Multielement liquid compound microorganism fertilizer and preparation method thereof
A technology for compounding microorganisms and fertilizers is applied in the field of organic fertilizers containing bacterial cultures, mycelium or other similar substances and their preparation, which can solve the problems of unbalanced nutrient content, limited application effects, and confusion in the microbial fertilizer market. , to achieve the effect of convenient management and control, saving labor costs, and saving batching time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
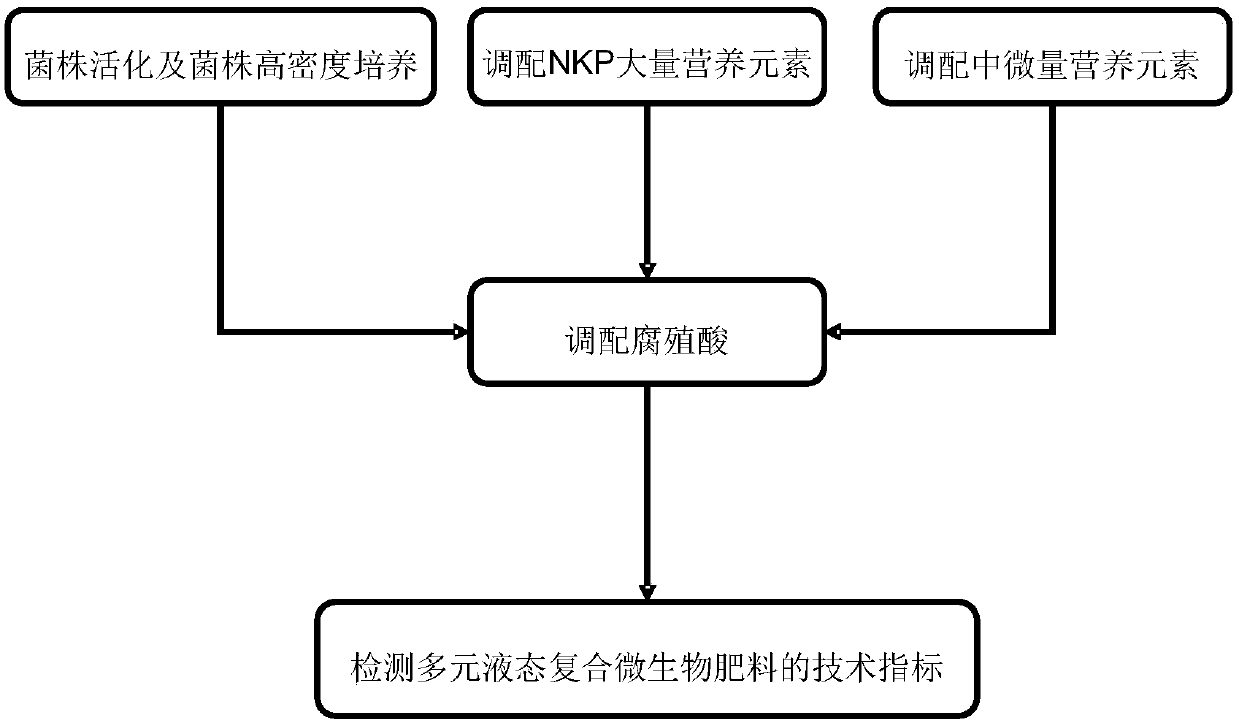
[0060] Such as figure 1 As shown, the multi-element liquid composite microbial fertilizer of this embodiment is prepared according to the following steps:
[0061] (1) Steps for high-density cultivation of Bacillus megaterium:
[0062] Under aseptic conditions, use the inoculation loop to pick 5 loops of Bacillus megaterium and inoculate it into 100mL medium (300mL Erlenmeyer flask), and then perform shake flask fermentation culture (first-level seed culture). The culture condition is: culture temperature 30℃ , Fermentation time 20h, rotation speed 180r / min, pH value 6.5. The above-mentioned cultivated first-level seeds were inoculated into a 2L medium (3.7L fermentor) at a ratio of 5% to carry out the fermentation culture of Bacillus megaterium. The culture conditions were: fermentation temperature 30℃, aeration volume 1.0vvm, rotation speed 180r / min, pH value is 6.5, fermentation time is 20h, after fermentation, the fermentation broth is stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for lat...
Embodiment 2
[0077] The difference between the multi-element liquid composite microbial fertilizer of this embodiment and the embodiment 1 is:
[0078] The composition of seed and fermentation medium in step (1) includes: potassium dihydrogen phosphate (chemically pure) 4.9g, magnesium sulfate (chemically pure) 0.45g, sodium chloride (chemically pure) 4.9g, glucose (chemically pure) 9.9 g. Peptone (biochemical reagent) 9.9g, yeast extract powder (biochemical reagent) 3.9g and Tween-80 (chemically pure) 2.9g, then add 990mL purified water, stir well, sterilize at 110°C for 40min .
[0079] The composition of seed and fermentation medium in step (2) includes: potassium dihydrogen phosphate (chemically pure) 5.1g, magnesium sulfate (chemically pure) 0.55g, sodium chloride (chemically pure) 5.1g, glucose (chemically pure) 10.1 g. Peptone (biochemical reagent) 10.1g, yeast extract powder (biochemical reagent) 4.1g and Tween-80 (chemically pure) 3.1g, then add 1010mL purified water, stir well, steri...
Embodiment 3
[0082] The difference between the multi-element liquid composite microbial fertilizer of this embodiment and the embodiment 2 is:
[0083] The deployment of NKP macronutrient elements in step (4) is carried out as follows:
[0084] Weigh 85g ammonium sulfate (analytical pure), 90g potassium dihydrogen phosphate (analytical pure), 25g potassium sulfate (analytical pure), 85g diammonium hydrogen phosphate (analytical pure) and 120g urea (analytical pure), and then add 650mL for purification Water, water temperature at 60℃, stirring at 300r / min for 15min, all reagents are dissolved, pH value is 5.0~6.0, (N+P 2 O 5 +K 2 O)≥200g / L, N+P 2 O 5 +K 2 O: 8-8-4(S), the deployment is completed and ready for use.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com