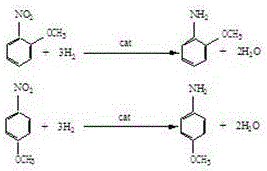
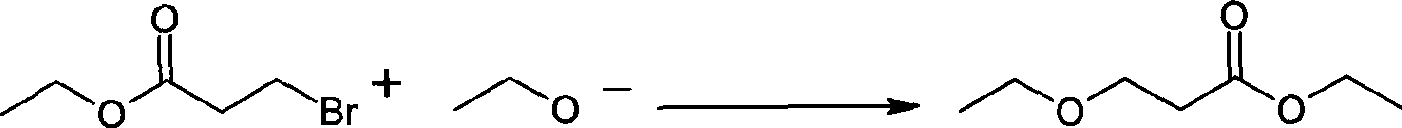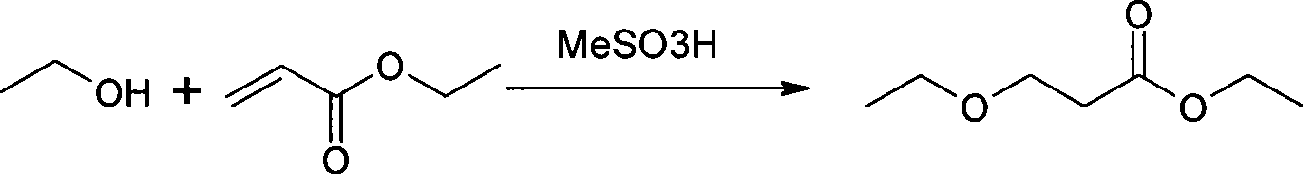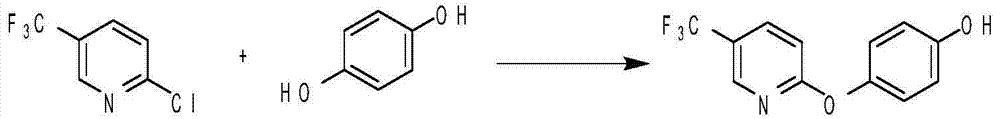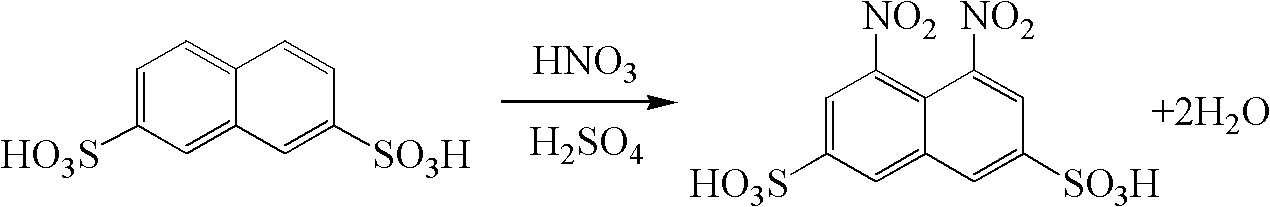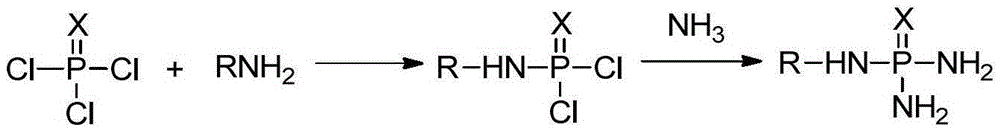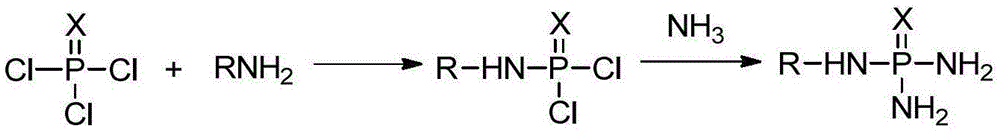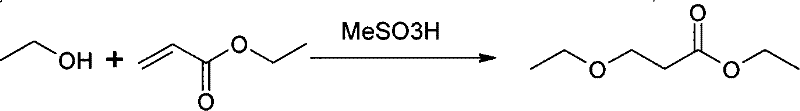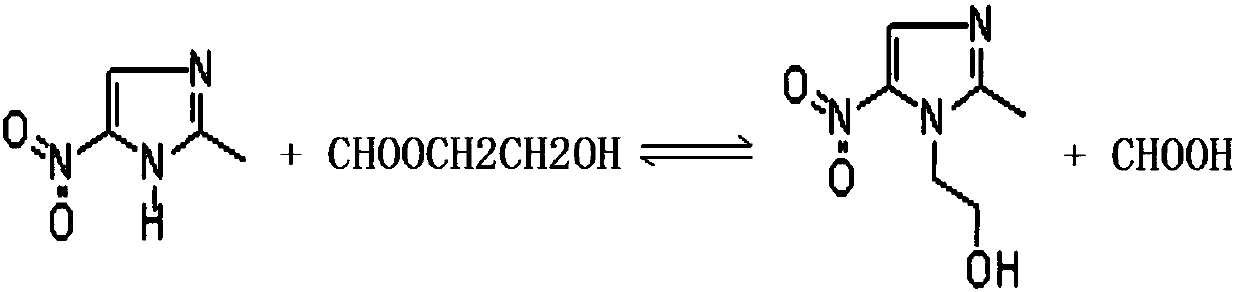Patents
Literature
85results about How to "Implement looping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
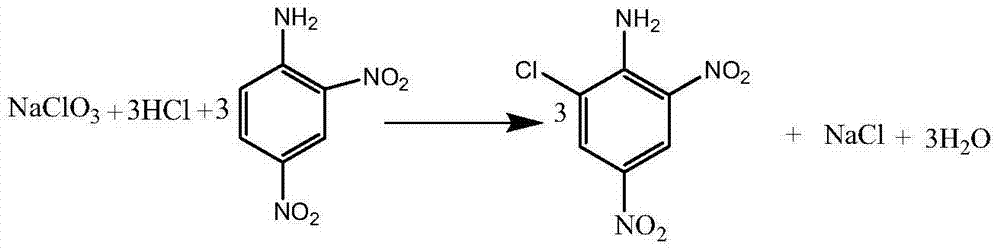
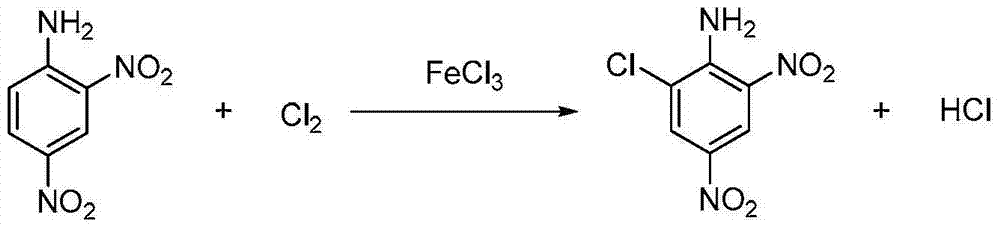
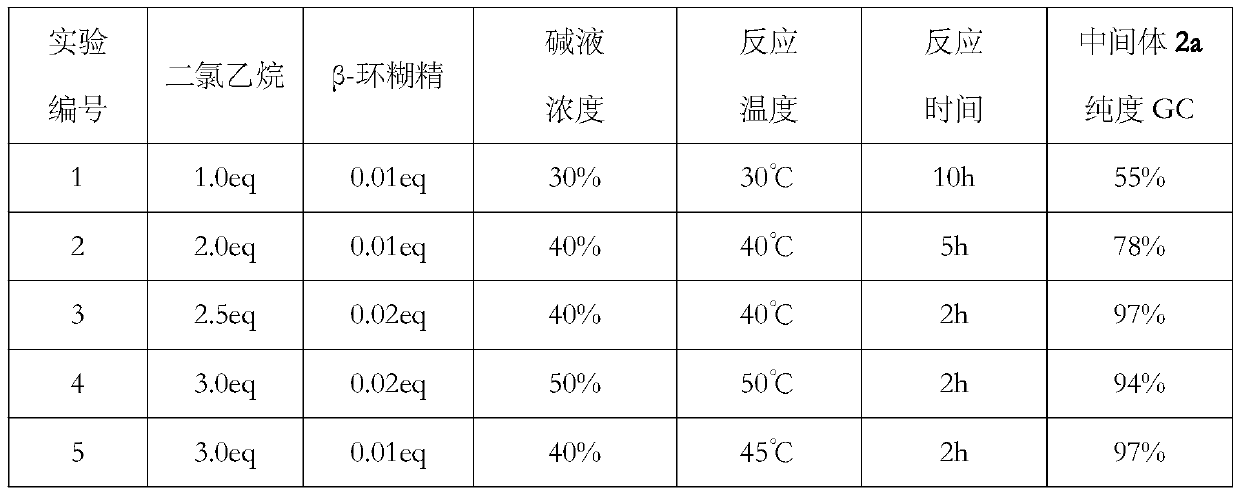
Clean production process of 6-chloro-2,4-dinitroaniline
ActiveCN103539680AFast responseLess side effectsOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationChemistryMother liquor
The invention discloses a clean production process of 6-chloro-2,4-dinitroaniline. The clean production process of 6-chloro-2,4-dinitroaniline comprises the following steps: 1, dispersing 2,4-dinitroaniline into hydrochloric acid solution for pulping, then introducing chlorine gas into the solution for reacting, and thus obtaining intermediate reaction solution; and 2, adding the intermediate reaction solution obtained in the step 1 into sodium chlorate solution for reacting, after the reaction is completed, processing the reaction solution to obtain the 6-chloro-2,4-dinitroaniline and mother solution, and returning the mother solution to the step 1 to serve as the hydrochloric acid solution. According to the production process, the chlorine gas and the sodium chlorate are sequentially employed as chloride agents for chlorinating in steps, so that the product purity and yield are improved and the cost of material is reduced; and the quantity of hydrochloric acid after the reaction is completed is kept stable basically, so that the mother solution is convenient to recycle for use and the pollution to environment is reduced.
Owner:浙江大井化工有限公司
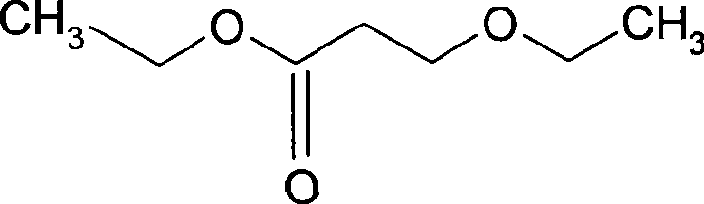
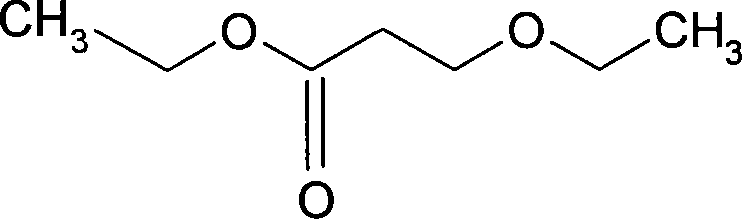
Preparation method of 3-ethoxyl ethyl propionate
ActiveCN101423475AReduce recyclingHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationChemical synthesisDistillation
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical synthesis, and in particular relates to a method for preparing 3-ethoxy ethyl propionate. The method comprises a synthesizing step and a refining step, wherein the synthesizing step adopts ethanol and ethyl acrylate as raw materials to carry out addition under the action of a catalyst, and the catalyst adopts alkali metal or alkali alcoholate. The method has the following advantages: 1, the method adopts one of the raw materials as solvent to react, so as to reduce solvent recovery and consumption in the production process; 2, the reaction catalyst uses basic catalyst such as sodium metal and the like, so as to improve reaction yield greatly; 3, the dosage of the reaction catalyst is reduced to about 2 percent, so as to lower amount of salt greatly after the reaction is finished, and reduce byproducts; 4, the reaction time can be shortened to 3 hours, so as to improve production efficiency; and 5, fore zeolite obtained in distillation can be used for next reaction, so as to achieve circular application, so that the proposal reaches green chemical requirement.
Owner:LINHAI LIANSHENG CHEM
Preparation method of clopidogrel hydrogen sulfate I crystal form spherical crystal
InactiveCN105061459AReduce claddingSimple removal processOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsSolvent2-Butanol
The invention overcomes the technological difficulty that a single solvent is different to prepare a spherical crystal. The single solvent 2-butanol is adopted, and the amount and grain diameters of added clopidogrel hydrogen sulfate I crystal form spherical crystal are controlled, so that clopidogrel hydrogen sulfate is stably separated out from a solution system in a spherical crystal form in a specific powder form range, the obtained clopidogrel hydrogen sulfate spherical crystal has the characteristics of specific powder and has superior state in the aspects of solvent residue, bulk density and mobility, and the preparation method is beneficial for the realization of powder vertical compression preparation technology. The invention also further discloses a medicine composition containing the clopidogrel hydrogen sulfate I crystal form spherical crystal prepared and obtained through the technology.
