Red fluorescence protein, fusion protein, separated nucleic acid, carrier and application
A red fluorescent protein, fluorescent protein technology, applied in the application, fusion polypeptide, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of fast photobleaching, low protein maturation rate, unsatisfactory FRET effect, etc., achieve high FRET effect, broad application prospects Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] The red fluorescent protein provided in this example has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4, which has the following amino acid mutation sites relative to the fluorescent protein mRuby3 (SEQ ID NO: 3): N8E, R10P, E114V, V116I, T177E and R179K.
[0060] Among them, asparagine at position 8 is mutated to glutamic acid (N8E), the amino acid structure becomes larger, and the carboxyl group on the side chain of glutamic acid is more likely to form a hydrogen bond with the amino group of asparagine at position 33; Arginine at position 10 is mutated to proline (R10P), and glutamic acid at position 114 is mutated to valine (E114V), favoring nonpolar proline at position 10 and nonpolar proline at position 114 Valine forms a hydrophobic bond; the 116th valine is mutated to isoleucine (V116I), which makes the amino acid side chain longer, and the 114th glutamic acid is mutated to valine, which is beneficial to the 116th Isoleucine with a longer side chain forms a hyd...
Embodiment 2
[0065] On the basis of the red fluorescent protein (SEQ ID NO: 4) in Example 1, further site-directed mutations were carried out to improve its brightness, extinction coefficient, quantum yield and other characteristics.
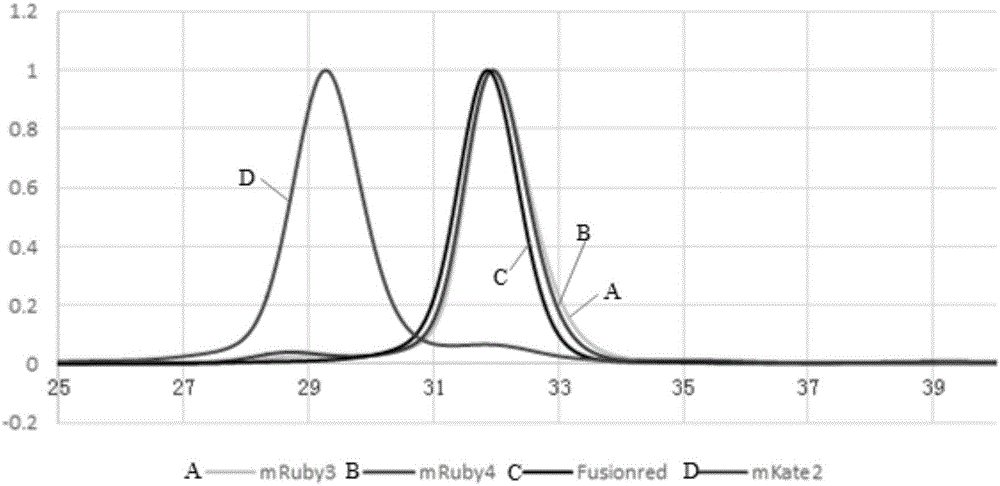
[0066] The red fluorescent protein provided by this embodiment is named as mRuby4, and its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. Compared with fluorescent protein mRuby3 (its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3), it not only has the following amino acid mutation sites: N8E, R10P, E114V, V116I, T177E and R179K; also have the following amino acid mutation sites: E16T, S18T, E111Q, V124E and N173S. The amino acid sequence alignment results of mRuby4 and mRuby3 are as follows figure 1 shown.
[0067] The red fluorescent protein (SEQ ID NO: 1) provided in this example not only has a high maturity rate, but also has high extinction coefficient, brightness and other characteristics.
[0068] The red fluorescent protein provided in this example ca...
Embodiment 3
[0070] This example provides a method for obtaining the red fluorescent protein (SEQ ID NO: 1) in Example 2. Of course, the method for obtaining the red fluorescent protein provided in Example 1 can also refer to this example. It should be noted that the method for obtaining the red fluorescent protein of the present invention is not limited to the method provided in this example. In other embodiments, the red fluorescent protein of the present invention obtained by other methods also belongs to the protection of the present invention. scope.
[0071] The method for obtaining red fluorescent protein (SEQ ID NO: 1) provided in this example is as follows.
[0072] (1) Design the corresponding nucleic acid sequence according to the amino sequence of the red fluorescent protein (SEQ ID NO:1) provided in Example 2, and the nucleic acid sequence encodes the red fluorescent protein (SEQ ID NO:1).
[0073] In this embodiment, the nucleotide sequence of the nucleic acid sequence encod...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Extinction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com