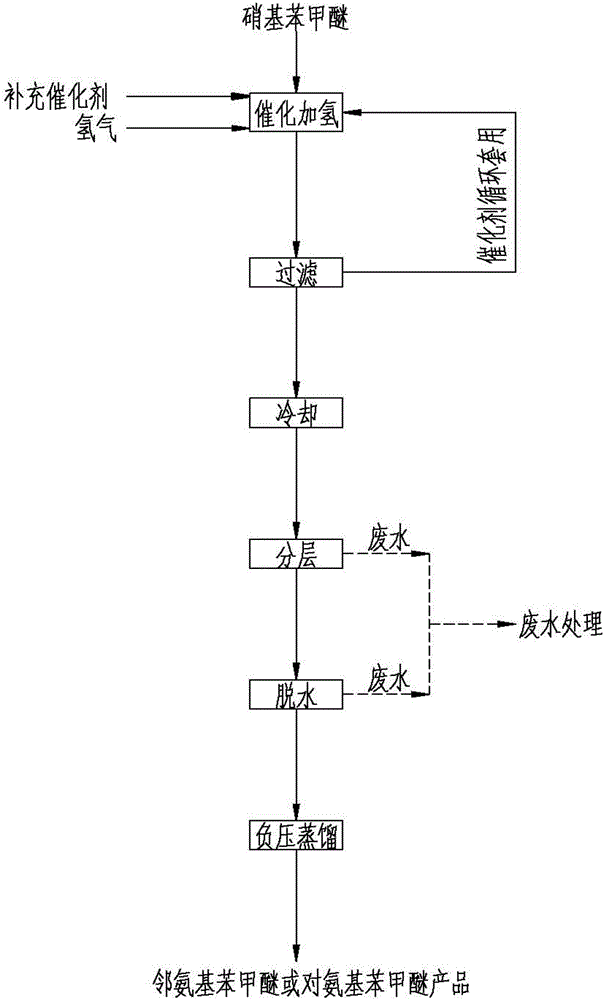
[0022] like figure 1 , the method steps of producing aminoanisole by solvent-free catalytic hydrogenation are as follows:
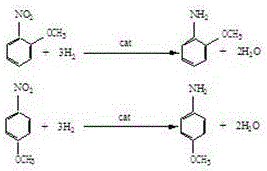
[0023] Put the measured o-nitroanisole and palladium / carbon catalyst into a 10m³ hydrogenation reactor, the catalyst dosage is 0.20% of the o-nitroanisole, fill it with nitrogen for 3 to 4 times, and take gas samples Analyze the oxygen content ≤ 0.1%, then replace it with hydrogen, take a gas sample to analyze the hydrogen content ≥ 99.0%, start stirring, raise the temperature to 70°C, feed hydrogen, control the reaction pressure at 0.6-1.0Mpa, and the reaction temperature at 80-100°C Catalytic hydrogenation reaction.
[0024] After the catalytic hydrogenation reaction is over, the reducing solution is pumped to the catalyst filter for catalyst recovery. The filtered catalyst is carried by a small part of the reducing solution back to the hydrogenation reactor for recycling, and most of the reducing solution after filtering the catalyst is removed. Redu...
Embodiment 2
[0029] like figure 1 , the method steps of producing aminoanisole by solvent-free catalytic hydrogenation are as follows:
[0030] Put metered p-nitroanisole and palladium / carbon catalyst into two series-connected 10m³ hydrogenation reactors, the amount of catalyst is 0.25% of p-nitroanisole, fill with nitrogen replacement 3 to 4 times, take The oxygen content of the gas sample analysis is ≤0.1%, and then replaced with hydrogen, the gas sample is taken to analyze the hydrogen content ≥99.0%, the stirring is started, the temperature is raised to 70°C, the hydrogen gas is introduced, the reaction pressure is controlled at 0.6-1.0Mpa, and the reaction temperature is 80- Batch or continuous catalytic hydrogenation reaction at 100°C.
[0031] After the catalytic hydrogenation reaction is over, the reducing solution is pumped to the catalyst filter for catalyst recovery. The filtered catalyst is carried by a small part of the reducing solution back to the hydrogenation reactor for ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] like figure 1 , the method steps of producing aminoanisole by solvent-free catalytic hydrogenation are as follows:
[0037] In two 10m³ hydrogenation reactors connected in series, put into the mixture of o-nitroanisole and p-nitroanisole and palladium / carbon catalyst, the amount of catalyst is o-nitroanisole, p-nitrobenzene 0.30% of the total amount of the mixture of methyl ether, filled with nitrogen to replace 3 to 4 times, take a gas sample to analyze the oxygen content ≤ 0.1%, and then replace it with hydrogen, take a gas sample to analyze the hydrogen content ≥ 99.0%, start stirring, and heat up to 70 °C, feed hydrogen, control the reaction pressure at 0.6-1.0Mpa, and the reaction temperature at 80-100 °C for intermittent or continuous catalytic hydrogenation reaction.
[0038] After the catalytic hydrogenation reaction is over, the reducing solution is pumped to the catalyst filter for catalyst recovery. The filtered catalyst is carried by a small part of the red...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com