Owner:SHENZHEN SALUBRIS PHARMA CO LTD +2
Method for preparing methanol and ethanol by methyl acetate by way of hydrogenation
ActiveCN103288594AReduce manufacturing costHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationDistillationGas phase
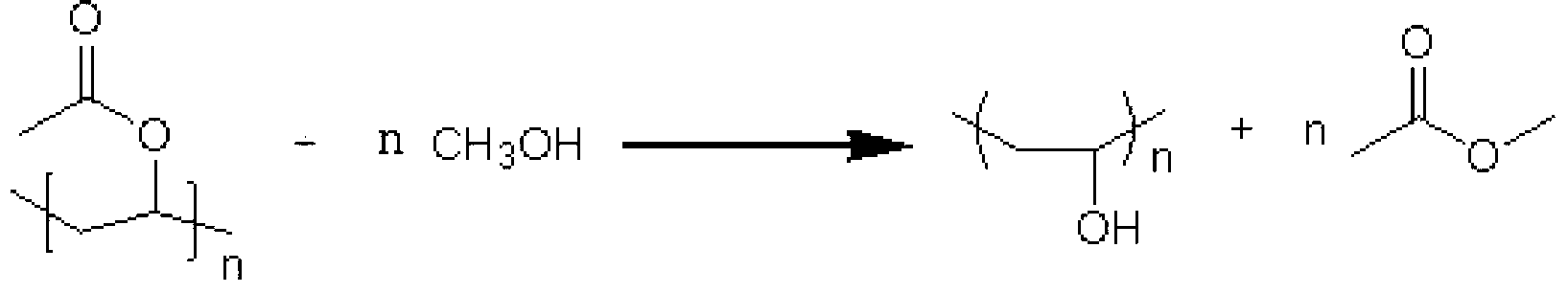
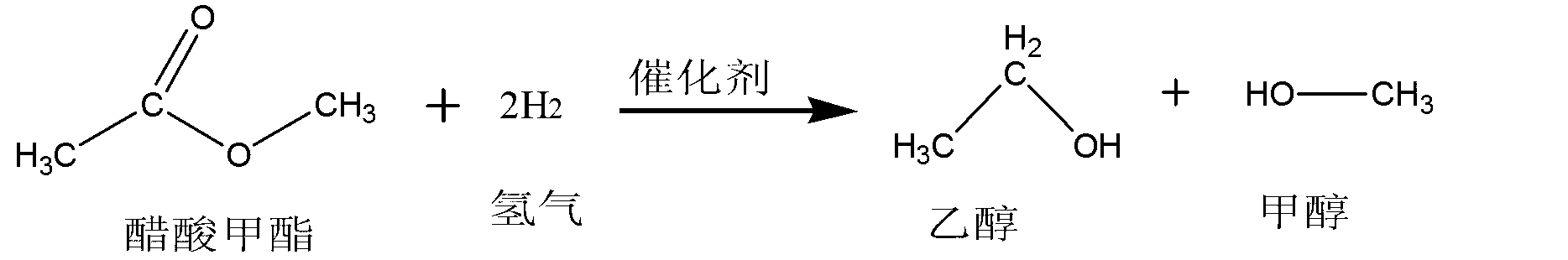
The invention relates to a method for preparing methanol and ethanol by methyl acetate by way of hydrogenation. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the methyl acetate with hydrogen, wherein the mixture enters into a reactor catalyst bed layer, and performing the hydrogenation reduction reaction under the effect of a catalyst, wherein the reaction temperature is 200-260 DEG C, and the reaction pressure is 1.8-3.0MPa; first, cooling the products generated by the hydrogenation reduction reaction and then, distilling to obtain methanol and ethanol. According to the method provided by the invention, methyl acetate with the purity of byproduct of 50-99% for preparing polyvinyl alcohol is directly used as a raw material, so that the method is low in production cost. The catalyst is adopted for hydrogenation reaction on methyl acetate, so that the efficiency is high and the selectivity is high. After reaction, the product does not contain water, and methanol and ethanol can be separated through simple distillation, so that the reaction percent conversion and the product quality are improved. The catalyst is long in service life, and matters obtained by distillation can be used for the next reaction. Mechanical circulation is realized, and the demand of greenness and environment-friendliness is realized.
Owner:LINHAI LIANSHENG CHEM
Method for producing aminoanisole by solvent-free catalytic hydrogenation
InactiveCN106496046AReduce consumptionSolve pollutionOrganic compound preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDistillationReaction temperature
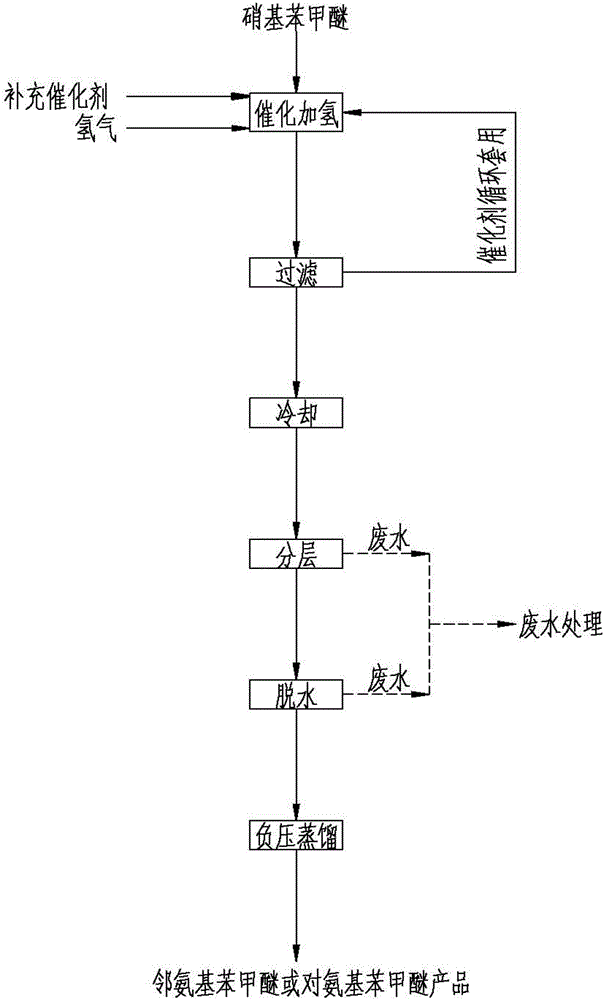
The invention discloses a method for producing aminoanisole by solvent-free catalytic hydrogenation. The method includes the steps: adding nitroanisole and catalysts into a hydrogenation reaction kettle; replacing oxygen with nitrogen in the hydrogenation reaction kettle until oxygen content is lower than or equal to 0.1%, replacing the oxygen with hydrogen until hydrogen content is higher than or equal to 99.0%, starting stirring, increasing temperature to 70+ / -10 DEG C, leading in hydrogen, controlling reaction pressure to be 0.6-1.0Mpa and performing catalytic hydrogenation reaction at the reaction temperature of 80-100 DEG C; finishing reaction, cooling filtered reduction liquid and then conveying the reduction liquid to a reduction liquid separator for automatic layering; conveying layered materials to a dewatering device for normal-pressure or negative-pressure dewatering, and conveying wastewater to a wastewater treatment device; performing negative-pressure distillation separation for the dewatered materials with water content lower than or equal to 0.1% to obtain a target product. Solvents are omitted, a solvent recovery device is omitted, the problems of environmental protection and solvent recovery of methanol solvents are fundamentally solved, equipment investment is saved, production cost is reduced, and equipment capacity is improved.
Owner:连云港泰盛化工有限公司
Method for producing alkyl phosphorus dichloride
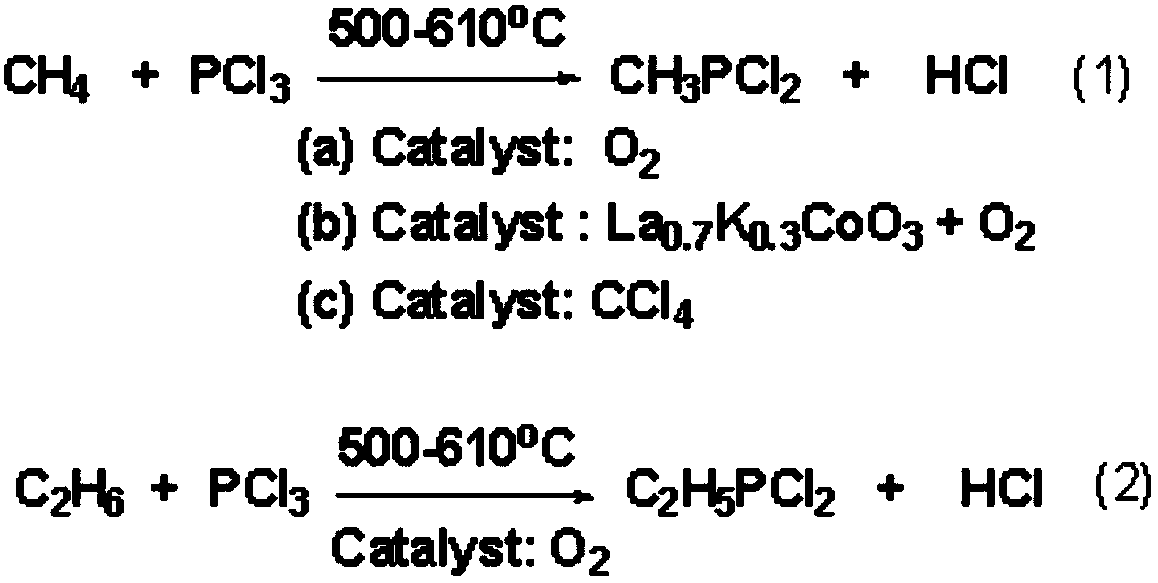
ActiveCN108864190AOvercoming the large amount of three wastesOvercome costsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAlkaneChemical industry
The invention relates to the field of chemical industry and further relates to a production method of an organic phosphorus intermediate, and in particular relates to a method for producing alkyl phosphorus dichloride. The method comprises the following specific step: in the presence of a catalyst, enabling phosphorus trichloride and alkane to react in a tubular reactor under high temperature andhigh pressure, so as to generate the alkyl phosphorus dichloride, wherein the alkane is selected from one or two of methane and ethane and the catalyst is selected from one or two of chloroform and dichloromethane. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of low production cost, great industrial feasibility, measurable and controllable technological conditions, high reaction conversion rate and selectivity, good product quality and the like.
Owner:HEBEI VEYONG BIO CHEM
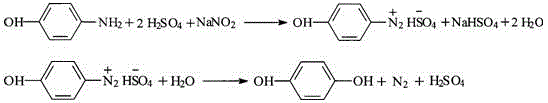
Hydrolysis process for hydroquinone
InactiveCN102746122AMake up for the disadvantage of high priceRealize cleaner productionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationP-AminophenolReaction temperature
The invention discloses a hydrolysis process for hydroquinone and relates to a hydrolysis process during hydroquinone synthesis by subjecting p-aminophenol to diazotization and hydrolysis processes. The process includes: adding basic cupric carbonate, cupric sulfate and solvents into a hydrolysis reaction kettle, dropwise adding diazonium solution of 0+ / -0.5 DEG C obtained by subjecting sodium nitrite and dilute sulfuric acid to diazotization and performing hydrolysis reaction at a reaction temperature of 85 DEG C-88 DEG C. Raffinate phase does not generate waste acid, and the copper recovery rate reaches to more than 99.5%, so that a disadvantage of high copper price is made up; and sodium sulfate is obtained by means of concentration and crystallization of filtrate, concentrated water is used for preparing acid for diazo reaction, and crystallized mother solution of the sodium sulfate is used for preparing cupric sulfate solution for hydrolysis, so that clean production is realized.
