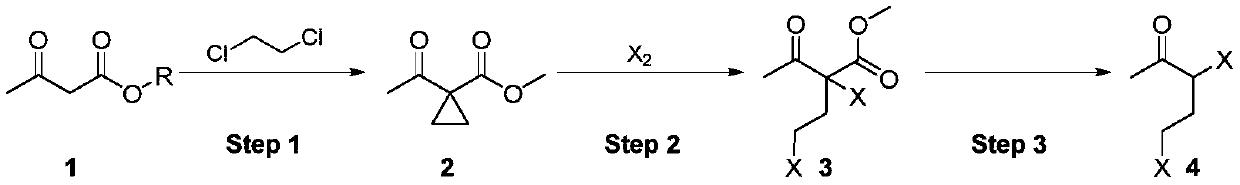
Synthesis method of 3,5-dihalogenated-2-pentanone
A synthetic method, a dihalogenated technology, applied in the field of synthesis of 3,5-dihalogenated-2-pentanone, which can solve the problems of high production safety risks, achieve high atom utilization, less waste, and simple reaction conditions Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
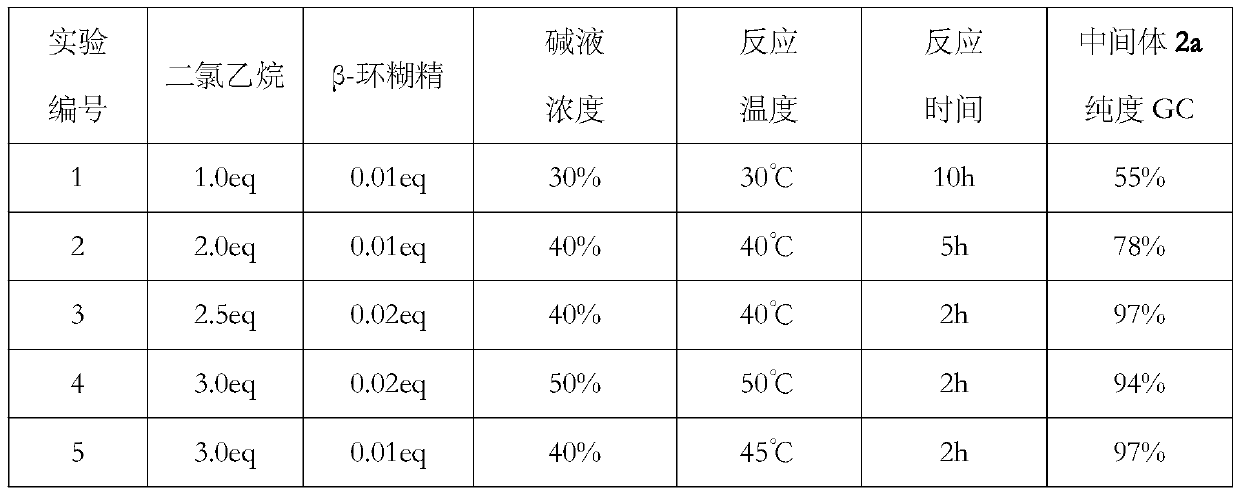
[0022] In the first step, add methyl acetoacetate 1a (116.1g, 1.0mol), dichloroethane (247.4g, 2.5eq) and β-cyclodextrin (22.7g, 0.02eq) into a 2L reaction flask, heat and stir To 40°C, slowly add 40% sodium hydroxide solution (400.0g, 4.0eq) from the dropping funnel, it takes 1.0h to finish dropping, control the temperature during the dropping process at 40-45°C, continue to keep stirring for 2.0 h.
[0023] Stop heating and drop to room temperature, separate the lye layer containing β-cyclodextrin for recycling, then separate the dichloroethane layer, add water to wash until neutral and directly use for ring-opening halogenation reaction, intermediate ( 2a) GC purity 97% (minus dichloroethane).
[0024] In the second step, chlorine gas (85.1 g, 1.2 mol) was introduced into the dichloroethane solution of the intermediate (2a) obtained above, and it took 2.0 hours to pass through. The temperature during the ventilation process was controlled at 0-5 ° C. After the ventilation ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The first step is the same as in Example 1.
[0029] In the second step, bromine (175.8g, 1.1mol) was added dropwise to the dichloroethane solution of the intermediate (2a) obtained in the first step, and it took 2.0h to complete the dropwise addition, and the dropping process controlled the temperature at 0-5 ℃, after the drop is completed, continue to keep stirring for 1.0h. The dichloroethane solution of the obtained intermediate (3b) was directly used in the hydrolysis decarboxylation reaction, and the gas chromatography purity of the intermediate (3b) was 93% (deducting dichloroethane).
[0030] In the third step, the ethylene dichloride solution of the intermediate (3b) is transferred to the dropping funnel, and slowly added dropwise to a reaction flask preheated to 80° C. with 20% hydrochloric acid (182.5g, 1.0eq), which takes time After 1.0h of dripping, the mixture was kept stirring for 2.0h.
[0031] Stop heating and cool down to room temperature, separate d...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The first step is the same as in Example 1.
[0034] In the second step, a solution prepared from iodine (279.2 g, 1.1 mol) and 300 g of dichloroethane was added dropwise to the dichloroethane solution of the intermediate (2a) obtained in the first step, and it took about 2.0 hours to complete the dropwise addition. During the dropping process, the temperature was controlled at 0-5°C, and the stirring was continued for 1.0 h after the dropping was completed. The dichloroethane solution of the obtained intermediate (3c) was directly used in the hydrolysis decarboxylation reaction, and the gas chromatography purity of the intermediate (3c) was 81% (dichloroethane was deducted).
[0035] In the third step, the ethylene dichloride solution of the intermediate (3c) is transferred to the dropping funnel, and slowly added dropwise to a reaction flask preheated to 80° C. with 20% hydrochloric acid (182.5g, 1.0eq), which takes time After 1.0h of dripping, the mixture was kept s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com