Vinylidene chloride copolymer-based carbon molecular sieve adsorbent compositions and processes therefor
A technology of polyvinylidene chloride and composition, applied in the field of molecular sieve composition, capable of solving undetermined and undisclosed problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1 to example 17 and comparative example 1 to comparative example 16
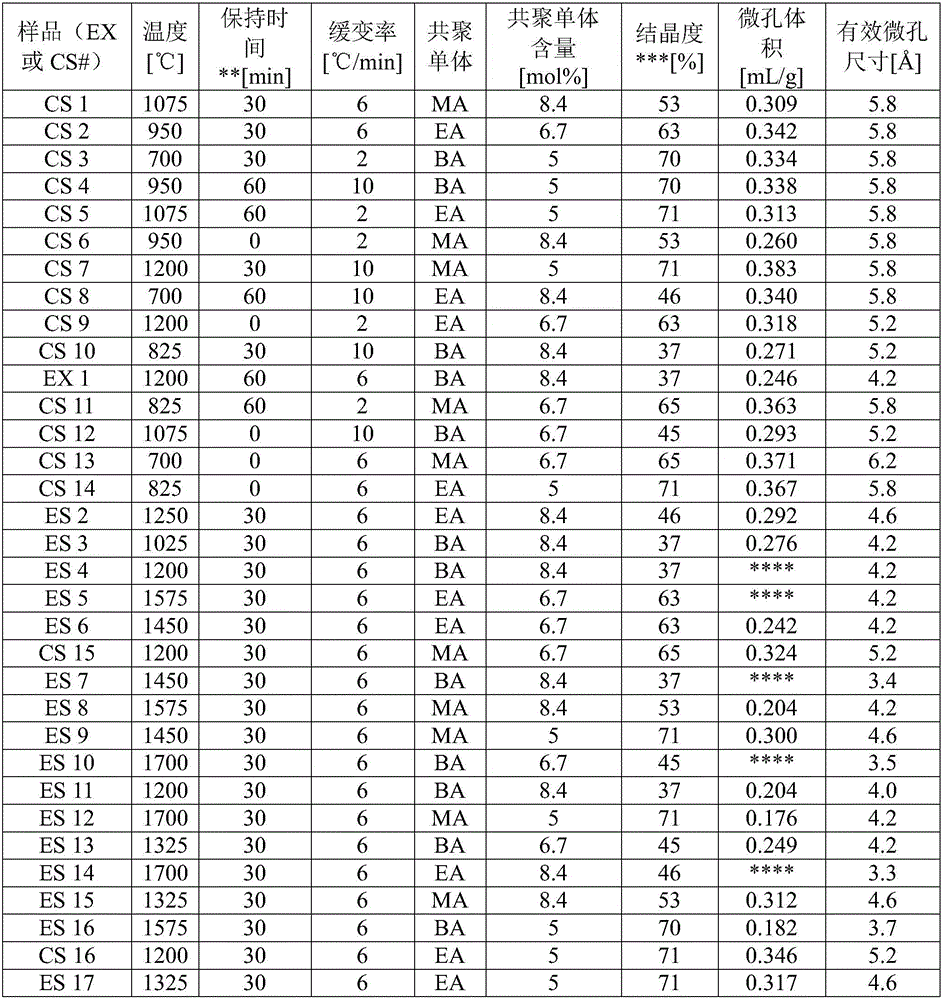
[0061] A series of Example (ES) and Comparative Example (CS) samples were prepared from polyvinylidene chloride copolymerized with a monomer selected from methyl acrylate (MA), ethyl acrylate (EA) or butyl acrylate (BA), whereby The monomers mentioned are present in the amounts indicated in Table 2 in each case. In each case, the copolymerization is effected by suspension polymerization. Generally, this involves mixing the selected monomers according to their weight ratio to the polymerization initiator, and then carrying out the polymerization reaction in the aqueous dispersion. The copolymer powder is then dried to remove water and any unreacted monomer. The powder was then sieved and its 30 to 50 US sieve portion selected to ensure consistency for CMS preparation.