Owner:JIANGSU YANGNONG CHEM GROUP +1
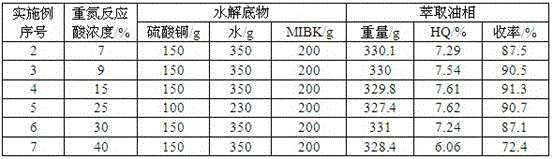
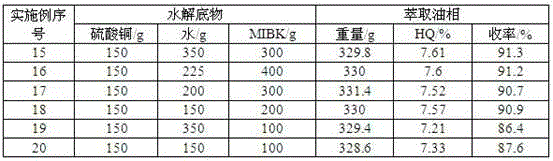
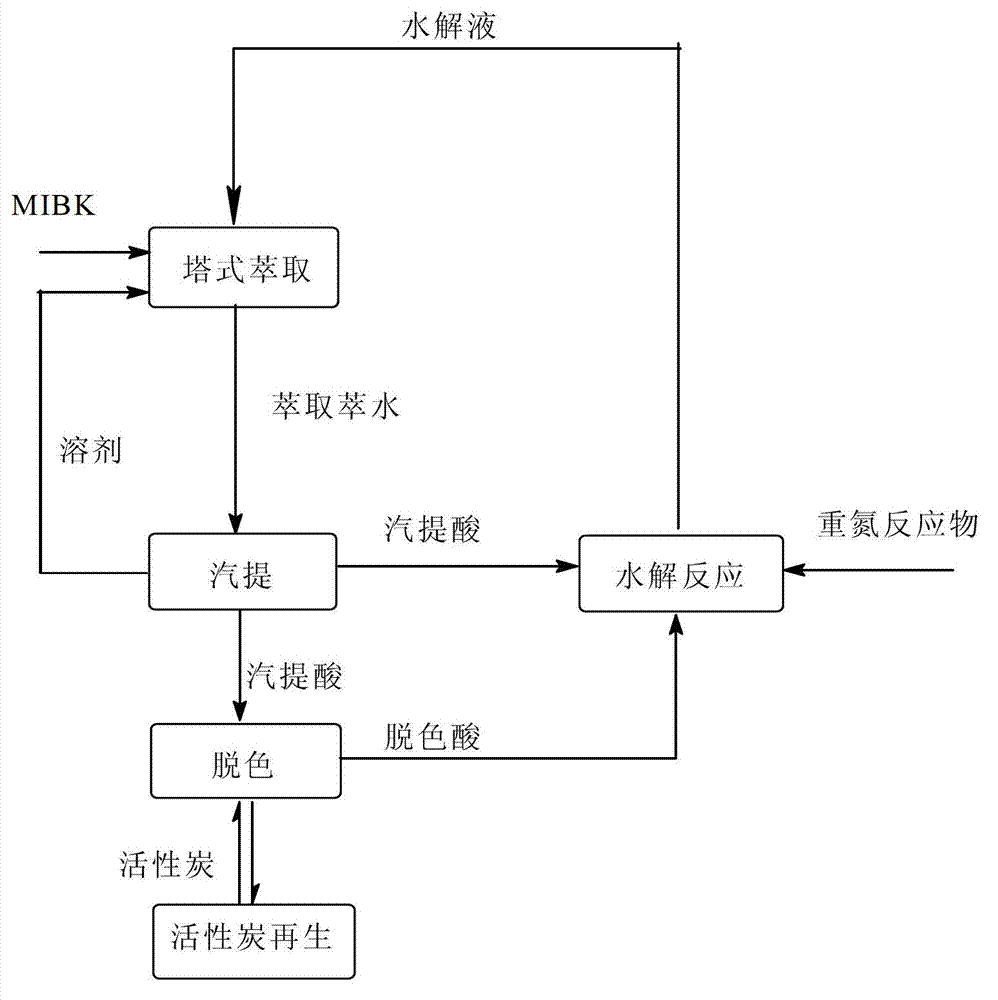
Cycling treatment method for waste acid produced in production of hydroquinone
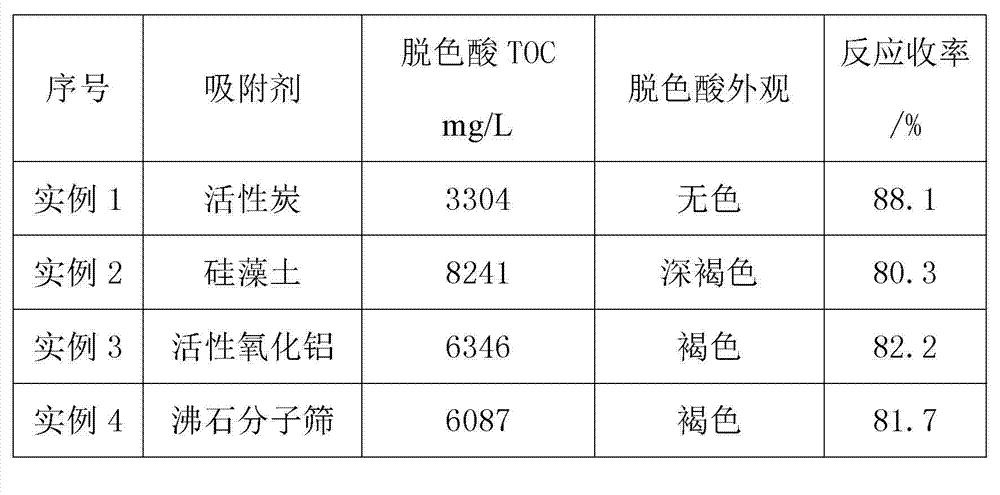
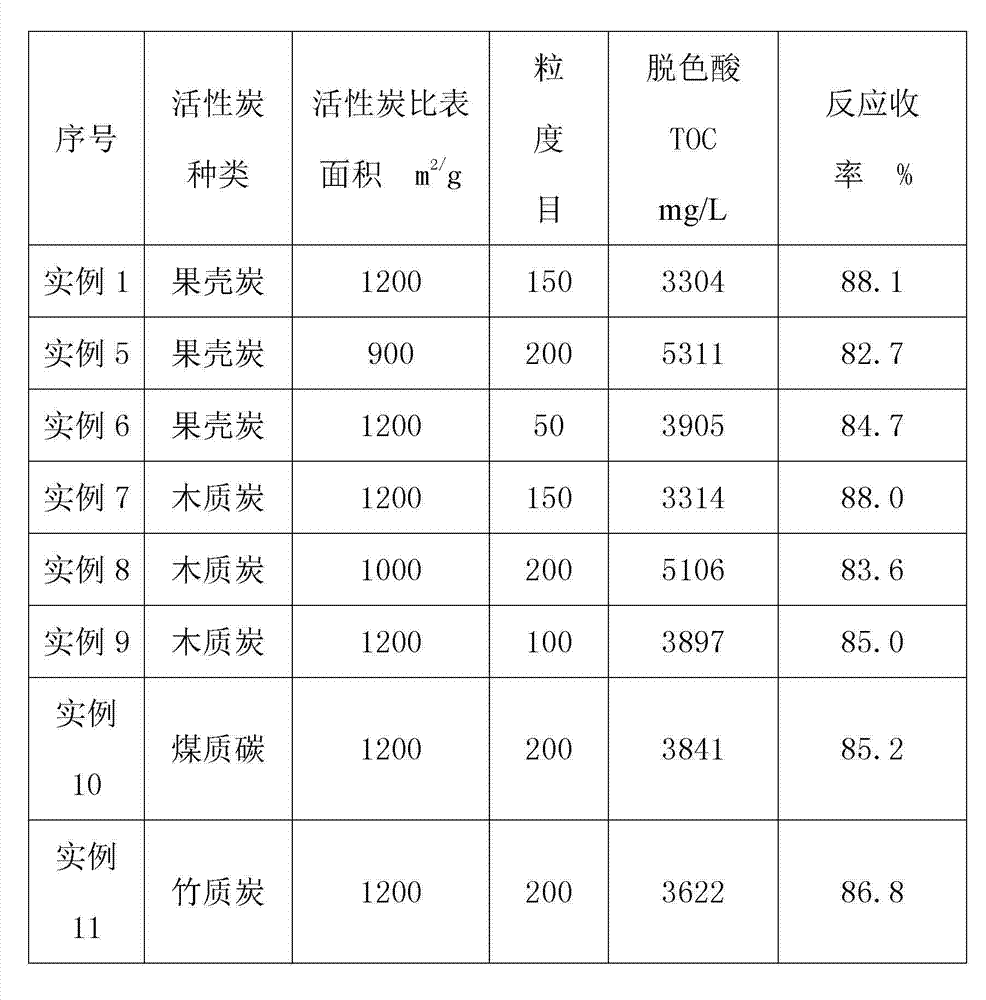
InactiveCN102826961AImplement loopingReduce consumptionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationHydrolysateSorbent
The invention relates to a cycling treatment method for waste acid produced in production of hydroquinone. The method comprises the following steps: (1) an extraction reaction: a step of allowing temperature to drop to 40 to 60 DEG C after a hydrolysis reaction in the synthesis process of hydroquinone is finished and adding an extracting agent into hydrolysate for extraction; (2) steam stripping: a step of putting a water layer obtained after extraction into a stripping vessel and carrying out stirring and heating, wherein a final temperature of steam stripping is 110 to 112 DEG C and the content of the extracting agent in stripping acid after steam stripping is lower than 1 wt%; (3) decoking and decolouring: a step of adding 50 wt% of the stripping acid and an adsorbent into a decolouring kettle, carrying out decoking and decolouring at a temperature of 100 DEG C, putting a reaction solution into a filter press for filtering after a reaction is ended so as to obtain decoloured acid and the recovered adsorbent, and merging and standing the decoloured acid and rest stripping acid for a next hydrolysis reaction; and (4) washing and recovery: putting water into the filter press to cyclically wash the recovered adsorbent so as to recover hydroquinone adsorbed by the adsorbent, subjecting the adsorbent to regeneration treatment with a solvent and adding the treated adsorbent into step (3) for cyclic usage.
Owner:JIANGSU YANGNONG CHEM GROUP +1
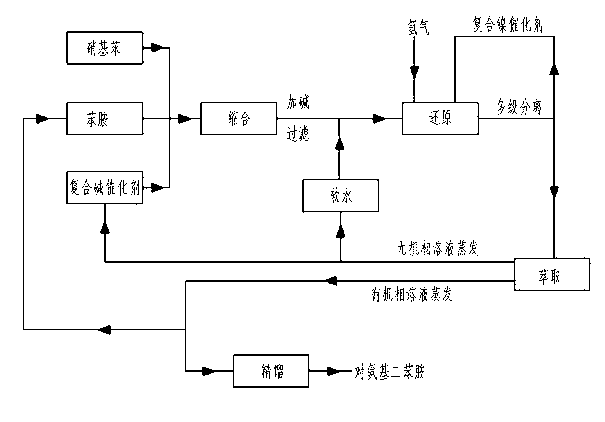
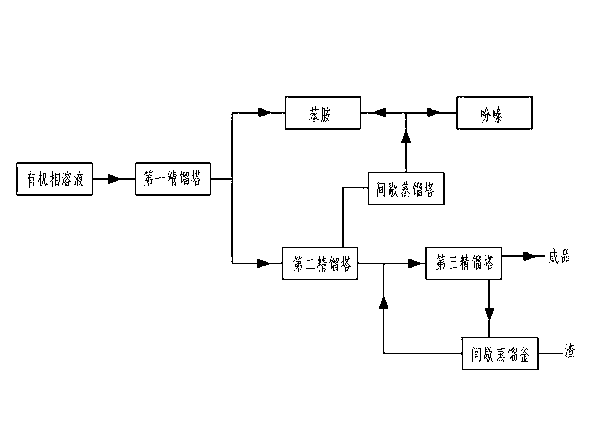
Preparation method for p-aminodiphenylamine
InactiveCN102796011AImprove continuityReduce operating unitAmino compound purification/separationOrganic compound preparationNickel catalystHydrogen
The invention relates to a preparation method for p-aminodiphenylamine, and belongs to the technical field of industrial preparation for p-aminodiphenylamine. The technical problem to-be-solved is to provide a preparation method for p-aminodiphenylamine with a condensation reaction catalyst capable of being activated and reused and a reduction reaction solvent having no danger and being easily separated. The technical solution adopted includes: a first step of feeding nitrobenzene, aniline and a complex alkali catalyst into a reactor for a condensation reaction to generate a condensation liquid; a second step of adding alkali to form salt to get a qualified condensation liquid; a third step of adding soft water and composite nickel catalyst slurry, and feeding hydrogen to perform a reduction reaction to get a reduction liquid; a fourth step of extracting and distilling the reduction liquid to get a rectification raw material; and a fifth step of performing a multi-stage rectification for the rectification raw material to get the finished p-aminodiphenylamine. The method can be widely applied to the field of p-aminodiphenylamine preparation.
Owner:山西翔宇化工有限公司
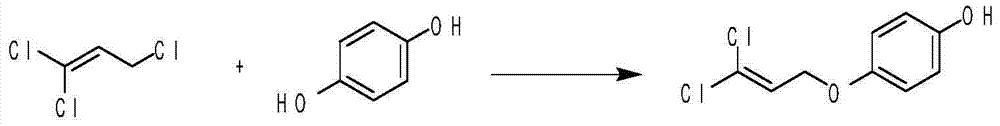
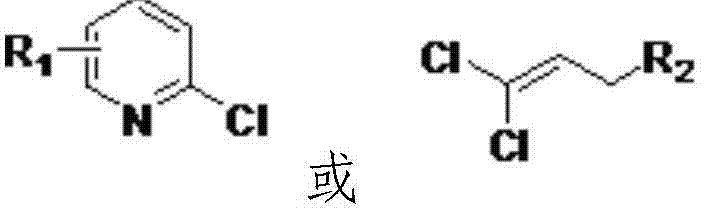
Method for preparing 4-substituted oxyphenol compound
ActiveCN104744352AHigh purityHigh selectivityEther preparation by ester reactionsHalogenOrganic synthesis
The invention belongs to the field of organic synthesis, and relates to a method for preparing a 4-substituted oxyphenol compound. The method comprising the following steps: condensing hydroquinone and a halogen compound in a polar aprotic solvent in a reducing agent and metal alkali system to obtain the 4-substituted oxyphenol compound; removing the solvent after the above reaction, adding a non-polar solvent, filtering, washing, and recovering the raw material hydroquinone; and washing the obtained filtrate through using water, extracting by using an alkaline solution, and adjusting the pH value of the obtained extract solution to obtain the 4-substituted oxyphenol compound. The method has the advantages of short route, simple operation, high selectivity, high yield, good atom economy, high product content, recovery convenience and recycling of the raw material, reduction of three wastes and the cost, and suitableness for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGHUA TECH CO LTD
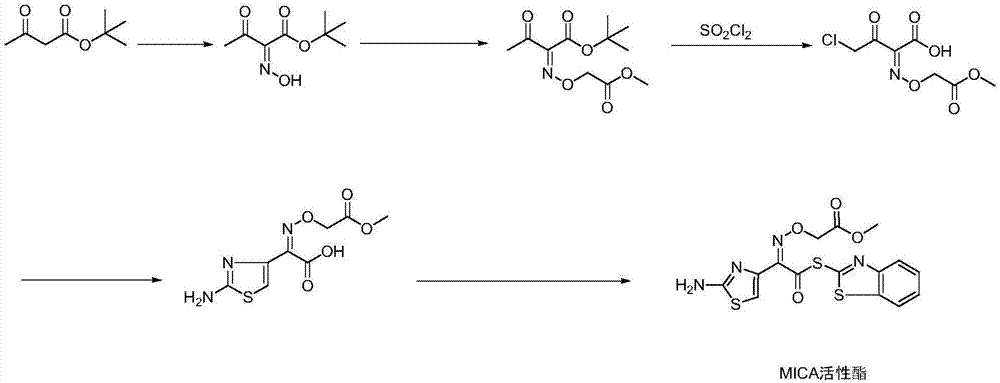
Environmental friendly production method of MICA active ester
The invention discloses an environmental friendly production method of a MICA active ester. The environmental friendly production method comprises the following steps: oximating, alkylating, chloridizing, cyclizing, and preparing an intermediate. The production method realizes the recycling of the materials, so that the cost is lowered, and the amount of produced wastes and wastewater is reduced; sodium acetate, a byproduct, is recrystallized in the S1 and used for cyclization in the S4, so that the amount of wastewater and the salt content of the waste water are reduced; the conventional process generally uses potassium carbonate to provide an alkaline environment in the S2, the use amount of the potassium carbonate is generally more than 2 equivalent weights, the defects are as follows: 1, the stirring is strenuous if the slat content is too high in the reaction process; 2, a large quantity of water is needed in the later processing to dissolve an inorganic salt, then a large quantity of high salt content wastewater is produced, but the amount of solid salt is greatly reduced in the reaction process after an organic alkali is used, the organic alkali is recycled in the later processing, and the cost and the amount of wastewater are reduced; a batch feeding mode is used in the S3, so that the use amount of sulfonyl chloride is reduced at the same conversion rate; 2-mercaptobenzothiazole, a byproduct produced in the reaction, is recycled in the S5, and is recycled again so as to be used in the synthesis of diphenyl thiazole disulfide.
