Method for electrolytically separating stannum-lead alloy through low eutectic solvent
A low eutectic solvent, tin-lead alloy technology, applied in the field of ionic liquid metallurgy, can solve the problems of high cell voltage and large energy consumption, and achieve the effects of low vapor pressure, simple preparation and easy availability of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
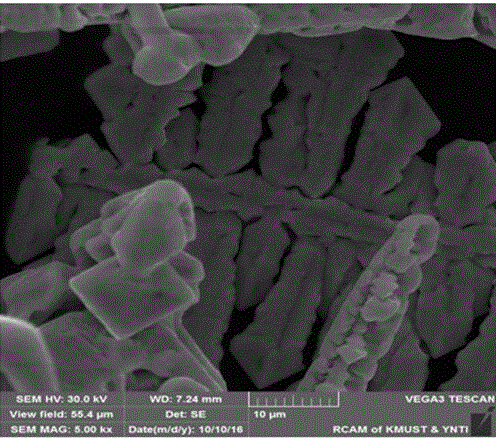
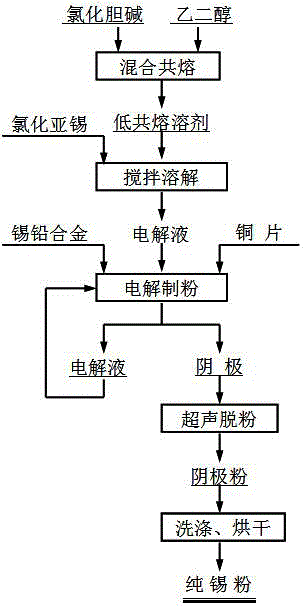
[0024] Such as figure 1 Shown, this utilizes the method for electrolytic separation of tin-lead alloy of deep eutectic solvent, and its specific steps are as follows:
[0025] Step 1. Mix choline chloride and ethylene glycol at a molar ratio of 1:2, then heat and stir at 80°C to eutectic to a clear and transparent liquid, and synthesize choline chloride-ethylene glycol deep eutectic solvent, referred to as 1ChCl:2EG DES;
[0026] Step 2. Add stannous chloride to the 1ChCl:2EG DES synthesized in step 1, stir and dissolve evenly, and prepare an electrolyte solution. The concentration of stannous chloride in the electrolyte solution is 0.1mol / L.
[0027] Step 3. Heat the electrolyte solution prepared in step 2 to 50°C, use the tin-lead alloy block as the anode (with a lead content of 5wt%) and the copper sheet as the cathode, and control the area ratio of the anode to the cathode to be 1:1. The spacing is 20mm, and the electrolyte is stirred at a stirring speed of 500r / min. At ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Such as figure 1 Shown, this utilizes the method for electrolytic separation of tin-lead alloy of deep eutectic solvent, and its concrete steps are as follows:
[0031] Step 1. Mix choline chloride and ethylene glycol at a molar ratio of 1:2, then heat and stir at 80°C to eutectic to a clear and transparent liquid, and synthesize choline chloride-ethylene glycol deep eutectic solvent, referred to as 1ChCl:2EG DES;
[0032] Step 2, add stannous chloride to the 1ChCl:2EG DES synthesized in step 1, stir and dissolve evenly, be mixed with electrolytic solution, the concentration of stannous chloride in the electrolytic solution is 0.05mol / L;
[0033] Step 3. Heat the electrolyte solution prepared in step 2 to 50°C, use the tin-lead alloy block as the anode (with a lead content of 5wt%) and the copper sheet as the cathode, and control the area ratio of the anode to the cathode to be 1:1. The spacing is 20mm, and the electrolyte is stirred at a stirring speed of 500r / min. A...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Such as figure 1 Shown, this utilizes the method for electrolytic separation of tin-lead alloy of deep eutectic solvent, and its concrete steps are as follows:
[0036] Step 1. Mix choline chloride and ethylene glycol at a molar ratio of 1:2, then heat and stir at 80°C to eutectic to a clear and transparent liquid, and synthesize choline chloride-ethylene glycol deep eutectic solvent, referred to as 1ChCl:2EG DES;
[0037] Step 2, add stannous chloride to the 1ChCl:2EG DES synthesized in step 1, stir and dissolve evenly, be mixed with electrolyte, the concentration of stannous chloride in the electrolyte is 0.1mol / L;
[0038] Step 3. Heat the electrolyte solution prepared in step 2 to 40°C, use the tin-lead alloy block as the anode (with a lead content of 5wt%), and the copper sheet as the cathode, and control the area ratio of the anode to the cathode to be 2:1. The spacing is 20mm, and the electrolyte is stirred at a stirring speed of 500r / min. At the same time, dir...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com