[0062] The precursor powder was then pretreated by dehydrochlorination in an oven purged by 2 liters per minute (L / min) of air at a temperature of 130° C. for 24 hrs, followed by 150° C. for 24 hrs.
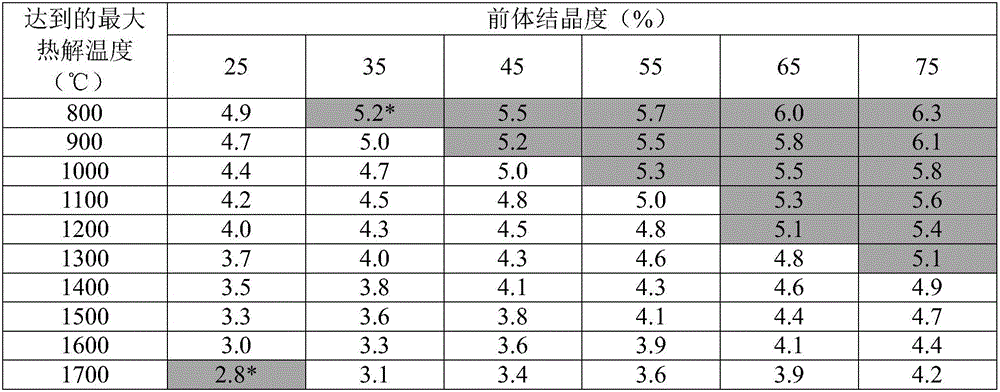
[0063] ...
example 18
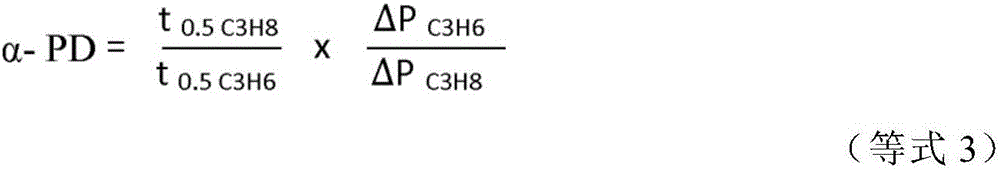
[0076] shown in Table 2 with Four (4) example samples (EX) of effective pore sizes of , designated ES 1 , ES6, ES 8 and ES 13, were used in experiments to compare high-throughput kinetic adsorption in the separation of propylene and propane. To calculate the selectivity, the formula shown in equation (3) is used.
[0077]
[0078] In the equation, "ΔP" represents the pressure drop due to adsorption (from 45 psi (0.31 MPa) starting pressure to equilibrium pressure), which is proportional to the amount of adsorption according to the ideal gas law. The half-adsorption time ("t0.5") represents the time at which 50% of the pressure drop (adsorption) occurs, which corresponds to the rate of diffusion. Selectivity ("α-PD") is specified in the equation below to account for both equilibrium and kinetic selectivity. The results tested for the 4 example samples are shown in Table 3.
[0079] Table 3: CMS samples: C of ES 1, ES 6, ES 8 and ES 13 2 h 4 / C 2 h 6 Kinetic Sorption ...
example 19
[0084] Ethylene / ethane selectivity measurements were performed using the ES 11 in a high-throughput kinetic adsorption. The results of the separation are shown in Table 4. These results show that not only does ethane adsorb to a much smaller extent than ethylene in the CMS of the invention, but it also adsorbs much more slowly by a factor of about 10 due to the pressure drop produced by the adsorption. Thus, two molecules can be separated easily and efficiently using the compositions of the present invention.
[0085] Table 4: CMS Sample: C of ES 11 2 h 4 / C 2 h 6 Kinetic Sorption Summary
[0086]
[0087]
[0088] *1psi=about 0.007MPa
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com