Owner:济南美高生物医药科技有限公司
One-pot ceftazidime side-chain acid ethyl ester synthesis method
The invention relates to a preparation method of a pharmaceutical intermediate, in particular to a one-pot ceftazidime side-chain acid ethyl ester synthesis method. The method comprises the following steps that 1, ethyl 4-bromoacetoacetate is dissolved in water, a sodium nitrite water solution and 15%-25% of sulfuric acid are added dropwise, heat preservation reaction is performed after adding is completed dropwise, extraction is performed after the reaction is completed, the extracting solution is washed with a saturated potassium or sodium carbonate solution, and distillation is performed to obtain an oximation solution; 2, thiourea is added into a water and methanol mixed solution, and then the oximation solution is added dropwise to obtain an ethyl 2-(2-aminothiazole-4-yl)-2-hydroxyiminoacetate solution; 3, the pH of the ethyl 2-(2-aminothiazole-4-yl)-2-hydroxyiminoacetate solution is regulated, then tert-butyl alpha-bromoisobutyrate and a phase transfer catalyst are added for heat preservation reaction, and after the reaction is completed, cooling and suction filter are performed to obtain the ceftazidime side-chain acid ethyl ester. The simple processing of the product is simple, the purity and the yield are high, and the yield is up to 96.5% or above.
Owner:SHANDONG JINCHENG PHARMACCUTICAL CHEM CO LTD
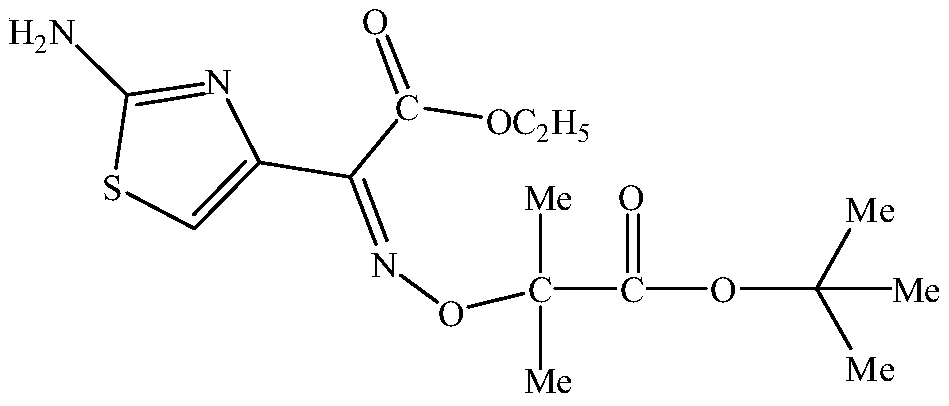
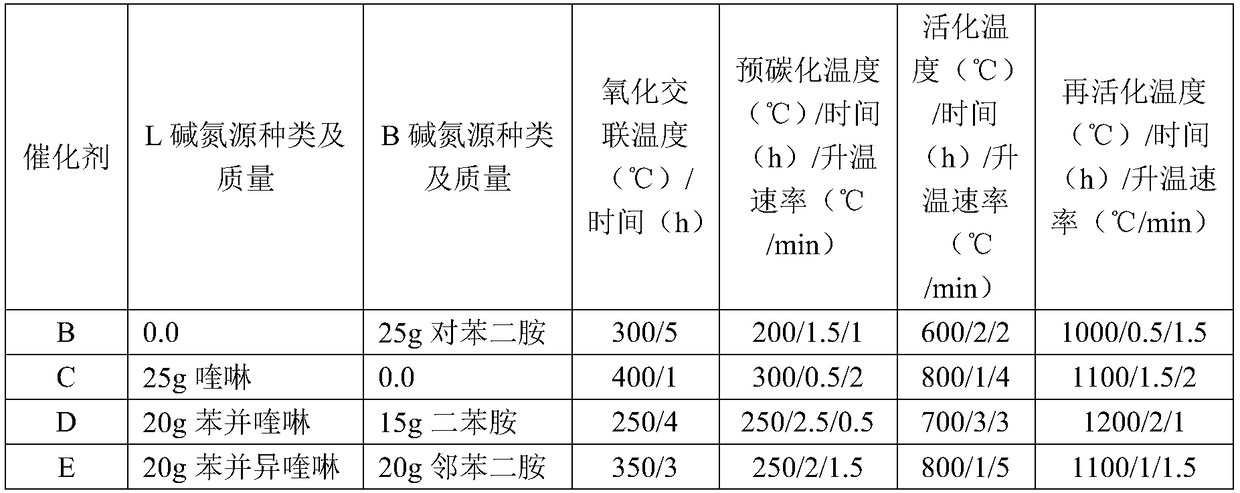
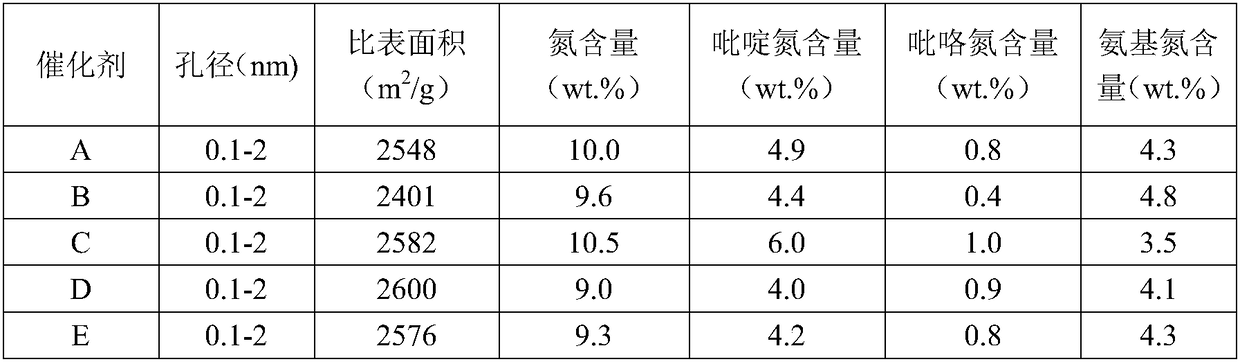
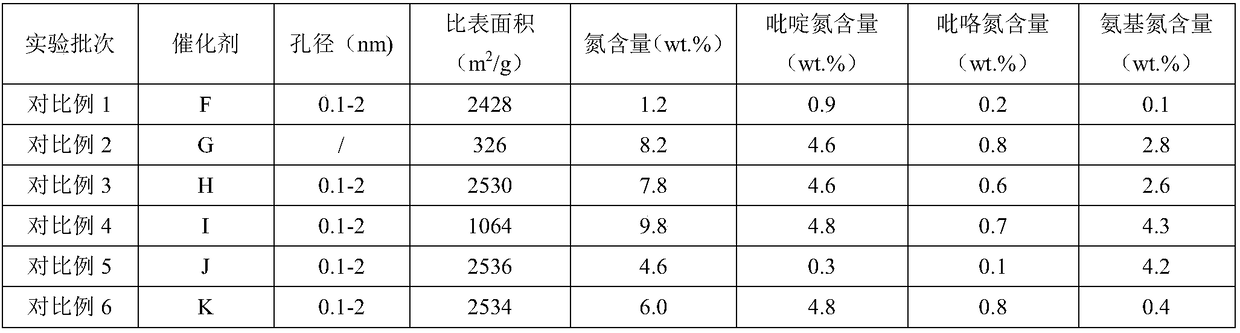
Nitrogen-doped porous carbon catalyst, preparation method of catalyst and preparation method of beta-isophorone
ActiveCN108579790AHigh value-added utilizationIncrease steric hindrancePhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationIsomerizationPorous carbon
The invention discloses a nitrogen-doped porous carbon catalyst, a preparation method of the catalyst and a preparation method of beta-isophorone. With coal-tar pitch as a raw material, the novel nitrogen-doped porous carbon catalyst containing L base and B base is prepared through the processes of oxidative crosslinking, pre-carbonization, activation and reactivation. The catalyst is used for preparing 3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-3-alkene-1-ketone through an isomerization reaction of 3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-3-alkene-2-ketone. The selectivity of the isomerization reaction reaches 99.6-99.9%. The preparation method has the advantages that the catalyst is easy to recycle, high in conversion rate and selectivity, environmentally friendly, high in space-time yield, capable of causing no corrosionto equipment and the like, and the high-additional-value utilization of coal resources is achieved.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
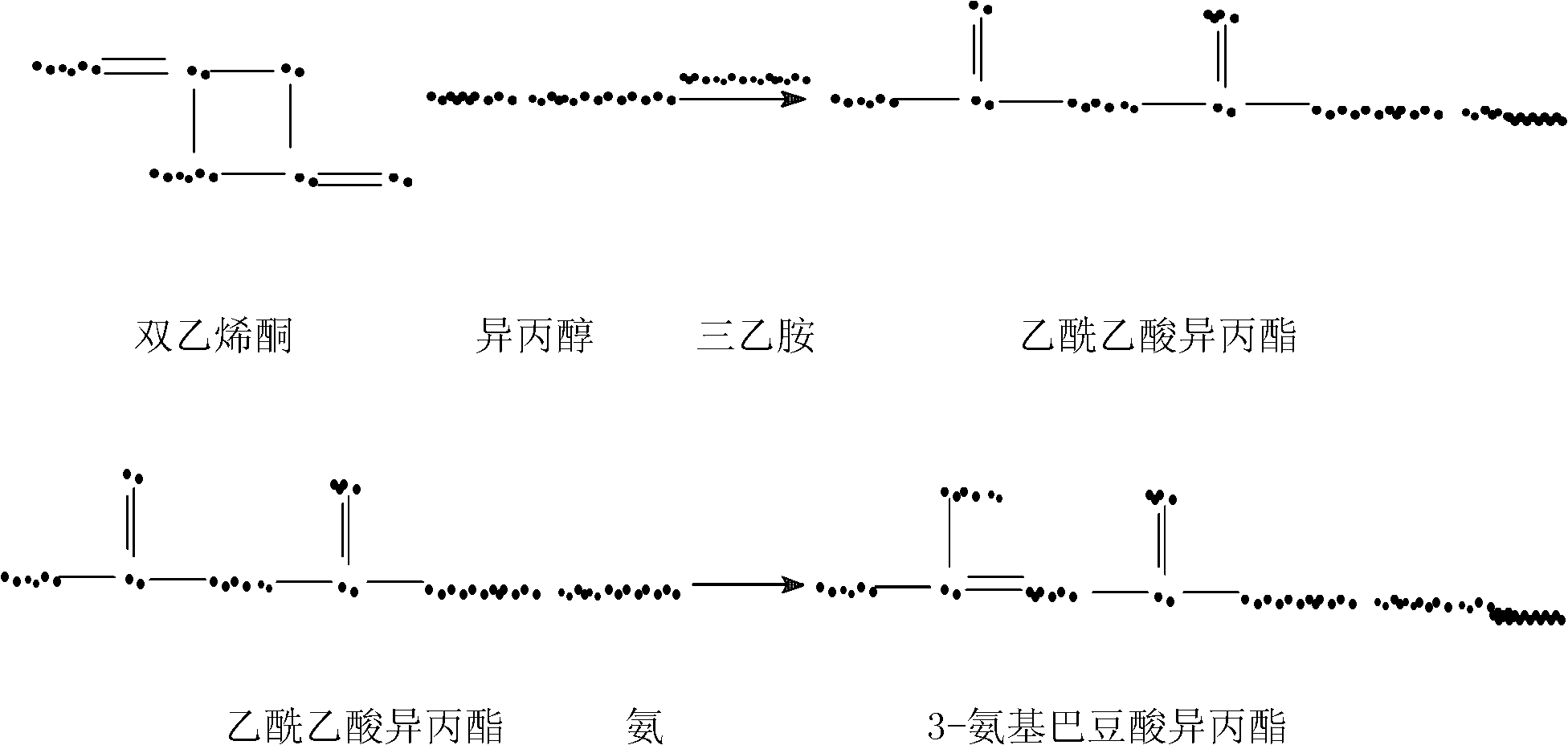
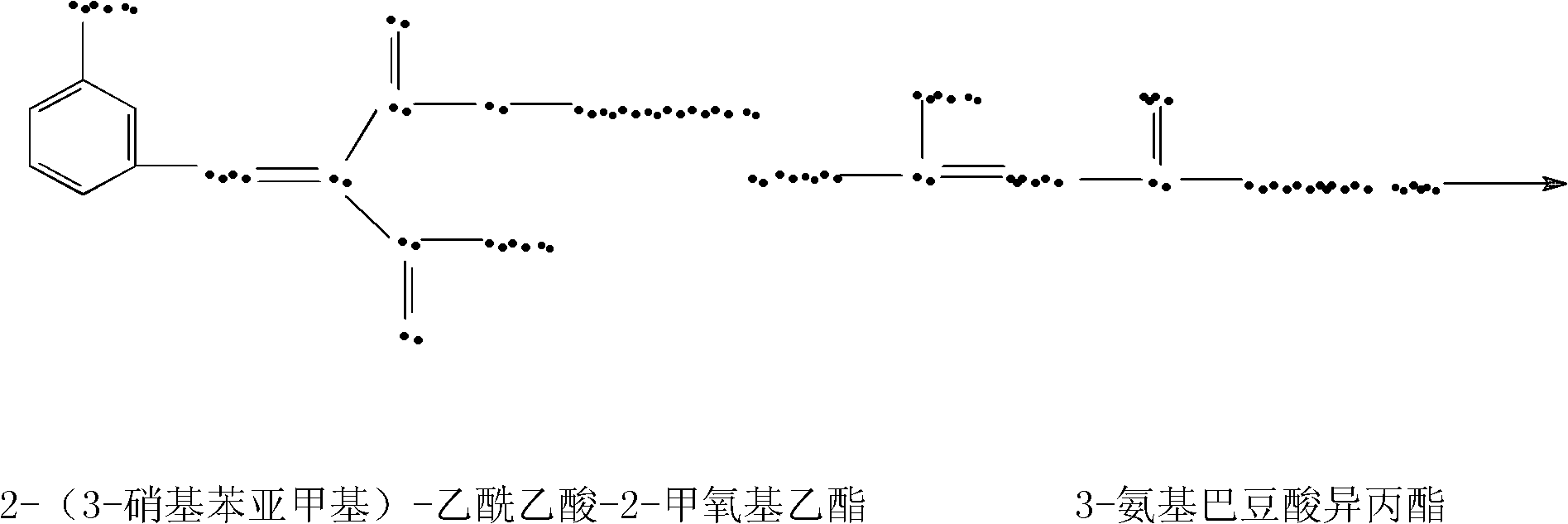
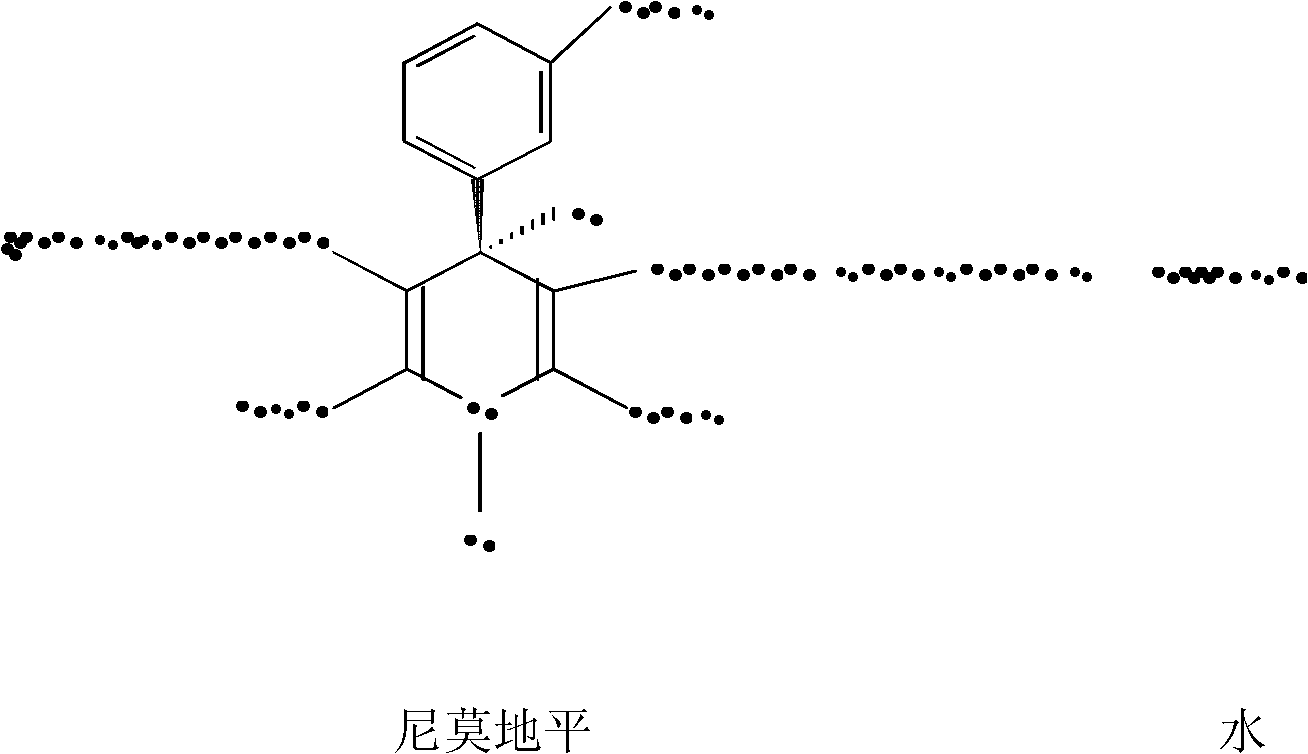
Preparation method of nimodipine
ActiveCN102174012AReduce hydrolysis reactionIncrease contentOrganic chemistryAcetic acidInorganic salts
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmacy, and in particular relates to a preparation method of nimodipine, comprising urethane reaction and cyclization reaction, wherein in the urethane reaction, after ammonia introducing reaction, adding an inorganic salt for dewatering the urethane reaction liquid, then rectifying to obtain isopropyl-3-aminocrotonate; and performing cyclization reaction with 2-(3-nitrobenzylidene)-acetoacetic acid-2-methoxyethyl ester by taking fatty alcohol as a reaction solvent. The invention has the advantages of high product yield and good quality, the primary yield can reach 85-89%, the solvent can be recovered for use, the raw material cost can be greatly reduced, and the content of total impurities is decreased from 0.4-1.0% of the original process to 0.1-0.3% by HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) detection.
Owner:SHANDONG XINHUA PHARMA CO LTD
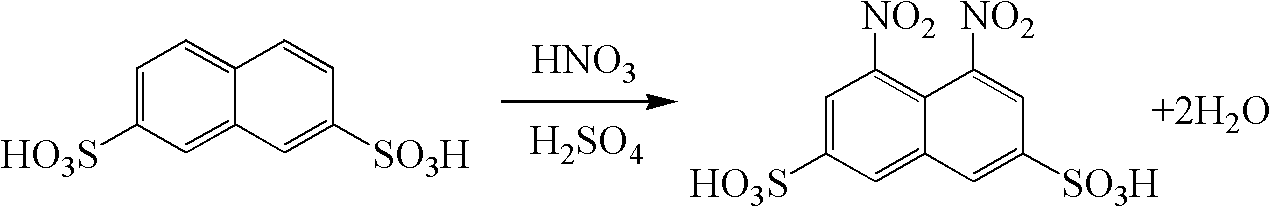
Clean preparation method of 1, 8-dinitro-3, 6-naphthalenedisulfonic acid
ActiveCN102936213ASolve the emission problemImplement loopingSulfonic acid preparationFlocculationWastewater
The invention provides a clean preparation method of 1, 8-dinitro-3, 6-naphthalenedisulfonic acid. A reaction formula is shown in the description. The method includes: taking 2, 7-naphthalenedisulfonic acid as a reaction raw material, adopting sulfuric acid as a solvent, and adding fuming nitric acid with a content of 98% dropwisely to prepare 1, 8-dinitro-3, 6-naphthalenedisulfonic acid; and after the end of the reaction, adding water to conduct dilution and isolating the product, subjecting the remaining nitrification mother solution to flocculation treatment so as to remove impurities, and then carrying out pressure reduction concentrating to recover the sulfuric acid as the solvent for next reaction. The method provided in the invention has the advantages of short technological process, simple operation, good quality product, and no wastewater discharge, thus being suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:中国中化股份有限公司 +1
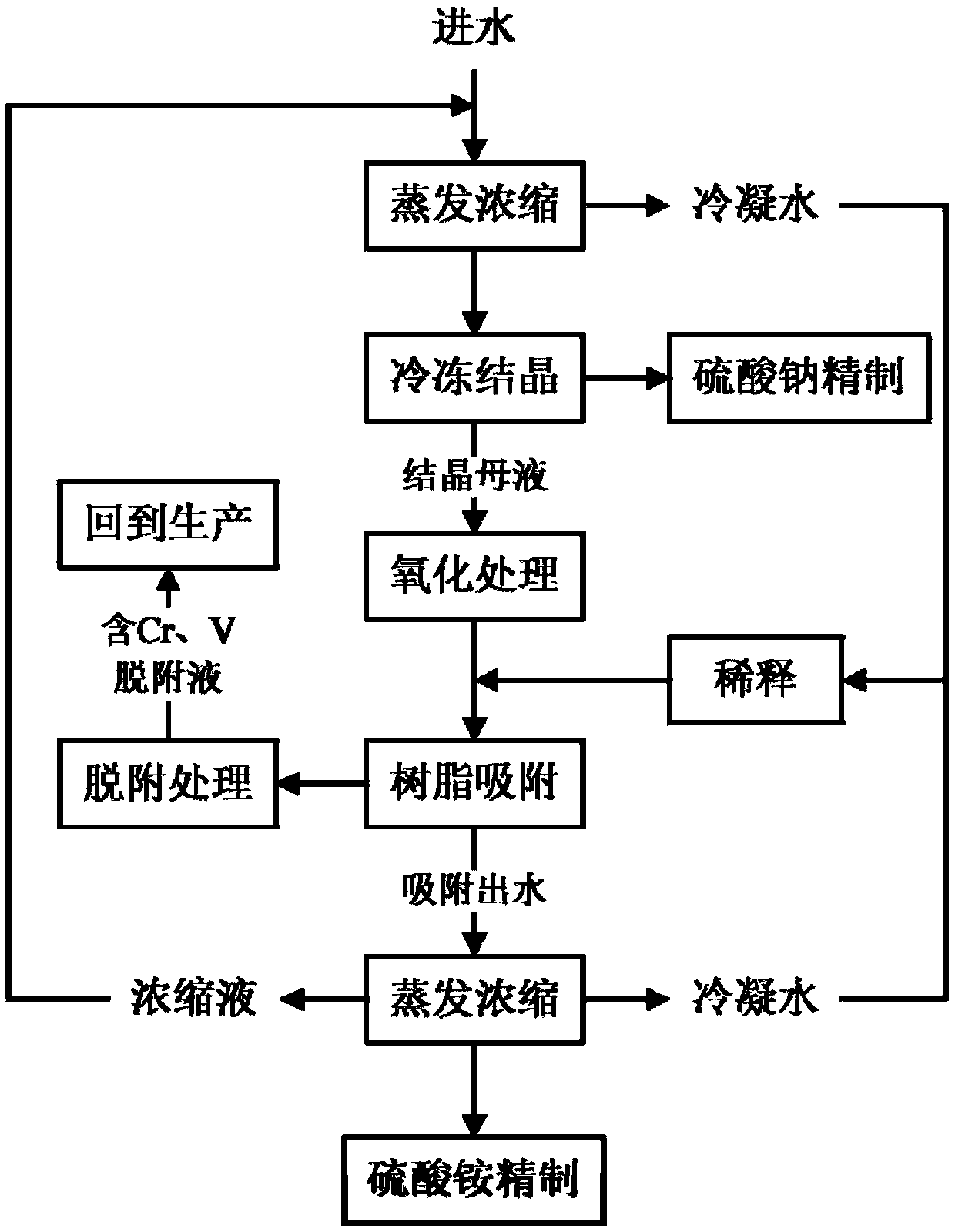
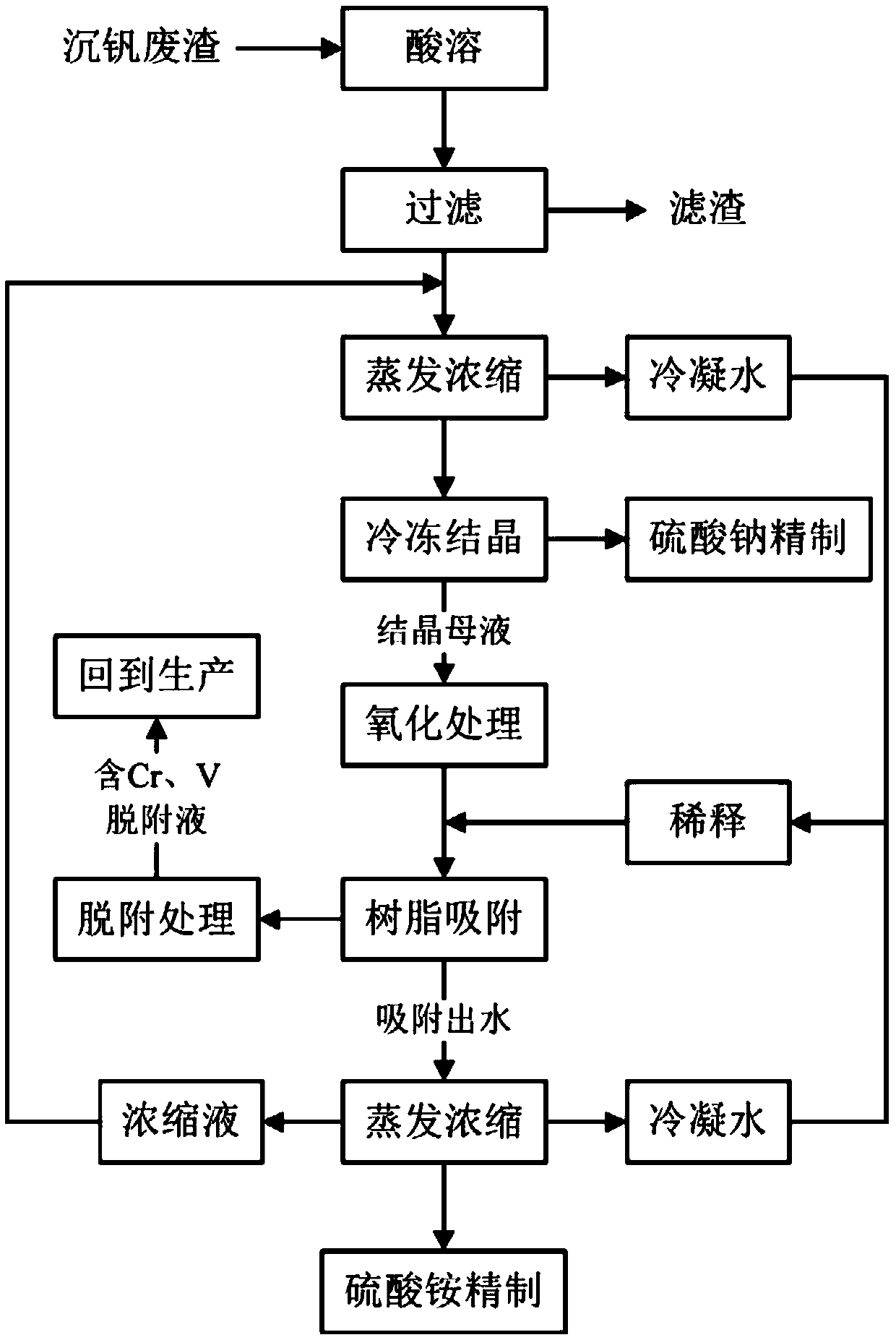
Method for processing high salinity wastewater containing chromium and vanadium and method for processing precipitated vanadium slag
InactiveCN109650406AHigh purityIncrease in sizeAmmonium sulfatesProcess efficiency improvementDesorptionHazardous substance
The invention discloses a method for processing high salinity wastewater containing chromium and vanadium and a method for processing precipitated vanadium slag, and belongs to the technical field ofwastewater processing. The wastewater processing method comprises following steps: evaporating and concentrating chromium-vanadium containing high salinity wastewater to a certain ratio, collecting the condensing water; freezing and crystallizing the concentrated mother liquor to obtain coarse sodium sulfate, then refining coarse sodium sulfate; preprocessing obtained crystallized mother liquor byan oxidizing agent so that chromium and vanadium exist in the solution in an anion state; mixing the condensing water with oxidized crystallized mother liquor, making the mixed solution go through resin to absorb chromium and vanadium; after desorption, applying the chromium-vanadium containing desorption liquor to production; evaporating and concentrating effluent from the resin to obtain coarseammonium sulfate, refining coarse ammonium sulfate to obtain solid ammonium sulfate; mixing the concentrate with water introduced into the system, and processing the solution in cycle. The provided wastewater processing method can reduce the discharge of harmful substances, sodium sulfate can be recovered, and the chromium, vanadium and ammonium sulfate are recycled.
Owner:JIANGSU NJU ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Preparation method of beta-phenylethyl alcohol
ActiveCN107089900AHigh activityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOil phaseHigh activity
The invention provides a preparation method of beta-phenylethyl alcohol. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding a catalyst, water and benzyl alcohol, introducing mixed gas of CO and H2, and reacting. The catalyst has high activity and selectivity, conversion ratio of the benzyl alcohol is more than 50%, and the total selectivity of beta-phenylethyl alcohol and phenylacetaldehyde is more than 90%. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages that a water soluble complex catalyst formed by water soluble ruthenium and rhodium metal salts and a water soluble ligand is used for carrying out homologation on the benzyl alcohol in a water-oil two-phase system, and better activity and selectivity can be obtained compared with the traditional cobalt-ruthenium homogeneous catalysis system; water and oil phases react, aftertreatment is convenient, a water-phase catalyst can be recycled, environment friendliness is realized, and fewer three wastes are discharged.
Owner:SHANDONG NHU PHARMA
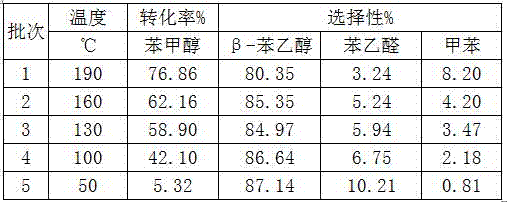
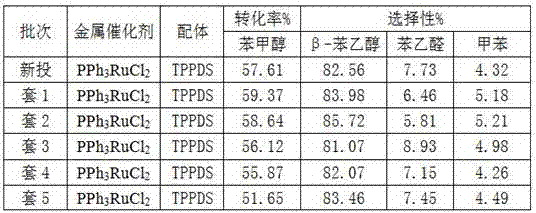
Production method of N-alkyl substituted phosphoric triamide
ActiveCN105399767AImprove mass transfer efficiencyFast responseGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphoric acidLiquid ammonia
The invention relates to a production method of N-alkyl substituted phosphoric triamide. In an organic solvent, liquid ammonia reacts with alkyl amino phosphorodichloridate. The production method further comprises steps as follows: (1), phosphoric trichloride and alkyl primary amine react in the presence of the organic solvent and an acid-binding agent, and alkyl amino phosphorodichloridate is generated; (2), a reaction liquid in the step (1) directly reacts with the liquid ammonia, temperature returning is performed, and N-alkyl substituted phosphoric triamide is generated. The liquid ammonia is preferably added in the step (2), and a reaction liquid in the step (1) is added for a reaction. According to the production method, a procedure can be intermittent or continuous, an intermediate is not required to be purified, the reaction condition is mild, few byproducts are produced, the yield is good, the purity is high, and the production method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:江西吉翔医药化工有限公司
Composite catalyst, preparation method thereof and application thereof in citral synthesis
PendingCN112058313AHigh catalytic activityImprove space effectOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemistryHigh activity
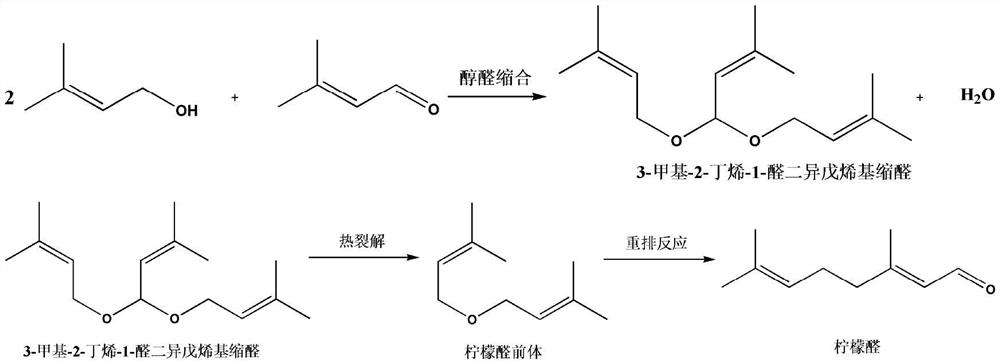
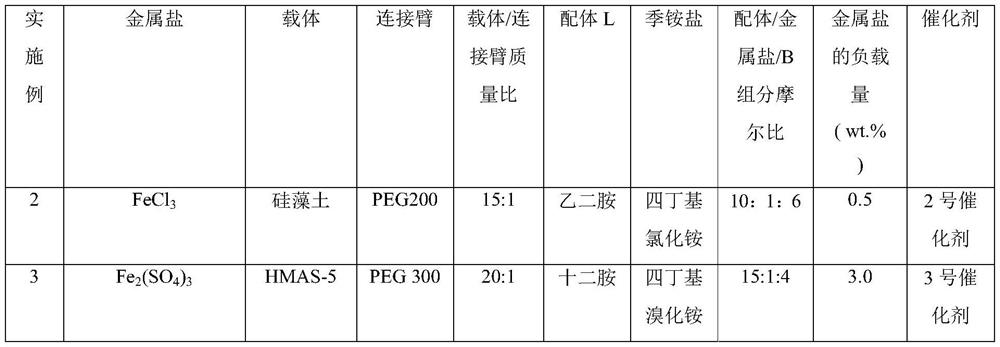
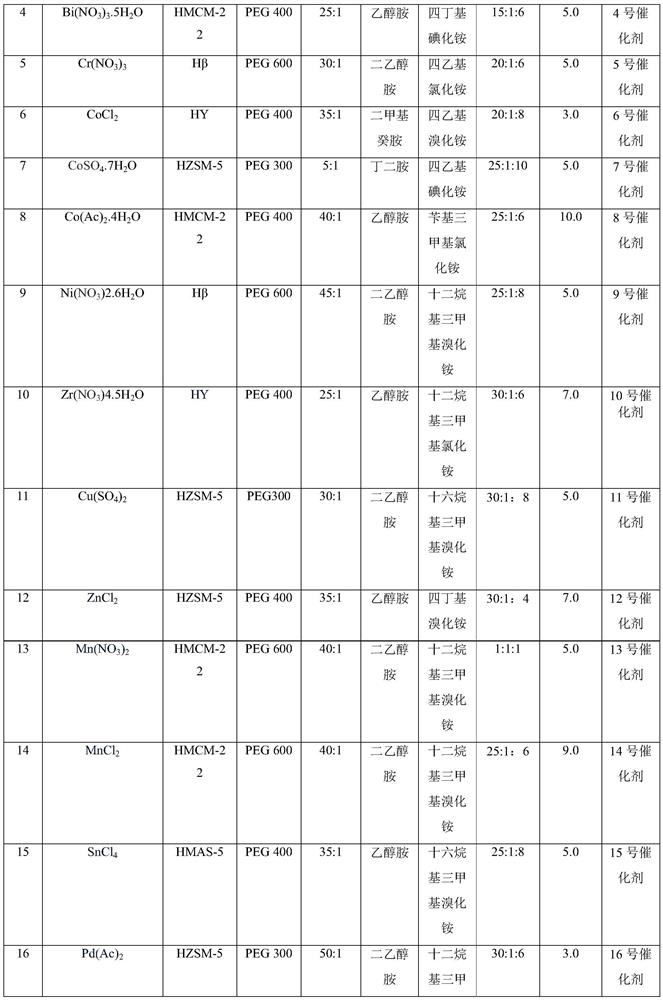
The invention discloses a composite catalyst, a preparation method thereof and an application of the composite catalyst in citral synthesis, the catalyst comprises a loading component and a carrier, and the loading component comprises an active component and other components; the active component is metal salt; the other components comprise a connecting arm R, a ligand L and a component B; in thepresence of the composite catalyst, isopentenal and isopentenol are subjected to alcohol-aldehyde condensation, thermal cracking and rearrangement reaction to synthesize citral with high activity andhigh selectivity, and the catalyst does not need to be replaced in the reaction process. The catalyst provided by the invention improves the selectivity of the product, can obtain higher yield, avoidsthe problem of equipment corrosion, prolongs the service life of the equipment, has obvious environmental protection benefits, is environment-friendly, and is beneficial to industrial mass production.
Owner:SHANDONG NHU PHARMA
Separation method of aldehyde/alcohol mixture
ActiveCN107417507AEfficient separationImplement loopingOrganic compound preparationChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsLiquid wasteThird party
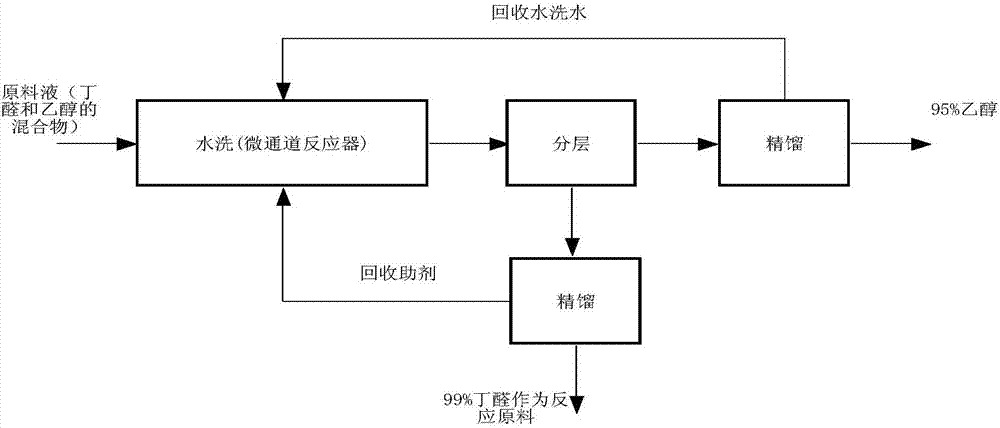
The invention relates to a separation method of an aldehyde / alcohol mixture. The invention provides the solving scheme as follows: a butyraldehyde / ethyl alcohol mixed solution is taken as a raw material; butyraldehyde is effectively separated from ethyl alcohol by adopting a corning G1 microchannel reactor through a process of adding a third-party assistant for washing, and the butyraldehyde with the content of 99% and industrial ethyl alcohol with the content of 95% are finally obtained, and therefore, resource utilization of a liquid waste is achieved, so that the butyraldehyde can be recycled and the raw material cost is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU YANGNONG CHEM GROUP +2
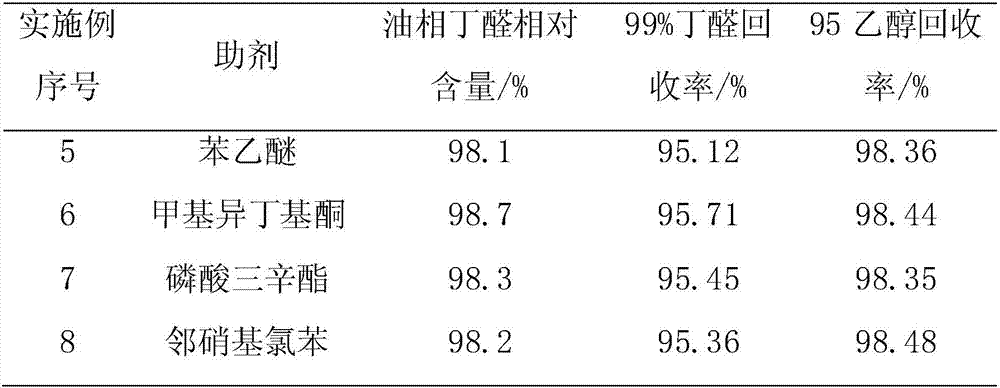
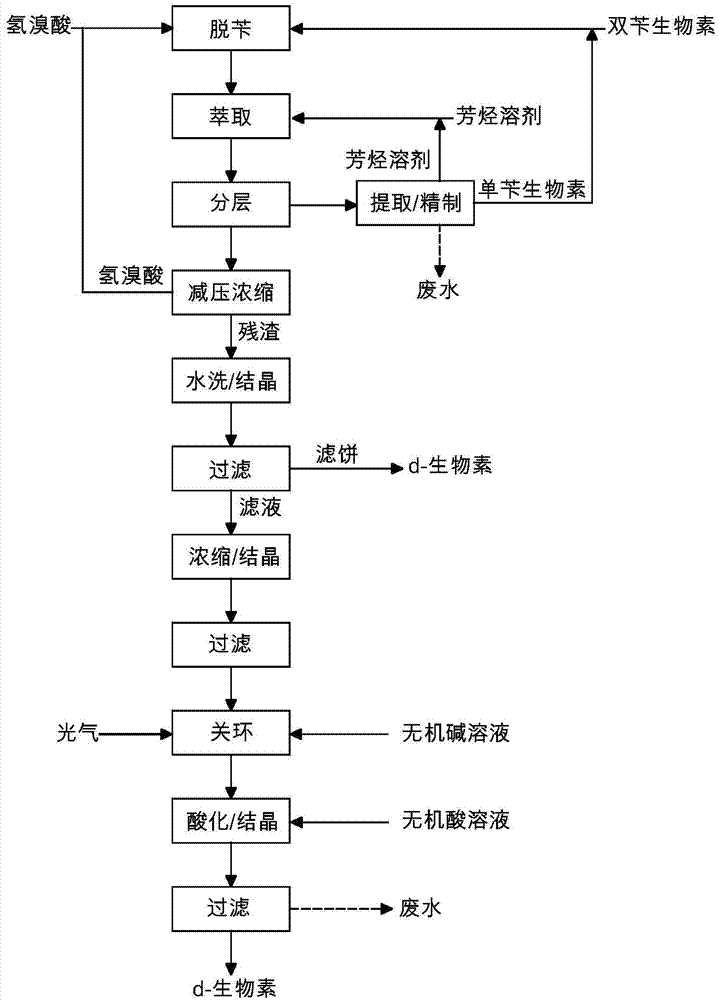
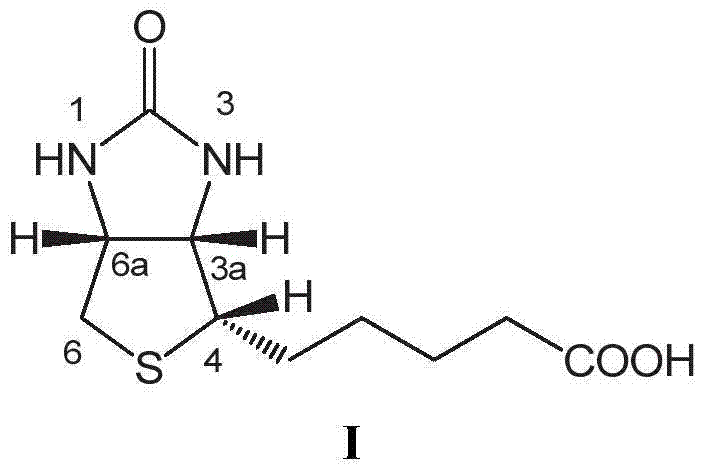
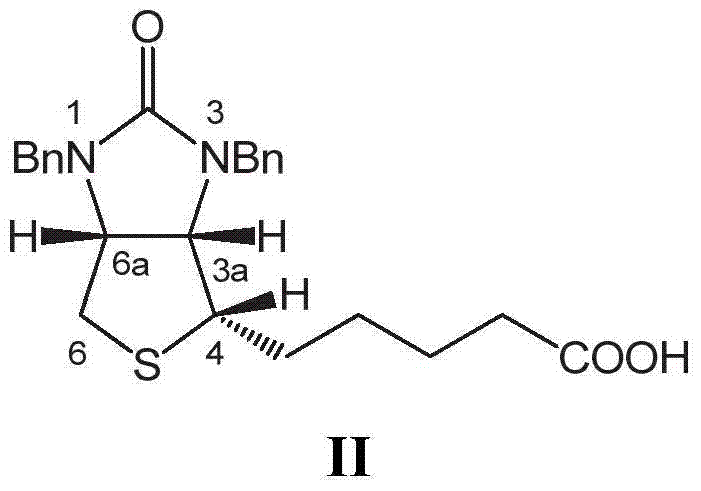
Improved method for preparing d-biotin from bisbenzyl biotin by debenzylation
The invention relates to an improved method for preparing d-biotin from bisbenzyl biotin by debenzylation, which has the advantages of high product quality, low cost and high environment friendliness. The method comprises the following steps: putting bisbenzyl biotin 5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)]-1,3-dibenzyl-2-oxohexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazolyl-4-yl]valeric acid in a reaction kettle; adding hydrobromic acid, stirring and heating to reflux, and reacting under reflux conditions until no raw material dots by TLC (thin layer chromatography) detection; adding an aromatic solvent for extraction, and separating an organic phase from a water phase; concentrating the water phase under reduced pressure to a dry state; adding pure water, stirring, standing to crystallize, and filtering to obtain a d-biotin crystal; concentrating the filtrate, standing to crystallize, filtering to obtain a diamido substance 5-[(2S,3S,4R)-3,4-diamidotetrahydrothienyl-2-yl]valeric acid hydrobromide, adding the diamido substance and an inorganic alkali solution into a reaction kettle, and adding phosgene to carry out cyclization reaction; after the cyclization reaction finishes, regulating the pH value to acidity with an inorganic acid solution, and standing to crystallize; and filtering to obtain the d-biotin 5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)]-2-oxohexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazolyl-4-yl]valeric acid. The method is used for producing d-biotin from bisbenzyl biotin.
Owner:FUYANG KEXING BIOCHEM
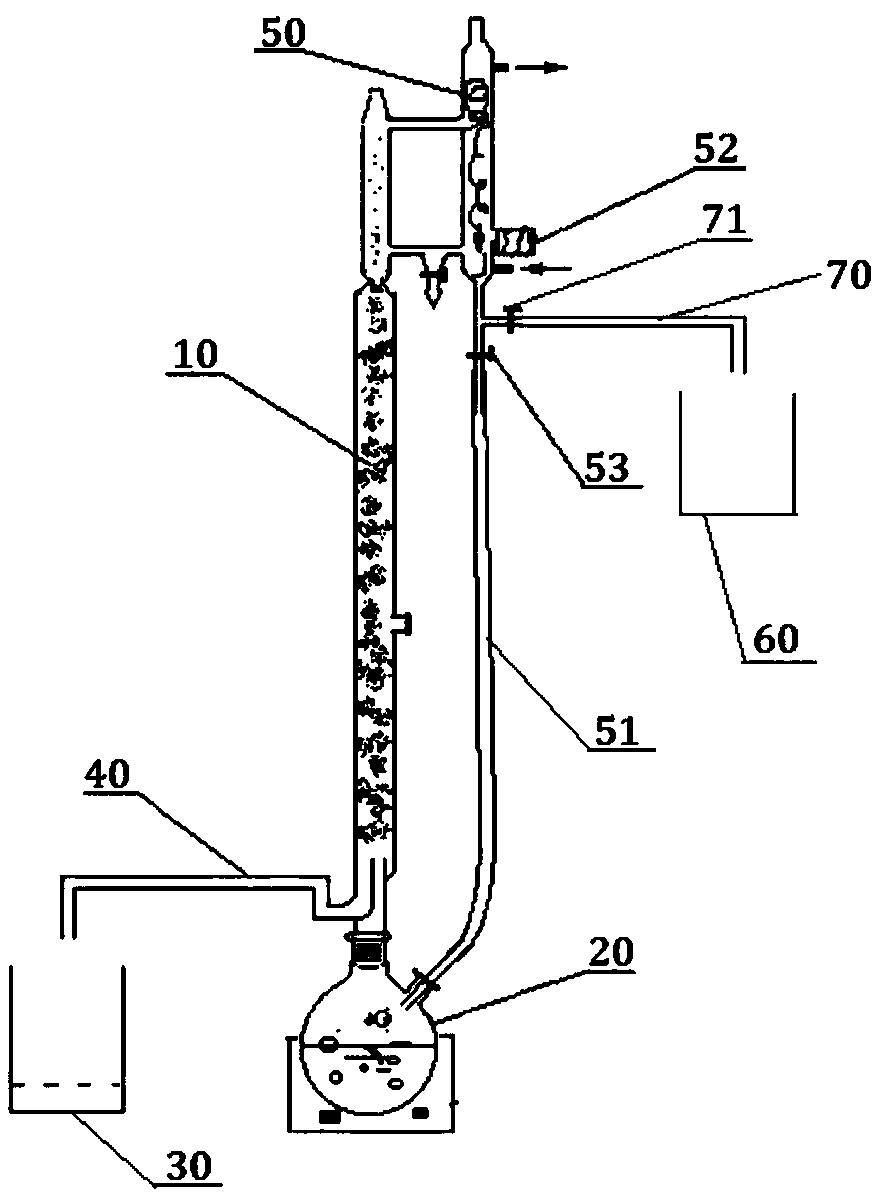
Metronidazole synthesizing device and metronidazole synthesizing method applying same
The invention provides a metronidazole synthesizing device and a metronidazole synthesizing method applying the same. The device comprises a rectifying tower, a reaction kettle, an alcohol storage tank, a condenser and an ester storage tank. The synthesizing method achieves circular application of ethylene glycol in the metronidazole synthesizing process. The device and method provided by the invention have the beneficial effects that circular application of ethylene glycol in the metronidazole synthesizing process is achieved, the resources are saved, and meanwhile, the continuity of the synthesizing process is ensured, the solvent is used circularly, and the equipment investment is little.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV
Method for preparing beta-aminopropionic acid with high selectivity
ActiveCN113603602AHigh yieldImplement loopingOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationInorganic saltsPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing beta-aminopropionic acid from acrylic acid. The method comprises the step that: in a tank reactor, acrylic acid and ammonia water react in the presence of a catalyst and a ligand, and then reaction liquid is subjected to deamination, concentration and crystallization treatment to prepare beta-aminopropionic acid, wherein the catalyst is a transition metal inorganic salt, and the ligand is a pyridine ligand. The method has the advantages of good product selectivity, high yield, convenience in purification, mild process conditions and the like. Experiments show that: with the catalyst and the ligand introduced, the conversion rate of the acrylic acid is greater than 99%, the yield of the single-pass product of the reaction is greatly improved to 82%, the difficulty of later purification is greatly reduced, a mother liquor can be recycled, and the recycling yield is greater than 95%.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
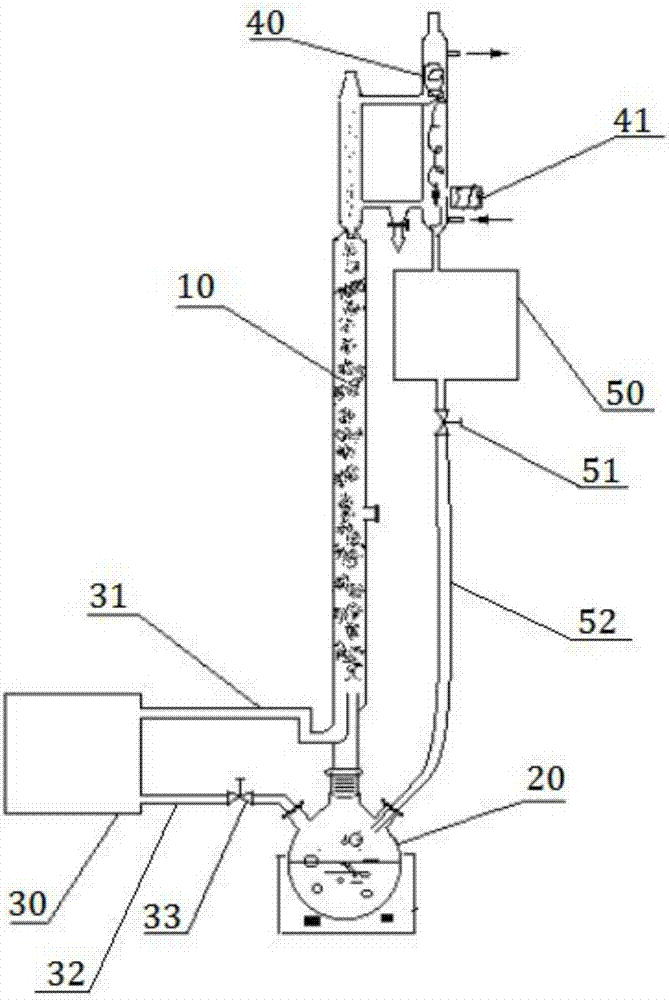
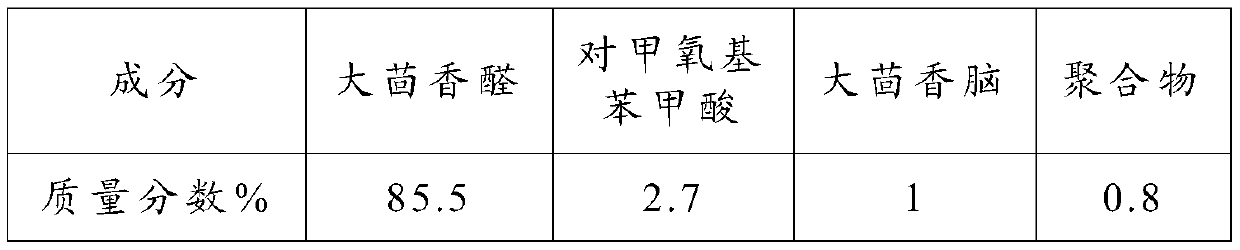
Synthesis method of natural anisaldehyde
ActiveCN110885285AGood aromaLow costOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationChemistryP-methoxybenzaldehyde
The invention provides a synthesis method of natural anisaldehyde. In the method, natural anethole is adopted as a raw material, oxygen or air is adopted as an oxidant, and the anisaldehyde is prepared under the action of a catalyst. The product obtained by this method has a pure aroma and excellent quality, which are obviously better than these of anisaldehyde obtained by pure chemical synthesismethods. The catalyst and solvent used in the method can be recycled and reused, thus reducing the cost and reducing generation of three wastes. The clean oxygen or air is adopted as the oxidant, thesource is wide, the reaction condition is mild, and corrosion is low, thus facilitating industrial production of the anisaldehyde.
Owner:ANHUI SHENGNUOBEI CHEM TECH
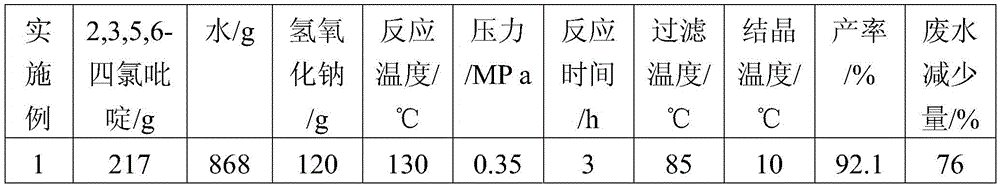
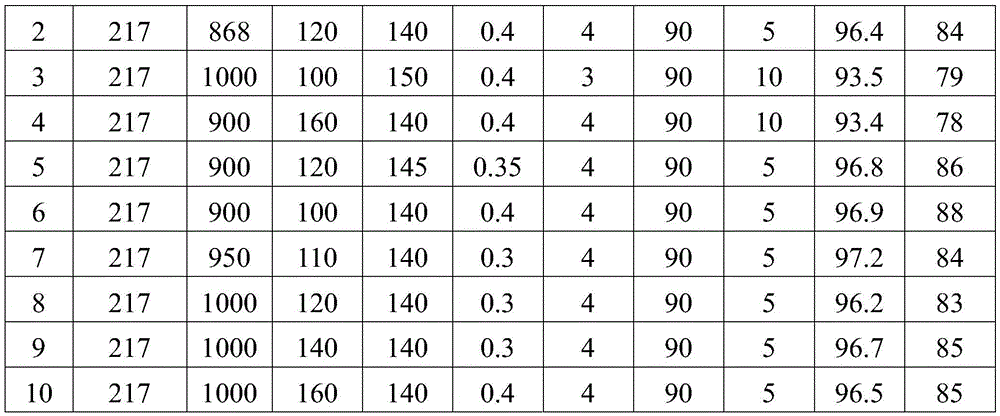
Synthesis method of 3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-ol sodium by using 2,3,5,6-tetrachloropyridine as raw material
The invention discloses a synthesis method of 3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-ol sodium by using 2,3,5,6-tetrachloropyridine as a raw material. The method comprises the steps of: (1) mixing 2,3,5,6-tetrachloropyridine with water, adding sodium hydroxide, reacting at high temperature and under high pressure for a period of time, cooling to 80-90 DEG C; (2) filtering 3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-ol sodium mixed solution while hot to obtain a first filtrate; (3) cooling the first filtrate the in an ice-water bath to 5-10 DEG C, and l precipitating sodium alkoxide crystalline; conducting pressure filtration to obtain a white 3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-ol sodium crystals and a secondary filtrate. The method uses 2,3,5,6-tetrachloropyridine as the raw material, which is cheap and readily available, to reduce production costs; and compared with the prior art, the method reaches the yield of 95%, has simple process operations, and high yield rate.
Owner:ANHUI COSTAR BIOCHEM CO LTD
Preparation method of 3-ethoxyl ethyl propionate
ActiveCN101423475BReduce recyclingHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationChemical synthesisDistillation
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical synthesis, and in particular relates to a method for preparing 3-ethoxy ethyl propionate. The method comprises a synthesizing step and a refining step, wherein the synthesizing step adopts ethanol and ethyl acrylate as raw materials to carry out addition under the action of a catalyst, and the catalyst adopts alkali metal or alkali alcoholate. The method has the following advantages: 1, the method adopts one of the raw materials as solvent to react, so as to reduce solvent recovery and consumption in the production process; 2, the reaction catalyst uses basic catalyst such as sodium metal and the like, so as to improve reaction yield greatly; 3, the dosage of the reaction catalyst is reduced to about 2 percent, so as to lower amountof salt greatly after the reaction is finished, and reduce byproducts; 4, the reaction time can be shortened to 3 hours, so as to improve production efficiency; and 5, fore zeolite obtained in distillation can be used for next reaction, so as to achieve circular application, so that the proposal reaches green chemical requirement.
Owner:LINHAI LIANSHENG CHEM
Method of removing inorganic salt from phenylalanine fermented liquid
InactiveCN108993151AReduce the burden onReduce loss rateOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationUltrafiltrationChemistry
The invention relates to a method of removing inorganic salt from phenylalanine fermented liquid. The method includes: performing ultrafiltration to a phenylalanine fermented liquid through an ultrafiltration membrane, regulating pH of a phenylalanine ultrafiltered clear liquid, injecting the phenylalanine ultrafiltered clear liquid into a first electrodialysis device for desalting the liquid; when the electrical conductivity of the phenylalanine ultrafiltered clear liquid is 5000-6000 [mu]s / cm, injecting the clear liquid into a second electrodialysis device, and crystallizing the second batchof the phenylalanine electrodialyzed concentrated liquid; separating the crystal from the mother liquid and drying the crystal to prepare phenylalanine crystal. The method is simple in control and isfree of addition of chemical substances and generation of solid residues during treatment, wherein the generated waste liquid can be recycled for the production of fermentation, so that the method isfree of environmental pollution. The method is suitable for being promoted and applied.
Owner:SHENGSHIYAOLAN SHENZHEN TECH CO LTD
Method for applying formic acid glycol ester in metronidazole production, device for achieving method and method for applying device
PendingCN107857732AReduce the amount of formic acidReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryChemistryMetronidazole
The invention provides a method for applying formic acid glycol ester in metronidazole production, a device for achieving the method and a method for applying the device. According to the method for applying formic acid and glycol ester in metronidazole production, circulation application of formic acid glycol ester in the synthesis process of metronidazole is achieved, a part of formic acid is replaced by formic acid glycol ester, the application amount of formic acid can be reduced, and the production cost is saved. The device for achieving the method comprises a rectifying tower, a reactionkettle, a heavy component liquid collection bottle, a heavy component outlet pipe, a light component liquid collection bottle, a condenser and a light component outlet pipe. The device is simple in structure, convenient to use and high in practicability.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV
Synthesis method of 3,5-dihalogenated-2-pentanone
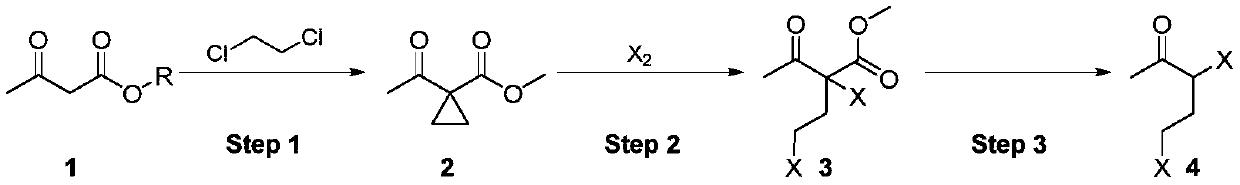
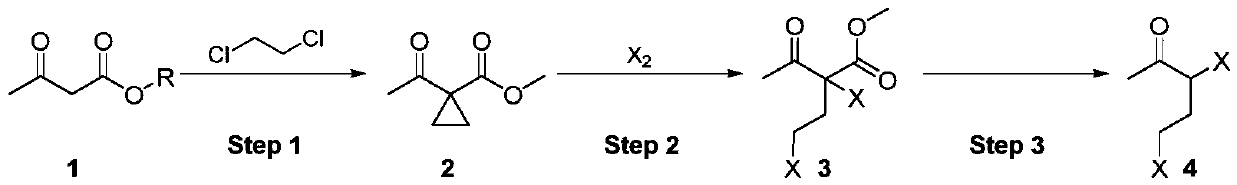
ActiveCN111205176ARaw materials are easy to obtainAtom utilization is highOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetoacetatesPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a synthetic method of 3,5-dihalogenated-2-pentanone, and belongs to the technical field of organic chemistry. According to the method, acetoacetate is taken as a raw material,and cyclopropanation, ring-opening halogenation and hydrolysis decarboxylation reactions are carried out successively so as to obtain 3,5-dihalogenated-2-pentanone. The method has the advantages of simple and accessible raw materials, high atom utilization ratio in the halogenation step and fewer wastes. The reaction conditions of all steps are simple, purification is not needed in the process, continuous feeding can be achieved, cyclic application of the cyclopropanation catalyst can be achieved, and potential industrial amplification prospects are achieved.
Owner:DALIAN JOIN KING FINE CHEM CO LTD
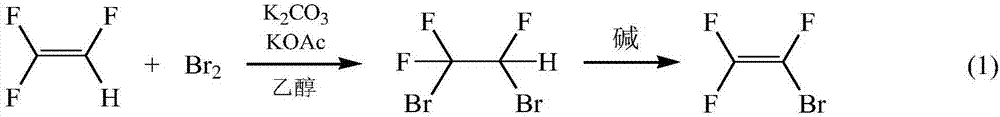
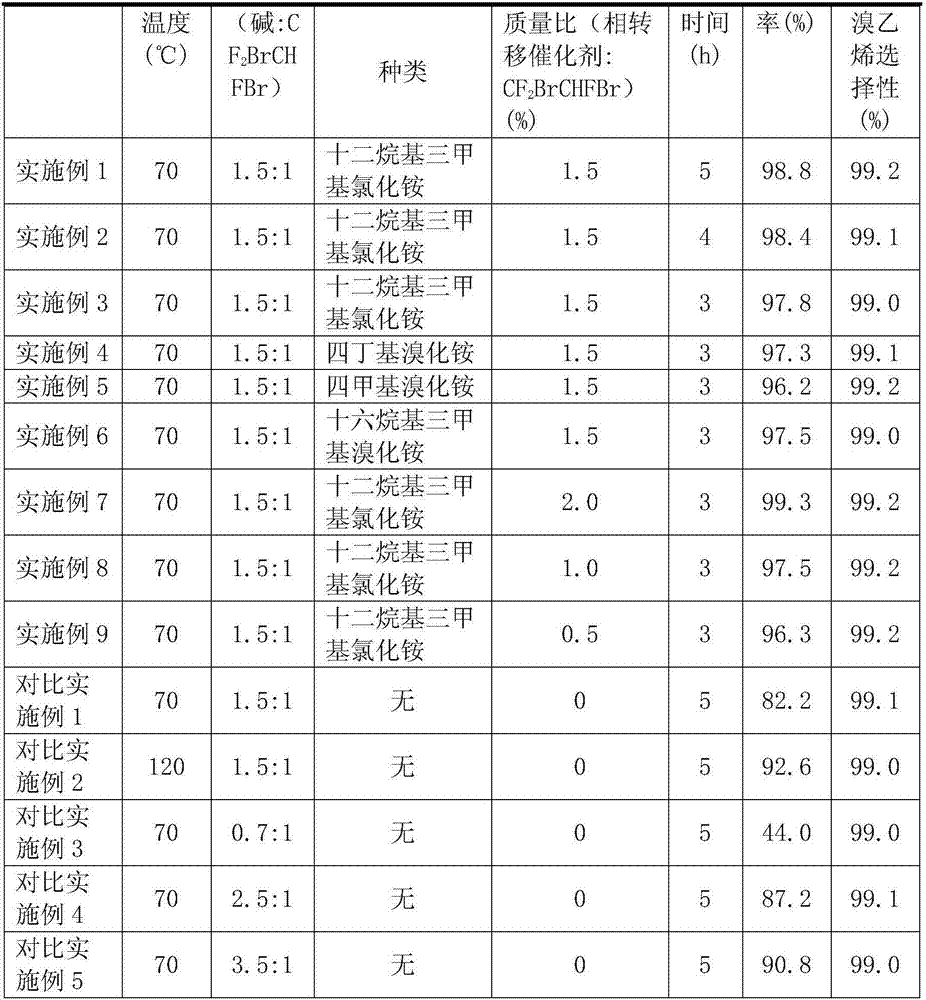
Method using phase-transfer catalysis to prepare trifluorobromoethylene
ActiveCN107032946AImplement loopingImprove mass transfer effectPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPhase-transfer catalystPhotochemistry
The invention discloses a method for preparing trifluorobromoethylene. The method includes: allowing 1, 2-dibromo-1, 1, 2-trifluoroethane to have dehydrobromination reaction in an alkaline solution under the effect of a phase-transfer catalyst to generate the trifluorobromoethylene. The method is fast in reaction, high in synthesizing efficiency, low in cost, green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LANTIAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION HI TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com